
A spherical convex surface separates object and image spaces of refractive index $1 \cdot 0$ and $1 \cdot 5$ respectively. If the radius of curvature of the surface is $25{\text{cm}}$, find its power.
A) $13 \cdot 0$
B) $33 \cdot 0$
C) $3 \cdot 3$
D) $1 \cdot 3$
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint:For a spherical surface, the rays of light from the object parallel to the principal axis will diverge or converge at the focal point. For a convex surface, the light rays will converge at the focal point. So if the object was placed at infinity then the corresponding image will be formed at the focal point of the convex surface. The power of the surface is the reciprocal of the focal length of the convex surface.
Formulas used:
-The power of a lens is given by, $P = \dfrac{1}{f}$ where $f$ is the focal length of the lens.
-The relation between the object distance and the image distance for a spherical surface is given by, $\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{n_2} - {n_1}}}{R}$ where ${n_1}$, ${n_2}$ are the refractive indices of the two media, $u$ is the object distance, $v$ is the image distance and $R$ is the radius of curvature of the spherical surface.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: List the parameters of the problem at hand.
Here we assume the object to be at infinity i.e., the object distance $u = \infty $ .
Then the corresponding image will be formed at the focal point and so the image distance will be $v = f$. This is represented in the figure below.
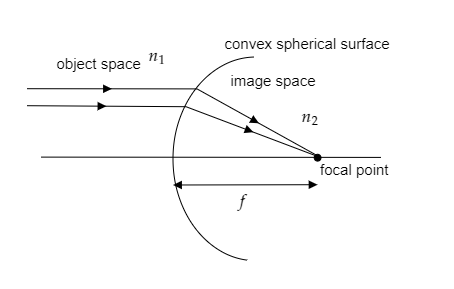
The radius of curvature of the spherical surface is given to be $R = 25{\text{cm}}$ .
The refractive index of the object space is given to be ${n_1} = 1 \cdot 0$ .
The refractive index of the image space is given to be ${n_2} = 1 \cdot 5$ .
Step 2: Express the relation between the object distance and the image distance of the given spherical surface to find the focal length of the surface.
The relation between the object distance and the image distance of the given convex surface can be expressed as $\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{n_2} - {n_1}}}{R}$ ------ (1)
Substituting for $u = \infty $, $v = f$, $R = 25{\text{cm}}$, ${n_1} = 1 \cdot 0$ and ${n_2} = 1 \cdot 5$ in equation (1) we get, $\dfrac{{1 \cdot 5}}{f} - \dfrac{1}{\infty } = \dfrac{{1 \cdot 5 - 1}}{{25}}$
$ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{{25 \times 1 \cdot 5}}{{0 \cdot 5}} = 75{\text{cm}}$
Thus the focal length of the convex surface is obtained as $f = 75{\text{cm}}$ .
Step 3: Express the power of the convex surface.
The power of the convex surface will be the reciprocal of its focal length i.e., $P = \dfrac{1}{f}$ ------- (2)
Substituting for $f = 0 \cdot 75{\text{m}}$ in equation (2) we get, $P = \dfrac{1}{{0 \cdot 75}} = 1 \cdot 33{\text{D}}$
$\therefore $ the power of the convex surface is $P = 1 \cdot 33{\text{D}}$ .
So the correct option is D.
Note:The power of a lens is expressed in the units of dioptres which is essentially ${{\text{m}}^{ - 1}}$ and equation (2) suggests that the focal length of the given convex surface has to be expressed in meters. So we made a conversion of the unit from centimetres to meters for the focal length as $f = 75{\text{cm}} = 0 \cdot 75{\text{m}}$ before substituting in equation (2).
Formulas used:
-The power of a lens is given by, $P = \dfrac{1}{f}$ where $f$ is the focal length of the lens.
-The relation between the object distance and the image distance for a spherical surface is given by, $\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{n_2} - {n_1}}}{R}$ where ${n_1}$, ${n_2}$ are the refractive indices of the two media, $u$ is the object distance, $v$ is the image distance and $R$ is the radius of curvature of the spherical surface.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: List the parameters of the problem at hand.
Here we assume the object to be at infinity i.e., the object distance $u = \infty $ .
Then the corresponding image will be formed at the focal point and so the image distance will be $v = f$. This is represented in the figure below.

The radius of curvature of the spherical surface is given to be $R = 25{\text{cm}}$ .
The refractive index of the object space is given to be ${n_1} = 1 \cdot 0$ .
The refractive index of the image space is given to be ${n_2} = 1 \cdot 5$ .
Step 2: Express the relation between the object distance and the image distance of the given spherical surface to find the focal length of the surface.
The relation between the object distance and the image distance of the given convex surface can be expressed as $\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{n_2} - {n_1}}}{R}$ ------ (1)
Substituting for $u = \infty $, $v = f$, $R = 25{\text{cm}}$, ${n_1} = 1 \cdot 0$ and ${n_2} = 1 \cdot 5$ in equation (1) we get, $\dfrac{{1 \cdot 5}}{f} - \dfrac{1}{\infty } = \dfrac{{1 \cdot 5 - 1}}{{25}}$
$ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{{25 \times 1 \cdot 5}}{{0 \cdot 5}} = 75{\text{cm}}$
Thus the focal length of the convex surface is obtained as $f = 75{\text{cm}}$ .
Step 3: Express the power of the convex surface.
The power of the convex surface will be the reciprocal of its focal length i.e., $P = \dfrac{1}{f}$ ------- (2)
Substituting for $f = 0 \cdot 75{\text{m}}$ in equation (2) we get, $P = \dfrac{1}{{0 \cdot 75}} = 1 \cdot 33{\text{D}}$
$\therefore $ the power of the convex surface is $P = 1 \cdot 33{\text{D}}$ .
So the correct option is D.
Note:The power of a lens is expressed in the units of dioptres which is essentially ${{\text{m}}^{ - 1}}$ and equation (2) suggests that the focal length of the given convex surface has to be expressed in meters. So we made a conversion of the unit from centimetres to meters for the focal length as $f = 75{\text{cm}} = 0 \cdot 75{\text{m}}$ before substituting in equation (2).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




