
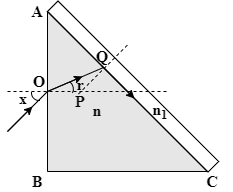
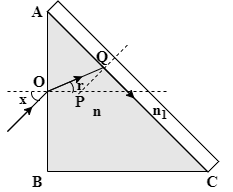
A right-angled prism (${45^ \circ },{90^ \circ },{45^ \circ }$) of refractive index n has a plate of refractive index ${n_1}({n_1} < n)$cemented to its diagonal face. The assembly is in the air. A ray is an incident on AB. If the angle of incidence at AB for which the ray strikes the diagonal face at the critical angle X in degrees. Find X.
Formula used:
Snell’s law tells us:
\[{n_i}\sin {\theta _i} = {n_r}\sin {\theta _r}\] ………... (1)
Where,
\[{n_i}\] is the refractive index of the medium light is coming from,
\[{\theta _i}\] is the angle of incidence,
\[{n_r}\] is the refractive index of the medium light is going into,
\[{\theta _r}\] is the angle of refraction.

Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: When light falls on the surface AB, after refraction it passes into the prism. Due to refraction the light beam bends towards the normal as the refractive index of the prism is greater than that of the air. Then this ray falls on the other surface at a critical angle; it gazes through the diagonal surface.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Given:
The prism is a right angled prism, i.e. $\angle A = {45^ \circ }$.
Refractive index of prism is n and that of the plate is ${n_1}$.
Angle of incidence of the ray at AB is $X$.
To find: The value of $X$.
Step 1
For refraction at the surface AB we have, \[{\theta _i} = X,{\theta _r} = r,{n_i} = 1,{n_r} = n\]. So, use these values in eq.(1) to get:
\[
1 \times \sin X = n \times \sin r \\
\therefore \sin X = n\sin r \\
\] ………………….(2)
Step 2
In the AC surface we have, \[{\theta _i} = {\theta _C},{\theta _r} = {90^ \circ },{n_i} = n,{n_r} = {n_1}\] where, \[{\theta _C}\] is the critical angle for AC surface. Now, use these values in eq.(1) to get:
\[
n \times \sin {\theta _C} = {n_1} \times \sin {90^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \sin {\theta _C} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n} \\
\Rightarrow {\theta _C} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n}} \right) \\
\] .....................(3)
Step 3
Now, focus on the quadrilateral AOPQ. For this quadrilateral we have $\angle AOP = \angle AQP = {90^ \circ }$and $\angle A = {45^ \circ }$. Hence, we get \[\angle OPQ = {360^ \circ } - ({90^ \circ } + {90^ \circ } + {45^ \circ }) = {135^ \circ }\].
For the triangle OPQ we have \[\angle OPQ = {135^ \circ }\]. Hence, we get:
$
\angle POQ + \angle PQO = {180^ \circ } - \angle OPQ \\
\Rightarrow r + {\theta _C} = {180^ \circ } - {135^ \circ } \\
\therefore r = {45^ \circ } - {\theta _C} \\
$.................4)
Step 4:
Substitute the values of r from eq.(4) and that of \[{\theta _C}\] from eq.(3) into eq.(2) to get the final relationship as:
\[
\sin X = n\sin \left( {{{45}^ \circ } - {\theta _C}} \right) \\
\therefore X = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left[ {n\sin \left( {{{45}^ \circ } - {{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n}} \right)} \right)} \right] \\
\]
$\therefore$ The value of X is \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left[ {n\sin \left( {{{45}^ \circ } - {{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n}} \right)} \right)} \right]\].
Note:
If you carefully notice the obtained incident angle term you can notice that here, \[{n_1}\] and n should be chosen in such a way that \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n}} \right)\] term be less than \[{45^ \circ }\]. Otherwise, the top angle $\angle A$ can be further increased to get a proper incident angle X for which the ray will fall at a critical angle on AC surface.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Given:
The prism is a right angled prism, i.e. $\angle A = {45^ \circ }$.
Refractive index of prism is n and that of the plate is ${n_1}$.
Angle of incidence of the ray at AB is $X$.

To find: The value of $X$.
Step 1
For refraction at the surface AB we have, \[{\theta _i} = X,{\theta _r} = r,{n_i} = 1,{n_r} = n\]. So, use these values in eq.(1) to get:
\[
1 \times \sin X = n \times \sin r \\
\therefore \sin X = n\sin r \\
\] ………………….(2)
Step 2
In the AC surface we have, \[{\theta _i} = {\theta _C},{\theta _r} = {90^ \circ },{n_i} = n,{n_r} = {n_1}\] where, \[{\theta _C}\] is the critical angle for AC surface. Now, use these values in eq.(1) to get:
\[
n \times \sin {\theta _C} = {n_1} \times \sin {90^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \sin {\theta _C} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n} \\
\Rightarrow {\theta _C} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n}} \right) \\
\] .....................(3)
Step 3
Now, focus on the quadrilateral AOPQ. For this quadrilateral we have $\angle AOP = \angle AQP = {90^ \circ }$and $\angle A = {45^ \circ }$. Hence, we get \[\angle OPQ = {360^ \circ } - ({90^ \circ } + {90^ \circ } + {45^ \circ }) = {135^ \circ }\].
For the triangle OPQ we have \[\angle OPQ = {135^ \circ }\]. Hence, we get:
$
\angle POQ + \angle PQO = {180^ \circ } - \angle OPQ \\
\Rightarrow r + {\theta _C} = {180^ \circ } - {135^ \circ } \\
\therefore r = {45^ \circ } - {\theta _C} \\
$.................4)
Step 4:
Substitute the values of r from eq.(4) and that of \[{\theta _C}\] from eq.(3) into eq.(2) to get the final relationship as:
\[
\sin X = n\sin \left( {{{45}^ \circ } - {\theta _C}} \right) \\
\therefore X = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left[ {n\sin \left( {{{45}^ \circ } - {{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n}} \right)} \right)} \right] \\
\]
$\therefore$ The value of X is \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left[ {n\sin \left( {{{45}^ \circ } - {{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n}} \right)} \right)} \right]\].
Note:
If you carefully notice the obtained incident angle term you can notice that here, \[{n_1}\] and n should be chosen in such a way that \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{n}} \right)\] term be less than \[{45^ \circ }\]. Otherwise, the top angle $\angle A$ can be further increased to get a proper incident angle X for which the ray will fall at a critical angle on AC surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




