
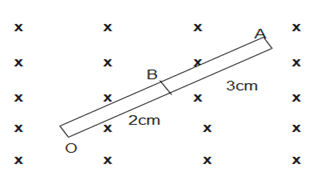
A rod of length 10 cm made up of conducting and non-conducting material (shaded part is non-conducting) The rod is rotated with constant angular velocity 10 rad/s about point $O$, in constant magnetic field of 2 T as shown in the figure. The induced emf between the point $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$ of rod will be
(A) $0.029 \mathrm{V}$
(B) $0.1 \mathrm{V}$
(C) $0.051 \mathrm{V}$
(D) $0.064 \mathrm{V}$

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: A emf is induced according to Faraday's law of induction when flux changes. When this rod moves to the right in the uniform magnetic field, A motional emf is induced between the rails. On the page, the magnetic field B is perpendicular to the moving rod and rails and therefore to the area surrounding them.
Formula used:
$E=\int_{0.07}^{0.1}{\text{B}}\omega \text{rdr}$
Complete solution Step-by-Step:
Because of the changes in the magnetic flux through it, it can be defined as the generation of a potential difference in a coil. In simpler words, when the flux linked to a conductor or coil changes, the electromotive force or EMF is said to be induced.
Given in the question
Given length of the rod $1=10~\text{cm}$
Magnetic field $\mathrm{B}=2 \mathrm{T}$
Angular speed $\omega=10 \mathrm{rad} / \mathrm{s}$
Considering an elemental length dr at a distance $x$ from end 0.
Emf experienced by the elementary length of the conductor $\text{dE}=\text{BVdx}$ here $\mathrm{v}=\omega \mathrm{r}$
Thus, the above equation becomes $\text{dE}=\text{B}\omega \text{rdr}$
Now potential difference between the points $(A)$ and $(B)$ is $E=\int_{0.07}^{0.1}{\text{B}}\omega \text{rdr}$
$\Rightarrow (\text{B}\omega \dfrac{{{\text{r}}^{2}}}{2})_{0.07}^{0.1}$
$\Rightarrow 2\times 10\times \dfrac{\left( {{0.1}^{2}}-{{0.07}^{2}} \right)}{2}$
$=0.051\quad \text{V}$
\[\therefore \] The induced emf between the point $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$ of rod will be $0.051\quad \text{V}$
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Between the electric force and the magnetic force, there are many connections. The fact that a moving electric field produces a magnetic field and, conversely, an electric field is produced by a moving magnetic field is part of why different manifestations of the same force are now considered to be electric and magnetic forces. This classic unification into what is called the electromagnetic force of electrical and magnetic forces is the inspiration for contemporary efforts to unify other fundamental forces.
Formula used:
$E=\int_{0.07}^{0.1}{\text{B}}\omega \text{rdr}$
Complete solution Step-by-Step:
Because of the changes in the magnetic flux through it, it can be defined as the generation of a potential difference in a coil. In simpler words, when the flux linked to a conductor or coil changes, the electromotive force or EMF is said to be induced.
Given in the question
Given length of the rod $1=10~\text{cm}$
Magnetic field $\mathrm{B}=2 \mathrm{T}$
Angular speed $\omega=10 \mathrm{rad} / \mathrm{s}$
Considering an elemental length dr at a distance $x$ from end 0.
Emf experienced by the elementary length of the conductor $\text{dE}=\text{BVdx}$ here $\mathrm{v}=\omega \mathrm{r}$
Thus, the above equation becomes $\text{dE}=\text{B}\omega \text{rdr}$
Now potential difference between the points $(A)$ and $(B)$ is $E=\int_{0.07}^{0.1}{\text{B}}\omega \text{rdr}$
$\Rightarrow (\text{B}\omega \dfrac{{{\text{r}}^{2}}}{2})_{0.07}^{0.1}$
$\Rightarrow 2\times 10\times \dfrac{\left( {{0.1}^{2}}-{{0.07}^{2}} \right)}{2}$
$=0.051\quad \text{V}$
\[\therefore \] The induced emf between the point $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$ of rod will be $0.051\quad \text{V}$
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Between the electric force and the magnetic force, there are many connections. The fact that a moving electric field produces a magnetic field and, conversely, an electric field is produced by a moving magnetic field is part of why different manifestations of the same force are now considered to be electric and magnetic forces. This classic unification into what is called the electromagnetic force of electrical and magnetic forces is the inspiration for contemporary efforts to unify other fundamental forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




