
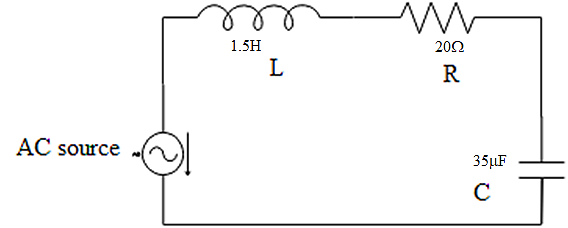
A series LCR circuit with $R=20\Omega $ , $L=1.5H$ and $C=35\mu F$ is connected to a variable-frequency $200V$ ac supply. When the frequency of the supply is equal to the natural frequency of the circuit, then what is the average power transferred to the circuit in a complete cycle?
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Here the frequency of supply gets equal to the natural frequency of the circuit. This is known as the resonance condition. For a LCR circuit, the impedance of the circuit is given by the equation,
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\left( \omega L-\dfrac{1}{\omega C} \right)}$
Complete step by step answer:
First of all let us discuss the term resonance in the LCR circuit. The resonance of a series LCR circuit happens when the inductive and capacitive reactance are similar in magnitude but cancel out each other since their phase is differing by $180{}^\circ $. The sharp minimum in impedance which happens is helpful in tuning applications. Electrical resonance is known to happen in a series LCR circuit when the circuit permits the maximum current for a particular frequency of the source of alternating supply for which capacitive reactance becomes similar to the inductive reactance. The impedance of LCR circuit is found to be minimum and hence current is given as maximum $0.707$
Now the impedance of the LCR series circuit can be given as,
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\left( \omega L-\dfrac{1}{\omega C} \right)}$
In which $R$ is the resistance, $L$ is the inductance and $C$ is the capacitance of the circuit.
Here
$\omega L=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
Therefore the impedance will become,
$Z=R$
And also we know that, current is given by the equation,
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$I=\dfrac{200}{20}=10A$
Therefore the power of the LCR series circuit given will be,
$P=V\times I=200\times 10=2000W$
Therefore the correct answer for the question has been obtained.
Note:
An important characteristic of a resonant circuit is termed as bandwidth. Bandwidth is described as the size of frequency range that is allowed or rejected by the tuned circuit. That is, the total number of cycles below and above the resonant frequency for which the current is similar to or greater than $0.707$ of its resonant value.
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\left( \omega L-\dfrac{1}{\omega C} \right)}$
Complete step by step answer:
First of all let us discuss the term resonance in the LCR circuit. The resonance of a series LCR circuit happens when the inductive and capacitive reactance are similar in magnitude but cancel out each other since their phase is differing by $180{}^\circ $. The sharp minimum in impedance which happens is helpful in tuning applications. Electrical resonance is known to happen in a series LCR circuit when the circuit permits the maximum current for a particular frequency of the source of alternating supply for which capacitive reactance becomes similar to the inductive reactance. The impedance of LCR circuit is found to be minimum and hence current is given as maximum $0.707$
Now the impedance of the LCR series circuit can be given as,
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\left( \omega L-\dfrac{1}{\omega C} \right)}$
In which $R$ is the resistance, $L$ is the inductance and $C$ is the capacitance of the circuit.
Here
$\omega L=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
Therefore the impedance will become,
$Z=R$
And also we know that, current is given by the equation,
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$I=\dfrac{200}{20}=10A$
Therefore the power of the LCR series circuit given will be,
$P=V\times I=200\times 10=2000W$
Therefore the correct answer for the question has been obtained.

Note:
An important characteristic of a resonant circuit is termed as bandwidth. Bandwidth is described as the size of frequency range that is allowed or rejected by the tuned circuit. That is, the total number of cycles below and above the resonant frequency for which the current is similar to or greater than $0.707$ of its resonant value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




