
A spring toy weighing 1 kg on a spring balance suddenly jumps upwards. A boy standing near the toy notices that the scale of the balance reads 1.05 kg. In this process the maximum acceleration of the toy is (\[g=10m{{s}^{2}}\])
\[\begin{align}
& A.\,0.05\,m{{s}^{2}} \\
& B.\,0.5\,m{{s}^{2}} \\
& C.\,1.05\,m{{s}^{2}} \\
& D.\,1\,m{{s}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Firstly, we will compute the normal force acting on the spring toy when the toy is at rest and when the toy jumps off the balance. Using these values, we will compute the net normal force acting on the spring toy. Finally, we will make use of this value to find the maximum acceleration of the toy.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& F=mg \\
& a=\dfrac{F}{m} \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step solution:
The formulae used are as follows:
The normal force acting on a body is,
\[F=mg\]
Where F is the normal force, m is the mass of the body and g is the gravitational constant.
The acceleration of the body is,
\[a=\dfrac{F}{m}\]
Where a is the acceleration, F is the force and m is the mass of the body.
From the data, we have the data as follows.
The weight of the spring toy, \[m=1kg\]
The gravitational constant, \[g=10m{{s}^{2}}\]
The toy jumps off the balance. This statement implies that the normal force acting on the balance will increase, that is given to be equal to the value of 1.05 kg.
The free-body diagram
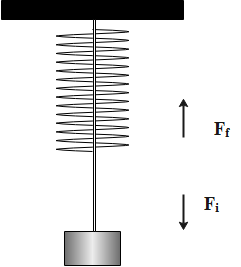
The normal force acting on the spring toy when, the toy jumps off the balance is calculated as follows,
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{f}}={{m}_{f}}g \\
& {{F}_{f}}=1.05\times 10 \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{f}}=10.5\,N \\
\end{align}\]
The normal force acting on the spring toy, initially, when, the toy was at rest is calculated as follows,
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{i}}=mg \\
& {{F}_{i}}=1\times 10 \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{i}}=10\,N \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the net normal force acting on the spring toy is calculated as follows.
\[F={{F}_{f}}-{{F}_{i}}\]
Substitute the given values and the obtained values in the above equation to find the value of the net normal force acting on the spring toy.
\[\begin{align}
& F=10.5-10 \\
& \Rightarrow F=0.5\,N \\
\end{align}\]
Now we will compute the maximum acceleration of the spring toy.
The acceleration is given as follows
\[a=\dfrac{F}{m}\]
Substitute the given values and the obtained values in the above equation.
\[\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{0.5}{1} \\
& a=0.5m{{s}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] The value of the maximum acceleration of the spring toy is \[0.5m{{s}^{2}}\].
As the value of the maximum acceleration of the spring is \[0.5m{{s}^{2}}\], thus, the option (B) is correct.
Note:
The units of the parameters should be taken care of. Calculating the normal force acting on the spring toy when it jumps off the balance is a very important step, as, if we miss this step, then the complete calculation goes wrong.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& F=mg \\
& a=\dfrac{F}{m} \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step solution:
The formulae used are as follows:
The normal force acting on a body is,
\[F=mg\]
Where F is the normal force, m is the mass of the body and g is the gravitational constant.
The acceleration of the body is,
\[a=\dfrac{F}{m}\]
Where a is the acceleration, F is the force and m is the mass of the body.
From the data, we have the data as follows.
The weight of the spring toy, \[m=1kg\]
The gravitational constant, \[g=10m{{s}^{2}}\]
The toy jumps off the balance. This statement implies that the normal force acting on the balance will increase, that is given to be equal to the value of 1.05 kg.
The free-body diagram

The normal force acting on the spring toy when, the toy jumps off the balance is calculated as follows,
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{f}}={{m}_{f}}g \\
& {{F}_{f}}=1.05\times 10 \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{f}}=10.5\,N \\
\end{align}\]
The normal force acting on the spring toy, initially, when, the toy was at rest is calculated as follows,
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{i}}=mg \\
& {{F}_{i}}=1\times 10 \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{i}}=10\,N \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the net normal force acting on the spring toy is calculated as follows.
\[F={{F}_{f}}-{{F}_{i}}\]
Substitute the given values and the obtained values in the above equation to find the value of the net normal force acting on the spring toy.
\[\begin{align}
& F=10.5-10 \\
& \Rightarrow F=0.5\,N \\
\end{align}\]
Now we will compute the maximum acceleration of the spring toy.
The acceleration is given as follows
\[a=\dfrac{F}{m}\]
Substitute the given values and the obtained values in the above equation.
\[\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{0.5}{1} \\
& a=0.5m{{s}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] The value of the maximum acceleration of the spring toy is \[0.5m{{s}^{2}}\].
As the value of the maximum acceleration of the spring is \[0.5m{{s}^{2}}\], thus, the option (B) is correct.
Note:
The units of the parameters should be taken care of. Calculating the normal force acting on the spring toy when it jumps off the balance is a very important step, as, if we miss this step, then the complete calculation goes wrong.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




