
A telephone cable at a place has four long straight horizontal wires carrying a current of 1.0 A in the same direction east to west. The Earth’s magnetic field at the place is 0.39 G and the angle of dip is ${{35}^{{}^\circ }}$. The magnetic declination is nearly zero. What are the resultant magnetic fields at points 4.0 cm below the cable?
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: The horizontal and vertical components of magnetic fields can be calculated using the given values of Earth’s magnetic field at a given point and the angle of dip. Use the formula ${{B}_{wire}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{I}{r}$ to find out the magnetic field produced due to the current flowing in a telephone cable. Finally, do a vector sum of all these magnetic fields to get a resultant magnetic field at a given point.
Complete answer:
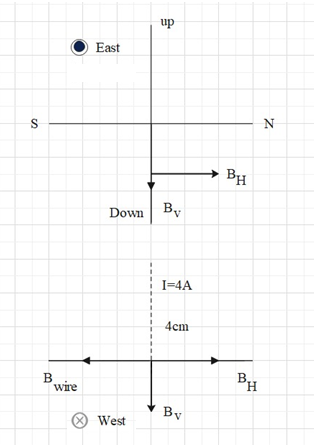
The figure illustrates the situation mentioned in the question.
Given that,
The current in the wire = I = 1.0 A
Earth’s magnetic field = B = 0.39 G
The angle of deep = $\delta ={{35}^{{}^\circ }}$
The horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is given as
$\begin{align}
& {{B}_{H}}=B\cos \delta \\
& {{B}_{H}}=0.39\cos {{35}^{{}^\circ }} \\
& {{B}_{H}}=0.39\times 0.8139 \\
& \therefore {{B}_{H}}=0.32G \\
\end{align}$
The vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field is given as
$\begin{align}
& {{B}_{V}}=B\sin \delta \\
& {{B}_{V}}=0.39\sin {{35}^{{}^\circ }} \\
& {{B}_{V}}=0.39\times 0.5736 \\
& \therefore {{B}_{V}}=0.22G \\
\end{align}$
The magnetic field due to the current in telephone cable is given as
${{B}_{wire}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{I}{r}$
We have to find the resultant magnetic fields at points 4.0 cm below the cable i.e. at r = 4.0 cm
Therefore,
${{B}_{wire}}={{10}^{-7}}\times \dfrac{1}{4\times {{10}^{-2}}}=2\times {{10}^{-5}}T=0.2G$
The net magnetic field at this point is given as
$\begin{align}
& {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{({{B}_{H}}-{{B}_{wire}})}^{2}}+{{B}_{V}}^{2}} \\
& {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{(0.32-0.2)}^{2}}+{{0.22}^{2}}} \\
& \therefore {{B}_{net}}=0.25G \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the resultant magnetic fields at points 4.0 cm below the cable is 0.25 G.
Note: Choose the units of all the quantities in the same system, later convert into the appropriate form of unit. Gauss (G) is the CGS unit of magnetic field whereas Tesla (T) is the SI unit of the magnetic field.
$\text{1T=1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-6}}}\text{G}$. The direction of the magnetic field produced by a current flowing through a straight wire is given by right hand thumb rule.
Complete answer:

The figure illustrates the situation mentioned in the question.
Given that,
The current in the wire = I = 1.0 A
Earth’s magnetic field = B = 0.39 G
The angle of deep = $\delta ={{35}^{{}^\circ }}$
The horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is given as
$\begin{align}
& {{B}_{H}}=B\cos \delta \\
& {{B}_{H}}=0.39\cos {{35}^{{}^\circ }} \\
& {{B}_{H}}=0.39\times 0.8139 \\
& \therefore {{B}_{H}}=0.32G \\
\end{align}$
The vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field is given as
$\begin{align}
& {{B}_{V}}=B\sin \delta \\
& {{B}_{V}}=0.39\sin {{35}^{{}^\circ }} \\
& {{B}_{V}}=0.39\times 0.5736 \\
& \therefore {{B}_{V}}=0.22G \\
\end{align}$
The magnetic field due to the current in telephone cable is given as
${{B}_{wire}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{I}{r}$
We have to find the resultant magnetic fields at points 4.0 cm below the cable i.e. at r = 4.0 cm
Therefore,
${{B}_{wire}}={{10}^{-7}}\times \dfrac{1}{4\times {{10}^{-2}}}=2\times {{10}^{-5}}T=0.2G$
The net magnetic field at this point is given as
$\begin{align}
& {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{({{B}_{H}}-{{B}_{wire}})}^{2}}+{{B}_{V}}^{2}} \\
& {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{(0.32-0.2)}^{2}}+{{0.22}^{2}}} \\
& \therefore {{B}_{net}}=0.25G \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the resultant magnetic fields at points 4.0 cm below the cable is 0.25 G.
Note: Choose the units of all the quantities in the same system, later convert into the appropriate form of unit. Gauss (G) is the CGS unit of magnetic field whereas Tesla (T) is the SI unit of the magnetic field.
$\text{1T=1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{-6}}}\text{G}$. The direction of the magnetic field produced by a current flowing through a straight wire is given by right hand thumb rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




