
A rigid square loop of side a carrying current ${I}_{2}$ is lying on a horizontal surface near a long current ${I}_{1}$ carrying wire in the same plane as shown in figure. The net force on the loop due to wire will be:
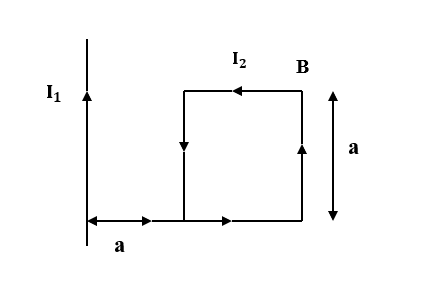
A. Attractive and equal to $\dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{3\pi}$
B. Repulsive and equal to $\dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{4\pi}$
C. Repulsive and equal to $\dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{2\pi}$
D. Zero

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, consider inward force from all sides of the loop. The force on top and bottom of the loop gets cancelled before they are in the opposite direction and have equal values. So, find the forces on remaining sides of the loop. To find the force on remaining sides of the loop, use the formula for force on a current carrying wire passing through a magnetic field. Now, subtract these forces to get the net force on the loop due to wire.
Formula used:
$F= IBl$
$B= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}I}{2 \pi a}$
Complete answer:
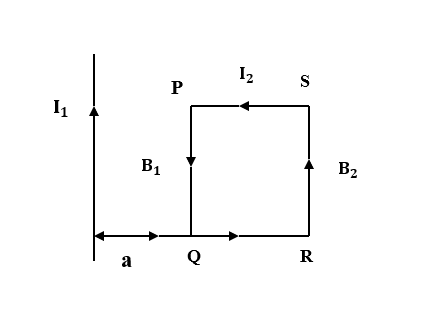
Given: Length of the wire (l)= a
Inward forces on side PS and QR cancel each other as they are equal and opposite in direction. So, the net force only depends on inward force on side PQ and side RS.
Force is given by,
$F= IBl$ …(1)
Where, I is the current
B is the magnetic field
l is the length of the wire
Thus, force on PQ will be given by,
${F}_{PQ}= {I}_{2}{B}_{1}a$ …(2)
We know, magnetic field is given by,
$B= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}I}{2 \pi a}$
Substituting this value in the equation. (2) we get,
${F}_{PQ}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}a}{2 \pi a}$
$\Rightarrow {F}_{PQ}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{2 \pi }$
Similarly, force on RS will be given by,
${F}_{RS}= {I}_{2}{B}_{2}a$
${F}_{RS}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}a}{2 \pi (a+a)}$
$\Rightarrow {F}_{RS}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}a}{2 \pi \times 2a }$
$\Rightarrow {F}_{RS}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{4 \pi }$
Net force is given by,
${F}_{net}={F}_{PQ}- {F}_{RS}$
Substituting the values in above expression we get,
${F}_{net}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{2 \pi }-\dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{4 \pi}$
$\Rightarrow {F}_{net}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{4 \pi }$
Hence, the net force on the loop due to wire will be repulsive and equal to $\dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{4\pi}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
To find the direction of force, right-hand rules can be used. Right-hand rule helps to know the direction of force from the direction of current. Thus, we have considered inward force because the current is in an anti-clockwise direction. So, students must remember these types of laws. Two parallel wires with current flowing in the same direction will attract each other. Whereas the two parallel wires with current flowing in opposite directions will repel each other.
Formula used:
$F= IBl$
$B= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}I}{2 \pi a}$
Complete answer:

Given: Length of the wire (l)= a
Inward forces on side PS and QR cancel each other as they are equal and opposite in direction. So, the net force only depends on inward force on side PQ and side RS.
Force is given by,
$F= IBl$ …(1)
Where, I is the current
B is the magnetic field
l is the length of the wire
Thus, force on PQ will be given by,
${F}_{PQ}= {I}_{2}{B}_{1}a$ …(2)
We know, magnetic field is given by,
$B= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}I}{2 \pi a}$
Substituting this value in the equation. (2) we get,
${F}_{PQ}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}a}{2 \pi a}$
$\Rightarrow {F}_{PQ}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{2 \pi }$
Similarly, force on RS will be given by,
${F}_{RS}= {I}_{2}{B}_{2}a$
${F}_{RS}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}a}{2 \pi (a+a)}$
$\Rightarrow {F}_{RS}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}a}{2 \pi \times 2a }$
$\Rightarrow {F}_{RS}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{4 \pi }$
Net force is given by,
${F}_{net}={F}_{PQ}- {F}_{RS}$
Substituting the values in above expression we get,
${F}_{net}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{2 \pi }-\dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{4 \pi}$
$\Rightarrow {F}_{net}= \dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{4 \pi }$
Hence, the net force on the loop due to wire will be repulsive and equal to $\dfrac {{\mu}_{0}{I}_{1}{I}_{2}}{4\pi}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
To find the direction of force, right-hand rules can be used. Right-hand rule helps to know the direction of force from the direction of current. Thus, we have considered inward force because the current is in an anti-clockwise direction. So, students must remember these types of laws. Two parallel wires with current flowing in the same direction will attract each other. Whereas the two parallel wires with current flowing in opposite directions will repel each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




