
A solid non-conducting sphere of radius $R$, having a spherical cavity of radius $\dfrac{R}{2}$ as shown, carries a uniformly distributed charge $q$. The electric field at the centre of the cavity is:
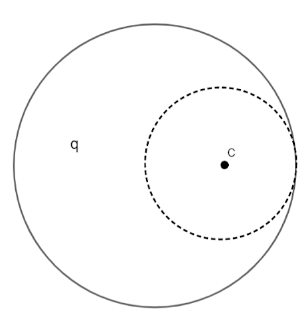

Answer
509.4k+ views
Hint: From the Gauss Law of Electrostatics we can find out the electric field.The electric field inside a non-conducting sphere is $0$. So, we have to find out the electric field only of the cavity. The electric field of the cavity is the same as the electric field at the surface of any sphere. Since, the cavity is in the positive direction of the X-axis so we will consider the outcome to be a positive value.
Complete step by step answer:
From the Gauss Law of Electrostatics we know,
$\oint {E.dS} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$ where $E$ is the electric field, $dS$ is the enclosed surface area, $q$ is the charge enclosed.
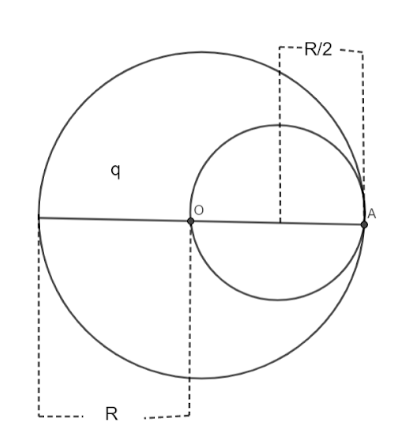
In the given figure O is the centre. Let $A$ be any point on the surface. The charge enclosed in the non-conducting sphere is$ = 0$. So, the electric field here is also $0$. We have to just find out the electric field of the cavity. According to the given question,
Charge enclosed by the sphere$ = q$.
The radius of the cavity is given as $\dfrac{R}{2}$.
Let the volume charge density over radius $R$ be $\rho $.
$q = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {R^3}$
So, the charge $q'$ over radius $\dfrac{R}{2}$ is $q = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)^3} = \rho \dfrac{{\pi {R^3}}}{6}$
$dS = $enclosed area of the cavity$ = 4\pi {\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)^2} = \pi {R^2}$
Substituting these values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$E.dS = \dfrac{{q'}}{\varepsilon }$
$\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{{\rho \dfrac{{\pi {R^3}}}{6}}}{{\pi {R^2}{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
\therefore E = \dfrac{{\rho R}}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}} \\ $
Thus now we get the electric field $E = \dfrac{{\rho R}}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}}$.
Note: Gauss Law is applicable in many cases as it is shown here. The electric field inside both a hollow sphere and a non-conducting sphere is $0$. But the electric field inside a conducting sphere is not $0$ as the charge does not reside outside the sphere.
Complete step by step answer:
From the Gauss Law of Electrostatics we know,
$\oint {E.dS} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$ where $E$ is the electric field, $dS$ is the enclosed surface area, $q$ is the charge enclosed.
In the given figure O is the centre. Let $A$ be any point on the surface. The charge enclosed in the non-conducting sphere is$ = 0$. So, the electric field here is also $0$. We have to just find out the electric field of the cavity. According to the given question,
Charge enclosed by the sphere$ = q$.
The radius of the cavity is given as $\dfrac{R}{2}$.

Let the volume charge density over radius $R$ be $\rho $.
$q = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {R^3}$
So, the charge $q'$ over radius $\dfrac{R}{2}$ is $q = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)^3} = \rho \dfrac{{\pi {R^3}}}{6}$
$dS = $enclosed area of the cavity$ = 4\pi {\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)^2} = \pi {R^2}$
Substituting these values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$E.dS = \dfrac{{q'}}{\varepsilon }$
$\Rightarrow E = \dfrac{{\rho \dfrac{{\pi {R^3}}}{6}}}{{\pi {R^2}{\varepsilon _0}}} \\
\therefore E = \dfrac{{\rho R}}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}} \\ $
Thus now we get the electric field $E = \dfrac{{\rho R}}{{6{\varepsilon _0}}}$.
Note: Gauss Law is applicable in many cases as it is shown here. The electric field inside both a hollow sphere and a non-conducting sphere is $0$. But the electric field inside a conducting sphere is not $0$ as the charge does not reside outside the sphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




