
A thin film of thickness t and index of refraction \[1.33\] coats a glass with index of refraction\[1.50\]. What is the least thickness/that will strongly reflect light with wavelength \[600\text{ }nm\] normal incidence?
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: The thin-film interference method or occurrence when a light wave is reflected off from the two surfaces with the surface separation is that of the wavelength distance. Due to this occurrence, the phase differences between the two surfaces are negligible when light passes from denser to rarer. Hence, the path difference for constructive interference of transmission of light is given as:
\[2\mu t=n\lambda \]
where \[\mu \] is the refractive index, \[t\] is the thickness of the refractive surface, \[n\] is the refractive index, \[\lambda \] is the wavelength.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us draw the diagram to show how the light ray when traveling from rarer to denser medium refracts and from denser to rarer reflects from surface 1 to 2 and from 2 to 1.
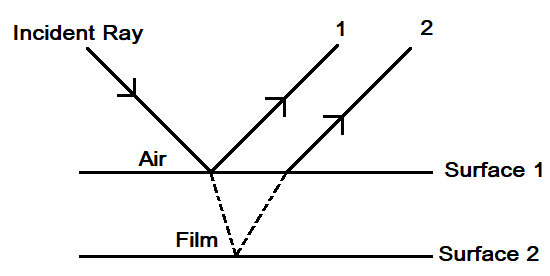
Hence, there are two types of transmission of light i.e. constructive and destructive. For constructive transmission, the phase difference between the travelling of light is 180 degrees. The light from the incident ray is reflected and refracted from the first surface and second surface simultaneously. Hence, the minimum thickness for the transmission of light from surface 1 to surface 2 is:
\[2\mu t=n\lambda \]
Placing the value of \[\lambda \], as \[\lambda =600nm\], \[\mu =1.33\] and \[n=1.5\] in the formula above:
\[t=\dfrac{n\lambda }{2\mu }\]
\[t=\dfrac{1.5\times 600}{2\times 1.33}\]
\[=338.34nm\]
\[\therefore \] The thickness of the glass for the transmission from surface 1 to surface 2 is \[338.34nm\].
Note:There are two constructive Interference for reflection and transmission are given as:
For constructive Interference for reflection is:
\[\dfrac{\left( 2n\text{ }+\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }\lambda }{2}=\text{ }2\mu t\text{ }\]
For constructive Interference for transmission is:
\[2\mu t=n\lambda \]
And the value of the wavelength transmission is \[\lambda \] and not \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2}\] due to higher refractive index.
\[2\mu t=n\lambda \]
where \[\mu \] is the refractive index, \[t\] is the thickness of the refractive surface, \[n\] is the refractive index, \[\lambda \] is the wavelength.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us draw the diagram to show how the light ray when traveling from rarer to denser medium refracts and from denser to rarer reflects from surface 1 to 2 and from 2 to 1.

Hence, there are two types of transmission of light i.e. constructive and destructive. For constructive transmission, the phase difference between the travelling of light is 180 degrees. The light from the incident ray is reflected and refracted from the first surface and second surface simultaneously. Hence, the minimum thickness for the transmission of light from surface 1 to surface 2 is:
\[2\mu t=n\lambda \]
Placing the value of \[\lambda \], as \[\lambda =600nm\], \[\mu =1.33\] and \[n=1.5\] in the formula above:
\[t=\dfrac{n\lambda }{2\mu }\]
\[t=\dfrac{1.5\times 600}{2\times 1.33}\]
\[=338.34nm\]
\[\therefore \] The thickness of the glass for the transmission from surface 1 to surface 2 is \[338.34nm\].
Note:There are two constructive Interference for reflection and transmission are given as:
For constructive Interference for reflection is:
\[\dfrac{\left( 2n\text{ }+\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }\lambda }{2}=\text{ }2\mu t\text{ }\]
For constructive Interference for transmission is:
\[2\mu t=n\lambda \]
And the value of the wavelength transmission is \[\lambda \] and not \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2}\] due to higher refractive index.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




