
A system of three polarizers ${{P}_{1}},{{P}_{2,}}{{P}_{3}}$ is set up such that the pass axis of ${{P}_{3}}$ is crossed with respect to that of${{P}_{1}}$. The pass axis of ${{P}_{2}}$ is inclined at ${{60}^{o}}$ to the pass axis of ${{P}_{3}}$when a beam of unpolarized light of intensity ${{I}_{O}}$ is incident on ${{P}_{1}}$the in of light transmitted by three polarized I. the ratio $\left( \dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{I} \right)$ equals (nearly):
$\begin{align}
& A.16.00 \\
& B.1.80 \\
& C.5.33 \\
& D.10.67 \\
\end{align}$
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: According to the malu’s law the intensity of the plane polarized light passing through a second polarized (also called as analyzers) is directly proportional to cosine of angle between axes of two polarizers when an unpolarized light is incident on a polarizer the intensity of light transmitted will always be half of the incident light.
Complete answer:
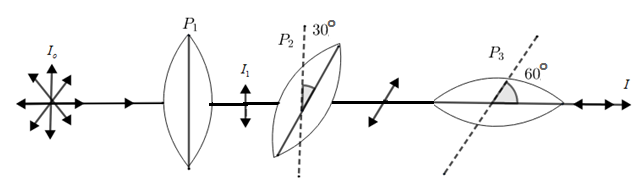
Given that intensity of light falling on polarizers ${{P}_{1}}$ and ${{I}_{O}}$. The intensity of light coming out from polarizer ${{P}_{3}}$ is I. so we have to find out ratio $\left( \dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{I} \right)$ i.e. ratio of intensity of incident light to intensity of transmitted light from the polarizer ${{P}_{3}}$. Also given that the incident light is unpolarized i.e. electric field in the incident light varies in all directions.
When this unpolarized light is incident on polarized ${{P}_{1}}$, the transmitted light through ${{P}_{1}}$ will be linearly polarized in which plane of vibration will in the plane of axis of polarizer. Therefore, the intensity of light that is transmitted through ${{P}_{1}}$ will be half of the intensity of incident light.
Let ${{I}_{1}}$ be the intensity of light that is transmitted through ${{P}_{1}}$
$\therefore {{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{2}$
This light will fall on the polarizer ${{P}_{2}}$
Given that the pass axis of ${{P}_{3}}$is crossed with the respect to that of ${{P}_{1}}$
Therefore the angle between the axis of polarizer ${{P}_{1}}$ and polarizer ${{P}_{3}}$ is ${{90}^{o}}$ also, the pass axis of ${{P}_{2}}$ is inclined at ${{60}^{o}}$ to the pass axis of ${{P}_{3}}$ therefore the angle between ${{P}_{2}}\text{ and }{{P}_{3}}$ is. Thus the angle between axes of polarizer ${{P}_{1}}$ and ${{P}_{2}}$ will be ${{30}^{o}}$. Let ${{I}_{2}}$ be the intensity of light transmitted through polarized ${{P}_{2}}$
Therefore according to Malus law
$\begin{align}
& {{I}_{2}}={{I}_{1}}{{\cos }^{2}}{{30}^{o}} \\
& =\dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{2}\times \dfrac{3}{4} \\
& {{I}_{2}}=\dfrac{3}{8}{{I}_{o}} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly the intensity of light that is transmitted through polarizer ${{P}_{3}}$ is
$\begin{align}
& I={{I}_{2}}{{\cos }^{2}}{{60}^{o}} \\
& \dfrac{3}{8}{{I}_{o}}\times \dfrac{1}{4} \\
& I=\dfrac{3}{32}{{I}_{o}} \\
& \therefore \dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{I}=\dfrac{32}{3} \\
& \dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{I}=10.67 \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the ratio $\left( \dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{I} \right)$ equals 10.67. Therefore the correct option is (D).
So, the correct answer is “Option d”.
Note:
Malu’s law helps to understand the polarization properties of light. This law gives the relation between intensity of light fall on a polarizer and the intensity of light transmitted through a same polarizer. Carefully take the angle students may get confused when plane polarized light is incident on a polarizer. In that case you have to consider the angle between the plane of polarization of incident light and the axis of the polarizer.
Complete answer:

Given that intensity of light falling on polarizers ${{P}_{1}}$ and ${{I}_{O}}$. The intensity of light coming out from polarizer ${{P}_{3}}$ is I. so we have to find out ratio $\left( \dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{I} \right)$ i.e. ratio of intensity of incident light to intensity of transmitted light from the polarizer ${{P}_{3}}$. Also given that the incident light is unpolarized i.e. electric field in the incident light varies in all directions.
When this unpolarized light is incident on polarized ${{P}_{1}}$, the transmitted light through ${{P}_{1}}$ will be linearly polarized in which plane of vibration will in the plane of axis of polarizer. Therefore, the intensity of light that is transmitted through ${{P}_{1}}$ will be half of the intensity of incident light.
Let ${{I}_{1}}$ be the intensity of light that is transmitted through ${{P}_{1}}$
$\therefore {{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{2}$
This light will fall on the polarizer ${{P}_{2}}$
Given that the pass axis of ${{P}_{3}}$is crossed with the respect to that of ${{P}_{1}}$
Therefore the angle between the axis of polarizer ${{P}_{1}}$ and polarizer ${{P}_{3}}$ is ${{90}^{o}}$ also, the pass axis of ${{P}_{2}}$ is inclined at ${{60}^{o}}$ to the pass axis of ${{P}_{3}}$ therefore the angle between ${{P}_{2}}\text{ and }{{P}_{3}}$ is. Thus the angle between axes of polarizer ${{P}_{1}}$ and ${{P}_{2}}$ will be ${{30}^{o}}$. Let ${{I}_{2}}$ be the intensity of light transmitted through polarized ${{P}_{2}}$
Therefore according to Malus law
$\begin{align}
& {{I}_{2}}={{I}_{1}}{{\cos }^{2}}{{30}^{o}} \\
& =\dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{2}\times \dfrac{3}{4} \\
& {{I}_{2}}=\dfrac{3}{8}{{I}_{o}} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly the intensity of light that is transmitted through polarizer ${{P}_{3}}$ is
$\begin{align}
& I={{I}_{2}}{{\cos }^{2}}{{60}^{o}} \\
& \dfrac{3}{8}{{I}_{o}}\times \dfrac{1}{4} \\
& I=\dfrac{3}{32}{{I}_{o}} \\
& \therefore \dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{I}=\dfrac{32}{3} \\
& \dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{I}=10.67 \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the ratio $\left( \dfrac{{{I}_{o}}}{I} \right)$ equals 10.67. Therefore the correct option is (D).
So, the correct answer is “Option d”.
Note:
Malu’s law helps to understand the polarization properties of light. This law gives the relation between intensity of light fall on a polarizer and the intensity of light transmitted through a same polarizer. Carefully take the angle students may get confused when plane polarized light is incident on a polarizer. In that case you have to consider the angle between the plane of polarization of incident light and the axis of the polarizer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




