
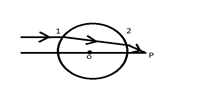
A sunshine recorder globe of 30cm diameter is made of glass of $\mu = 1.5$. A ray enters the globe parallel to its axis. Find the position from the centre of the sphere, where the ray crosses the axis.

Answer
576k+ views
Hint:Here the above question deals with two medium air and glass. Hence we have to find the image and object distance at the two surfaces A and B. apply the relation between the object distance $u$, image distance $v$, refractive index $n$ and radius of curvature $R$ for refraction at a spherical surface. Apply the given data to obtain the position from the centre of the sphere
Formula Used:
$\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{n_2} - {n_1}}}{R}$
Here$u$,$v$,$R$,$n$are object distance ,image distance, radius of curvature and refractive index
Complete step by step answer:
Bending of a light wave passing through one medium to another medium due to the change in wave speed is the Refraction. The ray bends towards the normal, when a light travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium.
For lenses the sign convention:
Focal length of a convex lens is positive and for a concave lens is negative.
The optical centre is taken by all the measurements.
All measurements are taken from the optical centre.
Optical centre of a lens lies on the origin of the x-y axis.
Here the light undergoes refraction twice. The incident light gets refracted at surface 1, that light gets refracted again at surface 2.
Let us first consider the surface 1, here ${n_1} = 1$ and ${n_2} = 1.5$.
$\dfrac{{1.5}}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{ - \infty }} = \dfrac{{1.5 - 1}}{{15}}$
$v = \dfrac{{15 \times 1.5}}{{0.5}}$
$v = 45cm$
For the second surface, here${n_1} = 1.5$,${n_2} = 1$; The image formed on surface 1 acts as the object for surface 2.
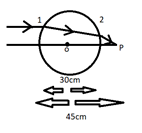
Hence the object distance $u = 45 - 30 = 15cm$
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{{1.5}}{{15}} = \dfrac{{1 - 1.5}}{{ - 15}}$
$v = \dfrac{{15}}{2} = 7.5cm$
Hence the position from the centre of the sphere $ = 15 + 7.5 = 22.5cm$
Note:While solving problems relating to lenses, we should take proper care of the signs of different quantities. The magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to that of the height of the object. Lens formula gives the relationship between object distance, image distance and the focal length.
Formula Used:
$\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{n_2} - {n_1}}}{R}$
Here$u$,$v$,$R$,$n$are object distance ,image distance, radius of curvature and refractive index
Complete step by step answer:
Bending of a light wave passing through one medium to another medium due to the change in wave speed is the Refraction. The ray bends towards the normal, when a light travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium.
For lenses the sign convention:
Focal length of a convex lens is positive and for a concave lens is negative.
The optical centre is taken by all the measurements.
All measurements are taken from the optical centre.
Optical centre of a lens lies on the origin of the x-y axis.
Here the light undergoes refraction twice. The incident light gets refracted at surface 1, that light gets refracted again at surface 2.
Let us first consider the surface 1, here ${n_1} = 1$ and ${n_2} = 1.5$.
$\dfrac{{1.5}}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{ - \infty }} = \dfrac{{1.5 - 1}}{{15}}$
$v = \dfrac{{15 \times 1.5}}{{0.5}}$
$v = 45cm$
For the second surface, here${n_1} = 1.5$,${n_2} = 1$; The image formed on surface 1 acts as the object for surface 2.

Hence the object distance $u = 45 - 30 = 15cm$
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{{1.5}}{{15}} = \dfrac{{1 - 1.5}}{{ - 15}}$
$v = \dfrac{{15}}{2} = 7.5cm$
Hence the position from the centre of the sphere $ = 15 + 7.5 = 22.5cm$
Note:While solving problems relating to lenses, we should take proper care of the signs of different quantities. The magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to that of the height of the object. Lens formula gives the relationship between object distance, image distance and the focal length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




