
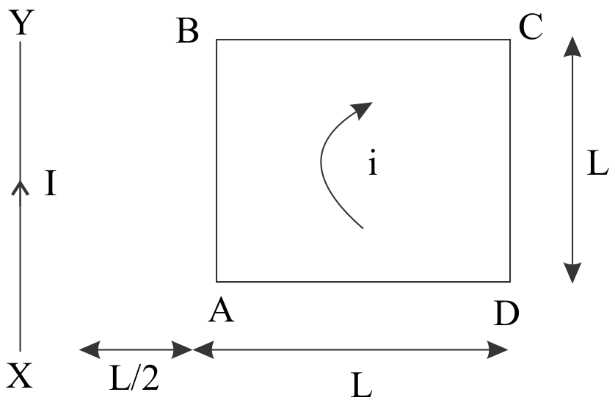
A square loop ABCD carrying a current I, is placed near and coplanar with a long straight conductor XY carrying a current I, the net force on the loop will be:
A.$\dfrac{{2{\mu _o}Ii}}{{3\pi }}$
B.$\dfrac{{{\mu _o}Ii}}{{2\pi }}$
C.$\dfrac{{2{\mu _o}IiL}}{{3\pi }}$
D.$\dfrac{{{\mu _o}IiL}}{{2\pi }}$

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint:- In this type of question firstly we have to find the magnetic field strength at the given distance from the current carrying wire. Then after finding the magnetic field strength we have to calculate force on the loop wires which are parallel to the current carrying wire and finally we have to find the resultant of the forces.
Complete step-by-step solution:As given in figure we have a current carrying wire having current of I ampere in it.
So we all know that magnetic field strength at particular point is given as :
Mathematically, $\vec B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi r}}$ where B is magnetic strength
I is current on the wire
r is distance from the loop wire from current carrying wire.
${\mu _o}$is permittivity of free space
$\therefore $in the given figure wire AB and CD will contribute in the force because they are parallel to current carrying wire while wire AC and BD will not contribute in the forces because these are perpendicular to the current carrying wire.
Now ,we know that force on the wire will be equal to $\vec Bil$
Mathematically $\vec F = \vec Bil$where $i$is current on the loop wire.
So ,firstly we will find the force on the wire AB
Magnetic field at wire AB will be ${\vec B_{AB}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi r}}$
So force on wire AB will be $
\vec F = \vec BiL \\
\vec F = \dfrac{{({\mu _o}I)iL}}{{2\pi \dfrac{L}{2}}} \\
\vec F = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}Ii}}{\pi } \\
$ on solving this equation ,we get
Now we will find the magnetic field strength at wire CD
${\vec B_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi \dfrac{{3L}}{2}}}$
${\vec B_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{3\pi L}}$
Now we will find the force on wire CD-
${\vec F_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}IiL}}{{3\pi L}}$
${\vec F_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}Ii}}{{3\pi }}$
$\therefore $current on the both wire is in opposite direction
So resultant forces will be ${\vec F_{net}} = {\vec F_{AB}} - {\vec F_{CD}}$
$
{{\vec F}_{net}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}Ii}}{\pi } - \dfrac{{{\mu _o}Ii}}{{3\pi }} \\
{{\vec F}_{net}} = \dfrac{{2{\mu _o}Ii}}{{3\pi }} \\
$
So the correct option will be option number A.
Note:-
The current carrying wire produces magnetic field strength. The magnetic field strength is different for the different locations. Magnetic field strength produces force on current carrying wire.by the use of the right hand thumb we can find the direction of force and magnetic field. By adding both the force vector we can find the direction of net force
Complete step-by-step solution:As given in figure we have a current carrying wire having current of I ampere in it.
So we all know that magnetic field strength at particular point is given as :
Mathematically, $\vec B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi r}}$ where B is magnetic strength
I is current on the wire
r is distance from the loop wire from current carrying wire.
${\mu _o}$is permittivity of free space
$\therefore $in the given figure wire AB and CD will contribute in the force because they are parallel to current carrying wire while wire AC and BD will not contribute in the forces because these are perpendicular to the current carrying wire.
Now ,we know that force on the wire will be equal to $\vec Bil$
Mathematically $\vec F = \vec Bil$where $i$is current on the loop wire.
So ,firstly we will find the force on the wire AB
Magnetic field at wire AB will be ${\vec B_{AB}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi r}}$
So force on wire AB will be $
\vec F = \vec BiL \\
\vec F = \dfrac{{({\mu _o}I)iL}}{{2\pi \dfrac{L}{2}}} \\
\vec F = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}Ii}}{\pi } \\
$ on solving this equation ,we get
Now we will find the magnetic field strength at wire CD
${\vec B_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi \dfrac{{3L}}{2}}}$
${\vec B_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{3\pi L}}$
Now we will find the force on wire CD-
${\vec F_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}IiL}}{{3\pi L}}$
${\vec F_{CD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}Ii}}{{3\pi }}$
$\therefore $current on the both wire is in opposite direction
So resultant forces will be ${\vec F_{net}} = {\vec F_{AB}} - {\vec F_{CD}}$
$
{{\vec F}_{net}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}Ii}}{\pi } - \dfrac{{{\mu _o}Ii}}{{3\pi }} \\
{{\vec F}_{net}} = \dfrac{{2{\mu _o}Ii}}{{3\pi }} \\
$
So the correct option will be option number A.
Note:-
The current carrying wire produces magnetic field strength. The magnetic field strength is different for the different locations. Magnetic field strength produces force on current carrying wire.by the use of the right hand thumb we can find the direction of force and magnetic field. By adding both the force vector we can find the direction of net force
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




