
A small source of light is 4m below the surface of a liquid of refractive index $ 5/3 $ . In order to cut off all the light coming out of the liquid surface, the minimum diameter of the disc placed on the surface of the liquid is
A) 3m
B) 4m
C) 6m
D) $ \infty $
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint : In order for the disc to block the light coming from the light source completely, it must have a radius large enough that the light coming from the source at all angles below than the critical angle can be blocked. We will then use some geometry to determine the diameter of the disc.
Formula used: In this solution, we will use the following formula:
Snell’s law: $ {\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2} $ where $ {\mu _1} $ and $ {\mu _2} $ are the refractive index of two different mediums and $ {\theta _1} $ and $ {\theta _2} $ are the angles made by the ray of light with the normal to the surface of refraction.
Complete step by step answer
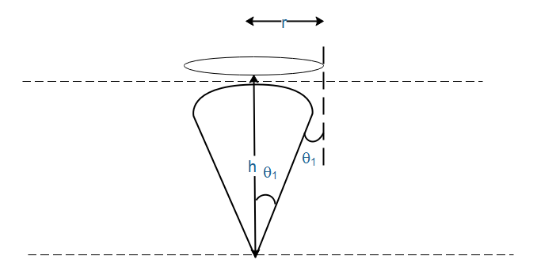
As we can see in the image above, the disc must have a large enough radius that it can block any ray of light that is approaching the interface of two mediums with an angle less than the critical angle of light. If the light approaches at any angle greater than the critical angle, it will be reflected back into the liquid.
So, let us start by finding the critical angle of light. Using Snells’ law we can write
$\Rightarrow {\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2} $
Substituting $ {\mu _1} = \,5/3 $ , $ {\mu _2} = 1 $ and $ {\theta _2} = 90^\circ $ , we get
$\Rightarrow \sin {\theta _1} = \dfrac{3}{5} $
Then we can calculate
$\Rightarrow \tan {\theta _1} = \dfrac{3}{4} $
Since $ \tan {\theta _1} = \dfrac{r}{h} $ , we can write
$\Rightarrow
\dfrac{r}{h} = \dfrac{3}{4} \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{{3h}}{4} \\
\ $
Substituting the value of $ h = \,4m $ , we get
$\Rightarrow r = 3m $
Hence the diameter of the disc will be 6m which corresponds to option (C).
Note
Here, we have treated the light source as a point object as compared to the diameter of the disc. Unless mentioned otherwise the refracted medium should be considered as air which has a refractive index of 1.
Formula used: In this solution, we will use the following formula:
Snell’s law: $ {\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2} $ where $ {\mu _1} $ and $ {\mu _2} $ are the refractive index of two different mediums and $ {\theta _1} $ and $ {\theta _2} $ are the angles made by the ray of light with the normal to the surface of refraction.
Complete step by step answer

As we can see in the image above, the disc must have a large enough radius that it can block any ray of light that is approaching the interface of two mediums with an angle less than the critical angle of light. If the light approaches at any angle greater than the critical angle, it will be reflected back into the liquid.
So, let us start by finding the critical angle of light. Using Snells’ law we can write
$\Rightarrow {\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2} $
Substituting $ {\mu _1} = \,5/3 $ , $ {\mu _2} = 1 $ and $ {\theta _2} = 90^\circ $ , we get
$\Rightarrow \sin {\theta _1} = \dfrac{3}{5} $
Then we can calculate
$\Rightarrow \tan {\theta _1} = \dfrac{3}{4} $
Since $ \tan {\theta _1} = \dfrac{r}{h} $ , we can write
$\Rightarrow
\dfrac{r}{h} = \dfrac{3}{4} \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{{3h}}{4} \\
\ $
Substituting the value of $ h = \,4m $ , we get
$\Rightarrow r = 3m $
Hence the diameter of the disc will be 6m which corresponds to option (C).
Note
Here, we have treated the light source as a point object as compared to the diameter of the disc. Unless mentioned otherwise the refracted medium should be considered as air which has a refractive index of 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




