
A time-varying current I is passed through a resistance as shown in the figure. The total heat generated in the resistance is:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }11i_{0}^{2}R{{t}_{0}} \\
& \text{B}\text{. }13i_{0}^{2}R{{t}_{0}} \\
& \text{C}\text{. }17i_{0}^{2}R{{t}_{0}} \\
& \text{D}\text{. }15i_{0}^{2}R{{t}_{0}} \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: Recall how energy loss depends on the resistance and current in a circuit. Use the equation \[H=i_{0}^{2}Rt\] to find the heat generated. Since the flow is not constant, split it into three parts: \[0\to {{t}_{0}}\] , \[{{t}_{0}}\to 2{{t}_{0}}\] and \[2{{t}_{0}}\to 3{{t}_{0}}\] integrate. And finally, add the three.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As you know, when current is allowed to pass through a conductor, due to internal friction or some other reasons, a resistance to the flow of electric current is created inside the conductor.
As current increases, the resistance also increases, leading to the generation of heat in the circuit. This heat will dissipate out. Electric current will thus be converting in the form of heat, which leads to energy loss. It is the reason why the copper wire gets heated up after the current passes through it.
The heat energy dissipated when current passes through a circuit is
\[H=i_{0}^{2}Rt\] ……………….(1)
Where
\[{{i}_{0}}\] - the time-dependent current
\[R\] - The resistance the circuit
\[t\] - time of flow of the current
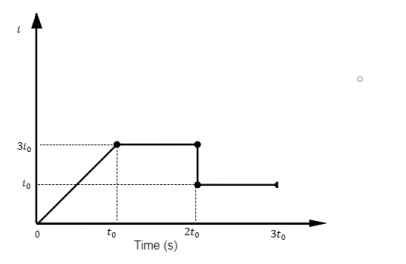
In the given figure what we can see is that the electric current is not constant. It varies with time. The value of \[{{i}_{0}}\] is continuously increasing from \[t=0\] to \[t={{t}_{0}}\] . Form \[t={{t}_{0}}\] to \[t=2{{t}_{0}}\] the current is constant. Then in the last section, from \[t=2{{t}_{0}}\] to \[t=3{{t}_{0}}\] , \[i={{i}_{0}}\] .
To find energy loss, we have to add all these together. Since it is a continuous function, what we are going to do is to integrate these with respect to time since the current is time-dependent.
Since the current is not constant, we have to split the limit into three segments.
\[0\to {{t}_{0}}\] , \[{{t}_{0}}\to 2{{t}_{0}}\] and \[2{{t}_{0}}\to 3{{t}_{0}}\] .
In the first segment, the current is continuously varying with time. Then adding the terms, we get
\[H=\left[ {{\int\limits_{0}^{{{t}_{0}}}{\left( \dfrac{3{{i}_{0}}t}{{{t}_{0}}} \right)}}^{2}}Rdt+{{\int\limits_{{{t}_{0}}}^{2{{t}_{0}}}{\left( 3{{i}_{0}} \right)}}^{2}}Rdt+\int\limits_{2{{t}_{0}}}^{3{{t}_{0}}}{i_{0}^{2}Rdt} \right]\]
\[H=\left[ \left[ \dfrac{9i_{0}^{2}}{t_{0}^{2}}\dfrac{{{t}^{3}}}{3} \right]_{0}^{{{t}_{0}}}R+\left[ 9i_{0}^{2}t \right]_{{{t}_{0}}}^{2{{t}_{0}}}R+\left[ i_{0}^{2}t \right]_{2{{t}_{0}}}^{3{{t}_{0}}}R \right]\]
\[H=\left[ \left[ \dfrac{9i_{0}^{2}}{t_{0}^{2}}\dfrac{t_{0}^{3}}{3} \right]R+\left[ 9i_{0}^{2}(2{{t}_{0}}-{{t}_{0}}) \right]R+i_{0}^{2}(3{{t}_{0}}-2{{t}_{0}})R \right]\] .
