
A sphere rolls without slipping on an inclined at $\theta $. Then minimum value of coefficient of friction so that the sphere rolls without slipping is
a) $\dfrac{1}{7}\tan \theta $
b) $\dfrac{2}{7}\tan \theta $
c) $\dfrac{5}{7}\tan \theta $
d) $\dfrac{3}{7}\tan \theta $
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Draw the free body diagram of the sphere and by using Newton’s second law of motion, write the equations of motion to find the value of friction in terms of $\theta $. For pure rolling, the calculated frictional force should be less than or equal to the maximum frictional force, i.e. $\mu N$. So, find the value of $\theta $ by using this result.
Complete step by step answer:
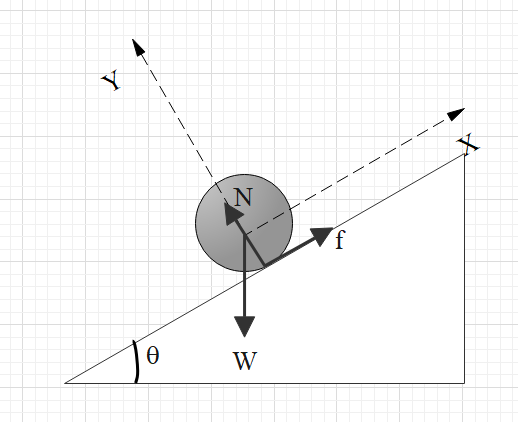
From the above diagram, by using Newton’s Law of motion: ${{F}_{net}}=ma$
We get the following equations:
$\begin{align}
& mg\sin \theta -f=ma......(1) \\
& N=mg\cos \theta ......(2) \\
\end{align}$
Since the sphere is rolling, so by using the formula: $F\times r=I\alpha $
We have:
$f\times r=I\alpha ......(3)$
As we know that: $a=R\alpha ......(4)$
So, put the value from equation (3) in equation (4), we get:
$a=\dfrac{f\times {{r}^{2}}}{I}......(5)$
Also, we know that, the moment of inertia of a sphere is: $I=\dfrac{2}{5}m{{r}^{2}}$
So, we get:
$\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{5f\times {{r}^{2}}}{2m{{r}^{2}}} \\
& =\dfrac{5f}{2m}......(6)
\end{align}$
Now, put the value of acceleration from equation (6) in equation (1), we get:
$ mg\sin \theta -f=m\dfrac{5f}{2m} \\ $
$ \implies mg\sin \theta =\dfrac{5f}{2}+f \\ $
$ \implies mg\sin \theta =f\left[ \dfrac{5}{2}+1 \right] \\ $
$ \therefore f=\dfrac{2}{7}mg\sin \theta ......(7) \\ $
For pure rolling, the calculated frictional force should be less than or equal to the maximum frictional force, i.e. $\mu N$
So, we can say that:
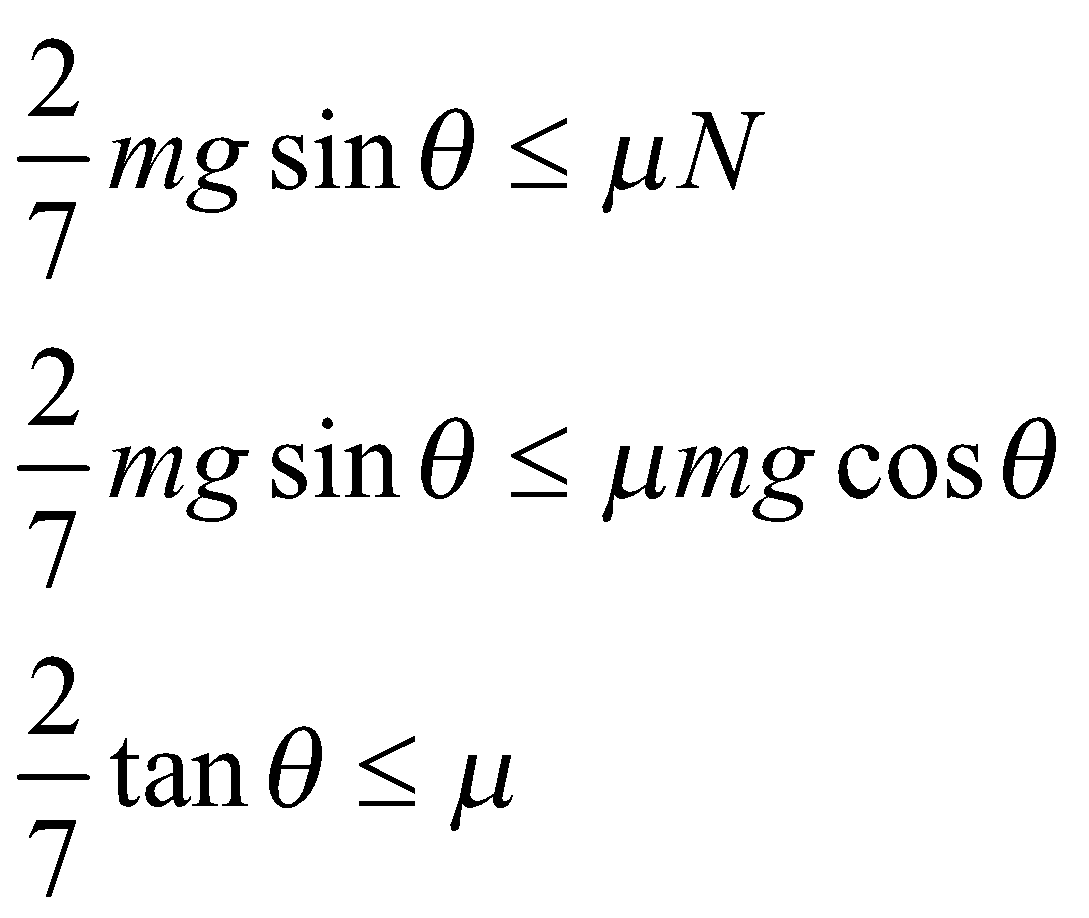
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Pure rolling is a case when the point of bottom contact of the rolling body with the ground remains at rest and the body is considered to be rotating about this point of contact. For example, if a ball is rolling on a fixed surface then the velocity of the point of contact must also zero. Moreover, friction is the force that is responsible for pure rolling.
