
A resistor R and \[2\text{ }\mu F\] capacitor in series is connected through a switch to 200 V direct supply. Across the capacitor is a neon bulb that lights up at 120 V. Calculating the value of R makes the bulb light up 5 s after the switch has been closed.
\[\left( {{\log }_{10}}2.5=0.4 \right)\]
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
\text{A}.\text{ }1.3\text{ x }{{10}^{4}}\Omega \\
\text{B}\text{. }1.7\text{ x }{{10}^{6}}\Omega \\
\text{C}\text{. }2.7\text{ x }{{10}^{6}}\Omega \\
\text{D}\text{. }3.3\text{ x }{{10}^{7}}\Omega \\
\end{array}\]
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: Any circuit containing a resistor, capacitor, voltage supply and bulb connected in series is a R.C. circuit. The voltage at any time is expressed in terms and respect to the initial voltage which has been supplied. Then, the constant of time and capacitance are applied to find the resistance in the circuit.
Complete answer:
Given data can be shown as,
A resistor of resistance R
A capacitor of capacitance \[2\text{ }\mu F\]
Let the capacitance be C.
Therefore,
\[C\text{ }=2\mu F\]
A switch
Direct voltage supply (or) Initial Voltage supply of 200 V
Let the initial voltage supply be \[{{V}_{0}}\].
Therefore,
\[{{V}_{0}}=200\text{ }V\]
Another voltage supply of 120 V
Let it be V
Therefore,
\[{{V}_{0}}=120\text{ }V\]
The time period is 5 seconds for the closing of the switch
Let the time period be t.
\[t\text{ }=\text{ }5\text{ }s\]
From the given data, it is clear that the given circuit is an R.C. circuit.
Let us draw the diagram for the R.C. circuit with the required details.
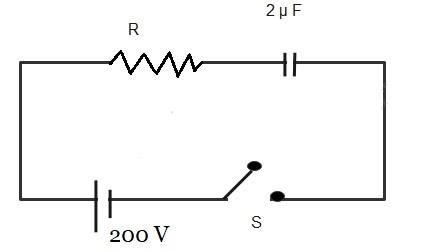
In an R.C. circuit,
Voltage,
\[V\text{ }=\text{ }{{V}_{0}}(1-{{e}^{-}}^{\dfrac{t}{\tau }})\]----(1)
Let this be equation (1)
Where,
e is the exponential
t is the time period for closing of switch
\[\tau \] is the constant of time.
And,
\[\tau =\text{ }R\text{ x }C\]----(2)
Let this be equation (2)
Where,
R is the resistance
C is the capacitance
Substitute the value of \[\tau \] in equation (1)
We obtain the value of voltage as,
\[V\text{ }=\text{ }{{V}_{0}}\left( 1-{{e}^{-}}^{\dfrac{t}{RC}} \right)\]---- (3)
Let this be equation (3)
Now, substitute the values of t, C, V, \[{{V}_{0}}\] in equation (3)
We get,
\[\text{120}=\text{200}\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]----(4)
Let this be equation (4)
Dividing equation (4) by 200,
We get,
\[\dfrac{\text{120}}{200}=\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]---(5)
Let this be equation (5)
\[\dfrac{3}{5}=\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]---(6)
Let this be equation (6)
From equation (6), we get,
\[1-\dfrac{3}{5}=\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]---(7)
Let this be equation (7)
From equation (7), we get,
\[\dfrac{2}{5}=\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]---(8)
Let this be equation (8)
From equation (8), we get,
\[\dfrac{2}{5}=\text{ }{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{2500000}{R} \right)}}\]---(9)
Let this be equation (9),
Taking logarithm on both sides in equation (9)
We get,
\[\log ~\dfrac{2}{5}=\text{ log}\left[ {{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{2500000}{R} \right)}} \right]\]-----(10)
Let this be equation (10)
\[\log {{~}_{e}}\dfrac{2}{5}=-\left( \dfrac{2500000}{R} \right)\]---(11)
Let this be equation (11).
From equation (11), we get the value of R equals to \[2.7\times {{10}^{6}}\text{ }\Omega \].
Therefore, the correct answer is (C).
Note:
It is important to note that the circuit is a D.C. circuit, then, power and current are the main factors involved in the circuit. In such cases, the voltage is expressed in terms of power and current primarily. After that, the resistance is derived from the above factors in the usual manner as always.
Complete answer:
Given data can be shown as,
A resistor of resistance R
A capacitor of capacitance \[2\text{ }\mu F\]
Let the capacitance be C.
Therefore,
\[C\text{ }=2\mu F\]
A switch
Direct voltage supply (or) Initial Voltage supply of 200 V
Let the initial voltage supply be \[{{V}_{0}}\].
Therefore,
\[{{V}_{0}}=200\text{ }V\]
Another voltage supply of 120 V
Let it be V
Therefore,
\[{{V}_{0}}=120\text{ }V\]
The time period is 5 seconds for the closing of the switch
Let the time period be t.
\[t\text{ }=\text{ }5\text{ }s\]
From the given data, it is clear that the given circuit is an R.C. circuit.
Let us draw the diagram for the R.C. circuit with the required details.

In an R.C. circuit,
Voltage,
\[V\text{ }=\text{ }{{V}_{0}}(1-{{e}^{-}}^{\dfrac{t}{\tau }})\]----(1)
Let this be equation (1)
Where,
e is the exponential
t is the time period for closing of switch
\[\tau \] is the constant of time.
And,
\[\tau =\text{ }R\text{ x }C\]----(2)
Let this be equation (2)
Where,
R is the resistance
C is the capacitance
Substitute the value of \[\tau \] in equation (1)
We obtain the value of voltage as,
\[V\text{ }=\text{ }{{V}_{0}}\left( 1-{{e}^{-}}^{\dfrac{t}{RC}} \right)\]---- (3)
Let this be equation (3)
Now, substitute the values of t, C, V, \[{{V}_{0}}\] in equation (3)
We get,
\[\text{120}=\text{200}\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]----(4)
Let this be equation (4)
Dividing equation (4) by 200,
We get,
\[\dfrac{\text{120}}{200}=\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]---(5)
Let this be equation (5)
\[\dfrac{3}{5}=\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]---(6)
Let this be equation (6)
From equation (6), we get,
\[1-\dfrac{3}{5}=\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]---(7)
Let this be equation (7)
From equation (7), we get,
\[\dfrac{2}{5}=\left[ 1-{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{5}{R\text{x2x1}{{\text{0}}^{-6}}} \right)}} \right]\]---(8)
Let this be equation (8)
From equation (8), we get,
\[\dfrac{2}{5}=\text{ }{{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{2500000}{R} \right)}}\]---(9)
Let this be equation (9),
Taking logarithm on both sides in equation (9)
We get,
\[\log ~\dfrac{2}{5}=\text{ log}\left[ {{e}^{-\left( \dfrac{2500000}{R} \right)}} \right]\]-----(10)
Let this be equation (10)
\[\log {{~}_{e}}\dfrac{2}{5}=-\left( \dfrac{2500000}{R} \right)\]---(11)
Let this be equation (11).
From equation (11), we get the value of R equals to \[2.7\times {{10}^{6}}\text{ }\Omega \].
Therefore, the correct answer is (C).
Note:
It is important to note that the circuit is a D.C. circuit, then, power and current are the main factors involved in the circuit. In such cases, the voltage is expressed in terms of power and current primarily. After that, the resistance is derived from the above factors in the usual manner as always.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




