
What is a test cross? Give examples.
Answer
525.7k+ views
Hint: Various types of crosses are done between organisms to determine their genotype and find individuals with a completely new genotype. These types of crosses are essential for scientific research as they help in knowing the genotype of each and every plant.
Complete answer :
In a test cross, a dominant phenotype organism is crossed with the homozygous recessive genotype organism in order to determine whether the dominant phenotype organism has homozygous dominant and heterozygous genotypes. Hence test cross is used to determine the zygosity of an organism with unknown genotype. This cross was first introduced by Gregor Mendel, father of genetics.
Consider the following example in plants: Suppose you have a tall and dwarf plant and tall characteristic (T) is dominant to dwarf(t). The dwarf plant must be homozygous for the recessive allele, but the genotype of the tall plant is unknown. It could be either TT or Tt. A testcross will decide the organism's genotype. The unknown genotype can be ascertained by examining the phenotypes of the resulting progeny. If crossing the unknown dominant phenotype (TT or Tt genotype) individual with the recessive phenotype individual produces only dominant phenotypes, then the plant with unknown genotype is homozygous dominant. If any recessive phenotypic plants emerge from the cross, then the unknown individual must possess the recessive allele, and have the heterozygous genotype.
Notes: In backcross, the F1 generation is crossbred with one of the parents or genetically identical individuals to the parent. A test cross is a type of back cross is the unknown dominant phenotypic generation is F1 progeny. But a backcross is not a test cross.
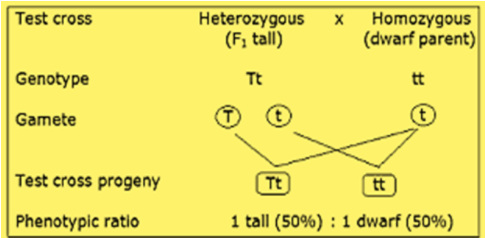
Complete answer :
In a test cross, a dominant phenotype organism is crossed with the homozygous recessive genotype organism in order to determine whether the dominant phenotype organism has homozygous dominant and heterozygous genotypes. Hence test cross is used to determine the zygosity of an organism with unknown genotype. This cross was first introduced by Gregor Mendel, father of genetics.
Consider the following example in plants: Suppose you have a tall and dwarf plant and tall characteristic (T) is dominant to dwarf(t). The dwarf plant must be homozygous for the recessive allele, but the genotype of the tall plant is unknown. It could be either TT or Tt. A testcross will decide the organism's genotype. The unknown genotype can be ascertained by examining the phenotypes of the resulting progeny. If crossing the unknown dominant phenotype (TT or Tt genotype) individual with the recessive phenotype individual produces only dominant phenotypes, then the plant with unknown genotype is homozygous dominant. If any recessive phenotypic plants emerge from the cross, then the unknown individual must possess the recessive allele, and have the heterozygous genotype.
Notes: In backcross, the F1 generation is crossbred with one of the parents or genetically identical individuals to the parent. A test cross is a type of back cross is the unknown dominant phenotypic generation is F1 progeny. But a backcross is not a test cross.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




