
A satellite of mass m is orbiting the earth in a circular orbit of radius r. It starts losing energy due to small air resistance at the rate of $CJ{s^{ - 1}}$. The time taken for the satellite to reach the earth is: $\dfrac{{GMm}}{{xC}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]$. Find the value of x.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: The circular orbit appears wherever the gravitational force on a satellite equals the centripetal force which is needed to move it with a uniform circular motion. Moreover, in a circular orbit, the kinetic energy of a satellite is half of its gravitational energy and is positive instead of negative.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now from the question
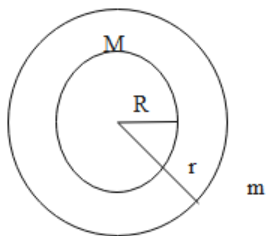
We are given, energy loss due to small air resistance $\dfrac{{\Delta E}}{t} = CJ{s^{ - 1}}$
We are given time taken by satellite to reach earth\[t = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{xC}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]\], we have to find x
Let radius of earth be $R$ and radius of satellite orbiting earth be$r$
Now initial energy of the satellite ${E_i} = - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2r}}$
And final energy of satellite when it reaches earth ${E_f} = - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2R}}$
Therefore energy lost by satellite
$\Delta E = {E_i} - {E_f}$
$\Rightarrow \Delta E = - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2r}} - \left[ { - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2R}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow \Delta E = \dfrac{{GMm}}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]$ …………………. (1)
Now we have
$\begin{gathered}
\dfrac{{\Delta E}}{t} = C \\
\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{\Delta E}}{C} \\
\end{gathered} $
Substituting value of $\Delta E$ from (1), we get
\[t = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2C}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]\]
This is the time taken by satellite to reach earth
Now comparing the given and calculated times, we get
\[\dfrac{{GMm}}{{xC}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right] = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2C}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]\]
$\Rightarrow x = 2$
Hence the answer is \[t = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2C}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]\].
Whenever the satellite starts losing energy the size of orbit gets smaller and smaller until and unless it gets into a part of air where the friction builds up so much that the satellite just burns up. Force of Gravity is the only force that keeps the satellite in orbit. There are three types of earth’s orbit;
High earth orbit, medium earth orbit, and Low earth orbit.
However, many kinds of weather and some communication satellites have High earth orbit as their first choice because it is farthest away from the surface.
Note: The orbit is completely dependent upon the total mass. Thus, the force of inertia and gravity has to be perfectly balanced for an orbit to happen whereas the orbit is the result of a perfect balance between the forward motion of a body in space.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now from the question

We are given, energy loss due to small air resistance $\dfrac{{\Delta E}}{t} = CJ{s^{ - 1}}$
We are given time taken by satellite to reach earth\[t = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{xC}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]\], we have to find x
Let radius of earth be $R$ and radius of satellite orbiting earth be$r$
Now initial energy of the satellite ${E_i} = - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2r}}$
And final energy of satellite when it reaches earth ${E_f} = - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2R}}$
Therefore energy lost by satellite
$\Delta E = {E_i} - {E_f}$
$\Rightarrow \Delta E = - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2r}} - \left[ { - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2R}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow \Delta E = \dfrac{{GMm}}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]$ …………………. (1)
Now we have
$\begin{gathered}
\dfrac{{\Delta E}}{t} = C \\
\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{\Delta E}}{C} \\
\end{gathered} $
Substituting value of $\Delta E$ from (1), we get
\[t = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2C}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]\]
This is the time taken by satellite to reach earth
Now comparing the given and calculated times, we get
\[\dfrac{{GMm}}{{xC}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right] = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2C}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]\]
$\Rightarrow x = 2$
Hence the answer is \[t = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2C}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{r}} \right]\].
Whenever the satellite starts losing energy the size of orbit gets smaller and smaller until and unless it gets into a part of air where the friction builds up so much that the satellite just burns up. Force of Gravity is the only force that keeps the satellite in orbit. There are three types of earth’s orbit;
High earth orbit, medium earth orbit, and Low earth orbit.
However, many kinds of weather and some communication satellites have High earth orbit as their first choice because it is farthest away from the surface.
Note: The orbit is completely dependent upon the total mass. Thus, the force of inertia and gravity has to be perfectly balanced for an orbit to happen whereas the orbit is the result of a perfect balance between the forward motion of a body in space.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




