
A small bulb is placed at the bottom of a tank containing water to a depth of 1 m. Find the critical angle for water air interface and also calculate the diameter of the circular bright patch of light formed on the surface of water. [Refractive index of water $ = 1.33 $ ].
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: Critical angle is the angle of incidence when the angle of refraction is 90 degrees. The maximum angle of light that would be seen in air is at critical angle.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formula;
$ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $ , where $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of incident medium, $ {\theta _1} $ is the angle of incidence, $ {n_2} $ is the refractive index of refractive medium, and $ {\theta _2} $ is the angle of refraction.
Complete step by step solution:
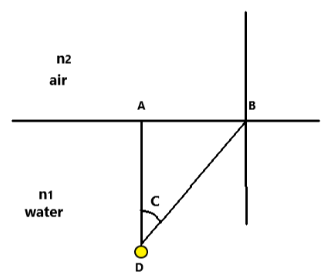
To calculate the critical angle, we must note the definition. It is defined as the angle of incidence of light, coming from a denser medium to a less dense medium, when the angle of refraction is equal to 90 degrees.
Hence, from Snell’s law which is $ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $ , where $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of incident medium, $ {\theta _1} $ is the angle of incidence, $ {n_2} $ is the refractive index of refractive medium, and $ {\theta _2} $ is the angle of refraction, the critical angle can be calculated as thus
$ {n_1}\sin C = {n_2}\sin 90 $ where $ C $ is the critical angle, and $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of water.
Hence, $ \sin C = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\sin 90 $
$ \Rightarrow C = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\sin 90 = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{1.33}} $
Hence,
$ C = 49^\circ $
Now, to calculate the diameter of the circular bright patch, we note that the critical angle is the widest angle of incidence which will be visible from air. Hence, as in the diagram AB will be the radius of the bright patch.
From trigonometry
$ \tan C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AD}} $
Hence, by insertion of values,
$ \tan 49^\circ = \dfrac{{AB}}{1} $ (since the depth AD is given as 1m)
Hence, $ AB = \tan 49^\circ = 1.15m $
Hence, the diameter is
$ d = 2\left( {AB} \right) = 2 \times 1.15 = 2.3m $ .
Note:
We say that the critical angle is the widest angle of light from the water which will be visible in air because, light as we know bends away from the normal when it travels from a dense medium to a less dense medium. Hence, as the angle of incidence increases, so does the angle of refraction, until the angle of refraction gets to 90 degrees. If the incident angle is further increased, the angle of refraction becomes greater than 90 and the direction of light travels back into the incident medium. This is known as total internal reflection.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formula;
$ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $ , where $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of incident medium, $ {\theta _1} $ is the angle of incidence, $ {n_2} $ is the refractive index of refractive medium, and $ {\theta _2} $ is the angle of refraction.
Complete step by step solution:

To calculate the critical angle, we must note the definition. It is defined as the angle of incidence of light, coming from a denser medium to a less dense medium, when the angle of refraction is equal to 90 degrees.
Hence, from Snell’s law which is $ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $ , where $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of incident medium, $ {\theta _1} $ is the angle of incidence, $ {n_2} $ is the refractive index of refractive medium, and $ {\theta _2} $ is the angle of refraction, the critical angle can be calculated as thus
$ {n_1}\sin C = {n_2}\sin 90 $ where $ C $ is the critical angle, and $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of water.
Hence, $ \sin C = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\sin 90 $
$ \Rightarrow C = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\sin 90 = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{1.33}} $
Hence,
$ C = 49^\circ $
Now, to calculate the diameter of the circular bright patch, we note that the critical angle is the widest angle of incidence which will be visible from air. Hence, as in the diagram AB will be the radius of the bright patch.
From trigonometry
$ \tan C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AD}} $
Hence, by insertion of values,
$ \tan 49^\circ = \dfrac{{AB}}{1} $ (since the depth AD is given as 1m)
Hence, $ AB = \tan 49^\circ = 1.15m $
Hence, the diameter is
$ d = 2\left( {AB} \right) = 2 \times 1.15 = 2.3m $ .
Note:
We say that the critical angle is the widest angle of light from the water which will be visible in air because, light as we know bends away from the normal when it travels from a dense medium to a less dense medium. Hence, as the angle of incidence increases, so does the angle of refraction, until the angle of refraction gets to 90 degrees. If the incident angle is further increased, the angle of refraction becomes greater than 90 and the direction of light travels back into the incident medium. This is known as total internal reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




