
A solenoid L and a resistor R are connected in series to a battery, through a switch. When the switch is put on, current I flowing through it varies with time t as shown in which of graphs given below:
A.)
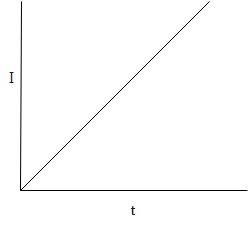
B.)
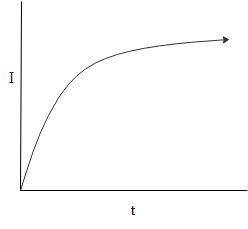
C.)
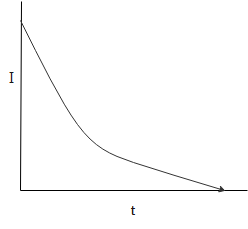
D.)
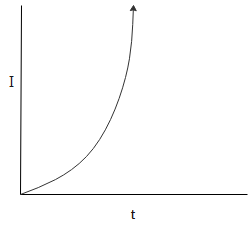




Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: First we need to draw a series circuit for resistance and inductor. Then we can apply the Kirchoff’s voltage law which states that all the voltages in a circuit add up to zero. Solving the obtained equation may give us the desired trend in current with time.
Detailed step by step solution:
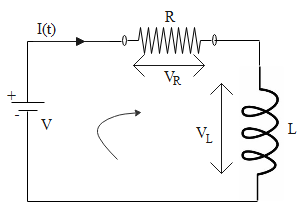
Consider a solenoid of inductance L and a resistor of resistance R connected in series with each other as shown in the figure. This series combination is connected to a constant source of voltage which is given as $V$. When the battery is connected to the circuit at time t = 0, the current starts flowing and increases with time. The voltage drop across resistance R is ${V_R}$ and voltage drop across inductance L is ${V_L}$.
We need to calculate the expression for variation of current in this circuit with time. This can be done by applying the Kirchoff’s voltage law which states that in a given circuit, all the voltages add up to zero.
Now, applying the Kirchoff’s voltage law to the above circuit we get
$
- V + {V_R} + {V_L} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow V - \left( {{V_R} + {V_L}} \right) = 0{\text{ }}...\left( i \right) \\
$
The voltage drop across the resistance R is governed by the Ohm’s law, therefore,
${V_R} = IR$
In the case of an inductor, the voltage drop occurring due to inductance is given as
${V_L} = L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}$
Using these expressions in equation (i), we get
$V = IR + L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}$
This is a first order differential equation which gives the following solution.
$I\left( t \right) = \dfrac{V}{R}\left( {1 - {e^{ - \dfrac{{Rt}}{L}}}} \right)$
This variation can be graphically represented as follows:
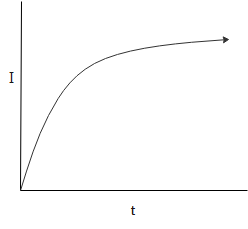
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: While applying the KIrchoff’s voltage law, we count voltages either in clockwise direction or anticlockwise direction. When we go from negative voltage to positive voltage, we use the negative sign for that particular voltage and vice-versa.
Detailed step by step solution:

Consider a solenoid of inductance L and a resistor of resistance R connected in series with each other as shown in the figure. This series combination is connected to a constant source of voltage which is given as $V$. When the battery is connected to the circuit at time t = 0, the current starts flowing and increases with time. The voltage drop across resistance R is ${V_R}$ and voltage drop across inductance L is ${V_L}$.
We need to calculate the expression for variation of current in this circuit with time. This can be done by applying the Kirchoff’s voltage law which states that in a given circuit, all the voltages add up to zero.
Now, applying the Kirchoff’s voltage law to the above circuit we get
$
- V + {V_R} + {V_L} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow V - \left( {{V_R} + {V_L}} \right) = 0{\text{ }}...\left( i \right) \\
$
The voltage drop across the resistance R is governed by the Ohm’s law, therefore,
${V_R} = IR$
In the case of an inductor, the voltage drop occurring due to inductance is given as
${V_L} = L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}$
Using these expressions in equation (i), we get
$V = IR + L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}$
This is a first order differential equation which gives the following solution.
$I\left( t \right) = \dfrac{V}{R}\left( {1 - {e^{ - \dfrac{{Rt}}{L}}}} \right)$
This variation can be graphically represented as follows:

Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: While applying the KIrchoff’s voltage law, we count voltages either in clockwise direction or anticlockwise direction. When we go from negative voltage to positive voltage, we use the negative sign for that particular voltage and vice-versa.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




