
A sinusoidal voltage of r.m.s value of 200 V is connected to the junction diode and a capacitor C in the circuit shown so that half rectification occurs. The final potential difference across C in volts is
A. 213
B. 170
C. 283
D. 325
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: Formula used:
The peak value of applied alternating current voltage is related to its rms value as:
$V_{rms} = \dfrac{V_m}{\sqrt{2}} $.
Complete answer:
In half wave rectification, the diode will work as an open circuit for the negative half cycle. The positive half cycle will get reproduced as it is past the diode as it will work just as a closed circuit in case of a positive half cycle. Therefore the output waveform is in the form of fluctuating dc and just consists of positive half cycles.
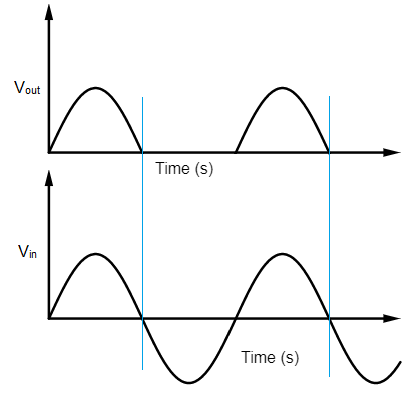
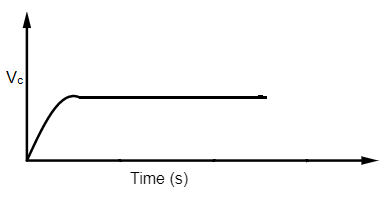
Now, as the current enters the capacitor with this waveform, it begins to charge till waveform reaches it's peak. As the current starts to go down, the capacitor begins discharging and maintains the same peak potential difference until the next peak.
Therefore, the potential difference that the capacitor has across it is simply the peak value of the input waveform i.e.,
$V_m = V_{rms} \sqrt{2}$
$\implies V_m = 200 \sqrt{2} = 282.84$V.
The capacitor will help us in getting a dc voltage of value 283 V.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
If there is a resistor in the circuit, then time constant t = RC determines the smoothness of the output d.c. If the capacitor has large RC, it will discharge over a longer time i.e., it will practically maintain the constant peak value until the next positive peak again charges it.
The peak value of applied alternating current voltage is related to its rms value as:
$V_{rms} = \dfrac{V_m}{\sqrt{2}} $.
Complete answer:
In half wave rectification, the diode will work as an open circuit for the negative half cycle. The positive half cycle will get reproduced as it is past the diode as it will work just as a closed circuit in case of a positive half cycle. Therefore the output waveform is in the form of fluctuating dc and just consists of positive half cycles.

Now, as the current enters the capacitor with this waveform, it begins to charge till waveform reaches it's peak. As the current starts to go down, the capacitor begins discharging and maintains the same peak potential difference until the next peak.
Therefore, the potential difference that the capacitor has across it is simply the peak value of the input waveform i.e.,
$V_m = V_{rms} \sqrt{2}$
$\implies V_m = 200 \sqrt{2} = 282.84$V.

The capacitor will help us in getting a dc voltage of value 283 V.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
If there is a resistor in the circuit, then time constant t = RC determines the smoothness of the output d.c. If the capacitor has large RC, it will discharge over a longer time i.e., it will practically maintain the constant peak value until the next positive peak again charges it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




