
(a) Show using a proper diagram how unpolarized light can be linearly polarized by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
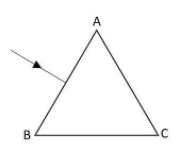
(b) The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index $\dfrac{3}{2}$, placed in water of refractive index $\dfrac{4}{3}$. Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC? Justify your answer.

Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The polarization of the unpolarized light upon reflection totally depends on its angle of incidence over the surface of the transparent glass. And this angle is known as Brewster’s angle. The refracted and reflected light waves will also be at right angles to each other, which we will consequently be able to find out.
In the second part, we can first find out the refractive index of glass-water combination and then on comparing it with the inverse of sine of apex angle, we will get the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
a. When an incident ray of an unpolarized light falls on a transparent glass surface, we will get a plane polarized reflected light when the refracted and the reflected light are perpendicular to each other.
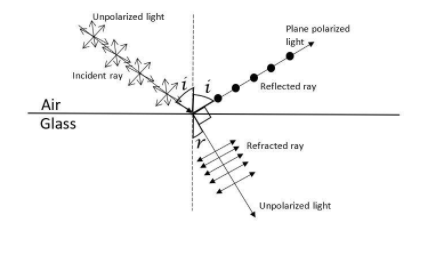
Suppose, $i$ be the angle of incidence and $r$ be the angle of refraction. Then, mathematically, $i+90^{\circ}+r=180\implies r=90^{\circ}-i$.
Assuming the refractive index of glass be $\mu$, we get
$\mu=\dfrac{sini}{sinr}=\dfrac{sini}{sin(90^{\circ}-i)}=\dfrac{sini}{cosi}=tani$
$\therefore \mu = tani$
This is called the Brewster’s law and the angle of incidence $i$ here, is called the Brewster’s angle. When a light ray falls on a glass surface at Brewster’s angle, the reflected part of light gets plane polarized.
b. It has been given that the refractive index of glass prism, $\mu_g = \dfrac{3}{2}$ and that of the water surrounding it is $\mu_w =\dfrac{4}{3}$. The incident ray is normal to the face AB so we can draw the following figure and can find the angles using geometry. We get
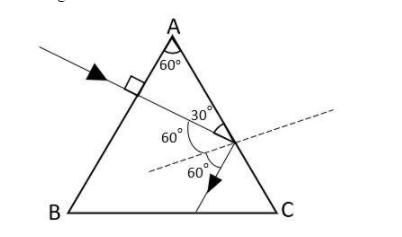
For, total internal reflection in an equilateral glass prism, the critical angle is defined as,
$\mu_A =\dfrac{1}{sin60^{\circ}}=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}=1.54$
Now, the refractive index of the prism with water is given by,
$\mu_{gw}=\dfrac{\mu_g}{\mu_w}=\dfrac{3/2}{4/3}=1.125$
Now, we know that for total internal reflection to happen, $\mu_A$ should be less than or equal to that of $\mu_{gw}$. But here, $\mu_{gw} < \mu_{A}$
Hence, total internal reflection will not take place.
Note: The law governing the polarization of reflected ray is Brewster's law and the angle of incidence for polarization is Brewster's angle. A polarized filter in lenses is often used by photographers in their cameras to reduce the effect of reflections coming from reflecting surfaces nearby.
In the second part of the question, we can also first find out the critical angle and then the angle of incidence and on comparing those, we can find out whether the total internal reflection will take place or not.
In the second part, we can first find out the refractive index of glass-water combination and then on comparing it with the inverse of sine of apex angle, we will get the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
a. When an incident ray of an unpolarized light falls on a transparent glass surface, we will get a plane polarized reflected light when the refracted and the reflected light are perpendicular to each other.

Suppose, $i$ be the angle of incidence and $r$ be the angle of refraction. Then, mathematically, $i+90^{\circ}+r=180\implies r=90^{\circ}-i$.
Assuming the refractive index of glass be $\mu$, we get
$\mu=\dfrac{sini}{sinr}=\dfrac{sini}{sin(90^{\circ}-i)}=\dfrac{sini}{cosi}=tani$
$\therefore \mu = tani$
This is called the Brewster’s law and the angle of incidence $i$ here, is called the Brewster’s angle. When a light ray falls on a glass surface at Brewster’s angle, the reflected part of light gets plane polarized.
b. It has been given that the refractive index of glass prism, $\mu_g = \dfrac{3}{2}$ and that of the water surrounding it is $\mu_w =\dfrac{4}{3}$. The incident ray is normal to the face AB so we can draw the following figure and can find the angles using geometry. We get

For, total internal reflection in an equilateral glass prism, the critical angle is defined as,
$\mu_A =\dfrac{1}{sin60^{\circ}}=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}=1.54$
Now, the refractive index of the prism with water is given by,
$\mu_{gw}=\dfrac{\mu_g}{\mu_w}=\dfrac{3/2}{4/3}=1.125$
Now, we know that for total internal reflection to happen, $\mu_A$ should be less than or equal to that of $\mu_{gw}$. But here, $\mu_{gw} < \mu_{A}$
Hence, total internal reflection will not take place.
Note: The law governing the polarization of reflected ray is Brewster's law and the angle of incidence for polarization is Brewster's angle. A polarized filter in lenses is often used by photographers in their cameras to reduce the effect of reflections coming from reflecting surfaces nearby.
In the second part of the question, we can also first find out the critical angle and then the angle of incidence and on comparing those, we can find out whether the total internal reflection will take place or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




