
A resistor of resistance R is connected to a cell of internal resistance $5\Omega $. The value of R is varied from $1\Omega $ to $5\Omega $. The power consumed by R is
A) Increases continuously
B) Decreases continuously
C) First decreases then increases
D) First increases then decreases
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: The resistance is connected in every circuit to control the flow of current in the circuit. Because the heavy flow of current leads to the breakdown of the circuit. Hence we can say that the resistance offers the resistive force against the current flow. And the voltage is provided by the cell in some circuits. While transferring the voltage to the circuit, the cell develops heat in it. This heat is due to the heavy flow of the voltage supply. To avoid this heavy flow of voltage, the cell itself develops a resistance called internal resistance.
Formula used:
We know that power is the product of voltage and current. Therefore, power,
$P = V \times I$
$P = {I^2}R$
$\therefore P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{{R^2}}}R$
Where,
$V$=voltage
$R$=resistance
Complete step by step answer:
(i) If the voltage is provided by the cell, it experiences the resistance called internal resistance. This is due to the heat produced in the battery. Hence the resistance in the circuit is $R + r$.
(ii) The equation for the power we derived is $P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{{R^2}}}R$
(iii) We have to calculate the power consumed by R and the circuit has an additional resistance called internal resistance. Hence the equation is converted in to
$P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{{{\left( {R + r} \right)}^2}}}R$
(iii) The resistance R is direct to power. Hence R increases, the power consumed by R also increases.
(iv) Therefore we can say that when the resistance R is varied from $1\Omega $ to $5\Omega $, the power consumed by R also increases continuously.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Additional information:
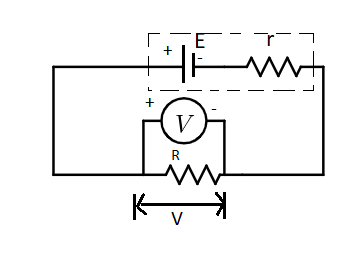
(i) The internal resistance is the resistance offered by the cell providing EMF. This is due to the heat produced in the cell. If the voltage provided by the cell is e. Then $e = I\left( {R + r} \right)$. The R is the resistance provided by the resistance.
(ii) From the previous equation, $e = IR + Ir$. We know that $V = IR$. Hence the equation becomes, $e = V + Ir$
(iii) From this equation, we can say that the voltage developed in the cell is greater than the voltage across the terminals.
(iv) The internal resistance is also measured in Ohms.
Note:
The internal resistance is the additional resistance developed in the circuit. If the internal resistance in the circuit is more, then the current flowing through the circuit will decrease and the power also decreases. And in turn, if the internal resistance is small, the current in the circuit increases, and power also increases. And the voltage developed in the cell is greater than the voltage across the terminals.
Formula used:
We know that power is the product of voltage and current. Therefore, power,
$P = V \times I$
$P = {I^2}R$
$\therefore P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{{R^2}}}R$
Where,
$V$=voltage
$R$=resistance
Complete step by step answer:
(i) If the voltage is provided by the cell, it experiences the resistance called internal resistance. This is due to the heat produced in the battery. Hence the resistance in the circuit is $R + r$.
(ii) The equation for the power we derived is $P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{{R^2}}}R$
(iii) We have to calculate the power consumed by R and the circuit has an additional resistance called internal resistance. Hence the equation is converted in to
$P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{{{\left( {R + r} \right)}^2}}}R$
(iii) The resistance R is direct to power. Hence R increases, the power consumed by R also increases.
(iv) Therefore we can say that when the resistance R is varied from $1\Omega $ to $5\Omega $, the power consumed by R also increases continuously.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Additional information:

(i) The internal resistance is the resistance offered by the cell providing EMF. This is due to the heat produced in the cell. If the voltage provided by the cell is e. Then $e = I\left( {R + r} \right)$. The R is the resistance provided by the resistance.
(ii) From the previous equation, $e = IR + Ir$. We know that $V = IR$. Hence the equation becomes, $e = V + Ir$
(iii) From this equation, we can say that the voltage developed in the cell is greater than the voltage across the terminals.
(iv) The internal resistance is also measured in Ohms.
Note:
The internal resistance is the additional resistance developed in the circuit. If the internal resistance in the circuit is more, then the current flowing through the circuit will decrease and the power also decreases. And in turn, if the internal resistance is small, the current in the circuit increases, and power also increases. And the voltage developed in the cell is greater than the voltage across the terminals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