Complete step by step answer:

From the above diagram, by using Newton’s Law of motion: ${{F}_{net}}=ma$
We get the following equations:
$\begin{align}
& mg\sin \theta -f=ma......(1) \\
& N=mg\cos \theta ......(2) \\
\end{align}$
Since the sphere is rolling, so by using the formula: $F\times r=I\alpha $
We have:
$f\times r=I\alpha ......(3)$
As we know that: $a=R\alpha ......(4)$
So, put the value from equation (3) in equation (4), we get:
$a=\dfrac{f\times {{r}^{2}}}{I}......(5)$
Also, we know that, the moment of inertia of a sphere is: $I=\dfrac{2}{5}m{{r}^{2}}$
So, we get:
$\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{5f\times {{r}^{2}}}{2m{{r}^{2}}} \\
& =\dfrac{5f}{2m}......(6)
\end{align}$
Now, put the value of acceleration from equation (6) in equation (1), we get:
$ mg\sin \theta -f=m\dfrac{5f}{2m} \\ $
$ \implies mg\sin \theta =\dfrac{5f}{2}+f \\ $
$ \implies mg\sin \theta =f\left[ \dfrac{5}{2}+1 \right] \\ $
$ \therefore f=\dfrac{2}{7}mg\sin \theta ......(7) \\ $
For pure rolling, the calculated frictional force should be less than or equal to the maximum frictional force, i.e. $\mu N$
So, we can say that:
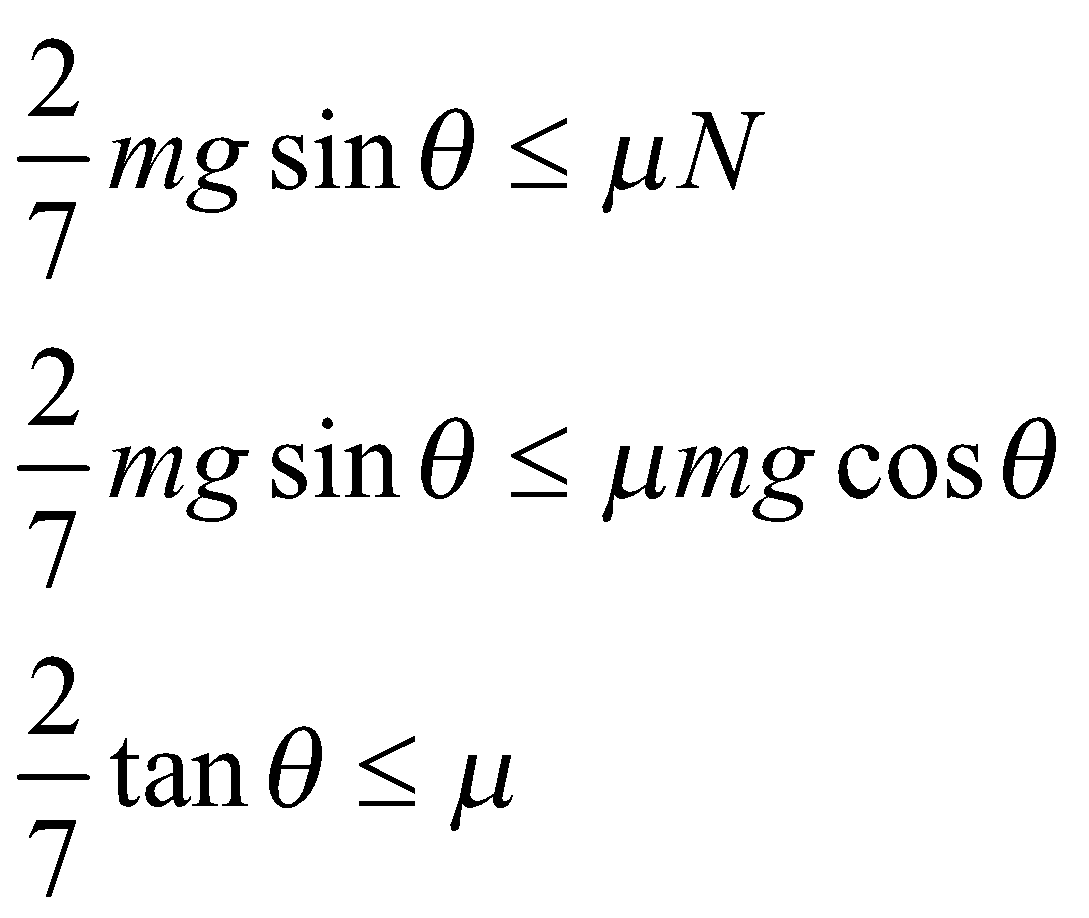
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Pure rolling is a case when the point of bottom contact of the rolling body with the ground remains at rest and the body is considered to be rotating about this point of contact. For example, if a ball is rolling on a fixed surface then the velocity of the point of contact must also zero. Moreover, friction is the force that is responsible for pure rolling.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