Simplifying,
\[H=3i_{0}^{2}{{t}_{0}}R+9i_{0}^{2}{{t}_{0}}R+i_{0}^{2}{{t}_{0}}R\]
\[H=13i_{0}^{2}{{t}_{0}}R\]
As current and resistance increases, the heat also increases.
Therefore, option B is the answer.
Note: Be careful while integrating the first term because \[0\to {{t}_{0}}\] the current increases continuously. It is a slanted line. Using the point of the line \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] and \[\left( 3{{i}_{0}},{{t}_{0}} \right)\] , write the equation for it. Since in the second and third term current are constants, we don’t have to convert it.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As you know, when current is allowed to pass through a conductor, due to internal friction or some other reasons, a resistance to the flow of electric current is created inside the conductor.
As current increases, the resistance also increases, leading to the generation of heat in the circuit. This heat will dissipate out. Electric current will thus be converting in the form of heat, which leads to energy loss. It is the reason why the copper wire gets heated up after the current passes through it.
The heat energy dissipated when current passes through a circuit is
\[H=i_{0}^{2}Rt\] ……………….(1)
Where
\[{{i}_{0}}\] - the time-dependent current
\[R\] - The resistance the circuit
\[t\] - time of flow of the current
In the given figure what we can see is that the electric current is not constant. It varies with time. The value of \[{{i}_{0}}\] is continuously increasing from \[t=0\] to \[t={{t}_{0}}\] . Form \[t={{t}_{0}}\] to \[t=2{{t}_{0}}\] the current is constant. Then in the last section, from \[t=2{{t}_{0}}\] to \[t=3{{t}_{0}}\] , \[i={{i}_{0}}\] .
To find energy loss, we have to add all these together. Since it is a continuous function, what we are going to do is to integrate these with respect to time since the current is time-dependent.
Since the current is not constant, we have to split the limit into three segments.
\[0\to {{t}_{0}}\] , \[{{t}_{0}}\to 2{{t}_{0}}\] and \[2{{t}_{0}}\to 3{{t}_{0}}\] .
In the first segment, the current is continuously varying with time. Then adding the terms, we get
\[H=\left[ {{\int\limits_{0}^{{{t}_{0}}}{\left( \dfrac{3{{i}_{0}}t}{{{t}_{0}}} \right)}}^{2}}Rdt+{{\int\limits_{{{t}_{0}}}^{2{{t}_{0}}}{\left( 3{{i}_{0}} \right)}}^{2}}Rdt+\int\limits_{2{{t}_{0}}}^{3{{t}_{0}}}{i_{0}^{2}Rdt} \right]\]
\[H=\left[ \left[ \dfrac{9i_{0}^{2}}{t_{0}^{2}}\dfrac{{{t}^{3}}}{3} \right]_{0}^{{{t}_{0}}}R+\left[ 9i_{0}^{2}t \right]_{{{t}_{0}}}^{2{{t}_{0}}}R+\left[ i_{0}^{2}t \right]_{2{{t}_{0}}}^{3{{t}_{0}}}R \right]\]
\[H=\left[ \left[ \dfrac{9i_{0}^{2}}{t_{0}^{2}}\dfrac{t_{0}^{3}}{3} \right]R+\left[ 9i_{0}^{2}(2{{t}_{0}}-{{t}_{0}}) \right]R+i_{0}^{2}(3{{t}_{0}}-2{{t}_{0}})R \right]\] .
Simplifying,
\[H=3i_{0}^{2}{{t}_{0}}R+9i_{0}^{2}{{t}_{0}}R+i_{0}^{2}{{t}_{0}}R\]
\[H=13i_{0}^{2}{{t}_{0}}R\]
As current and resistance increases, the heat also increases.
Therefore, option B is the answer.
Note: Be careful while integrating the first term because \[0\to {{t}_{0}}\] the current increases continuously. It is a slanted line. Using the point of the line \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] and \[\left( 3{{i}_{0}},{{t}_{0}} \right)\] , write the equation for it. Since in the second and third term current are constants, we don’t have to convert it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




