
A resistor of R=6ohm, an inductor of L=1 H and a capacitor of C=17.36 micro farad are connected in series with an AC source. Find the Q-factor.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: In this question we will use the direct formula of the quality factor. Now, by substituting the given values of resistor, capacitor and inductor, we get the required answer. Further, we will know the basics of an LCR circuit for our better understanding.
Formula used:
$Q - factor = \dfrac{1}{R}\sqrt {\dfrac{L}{C}} $
Complete step by step solution:
It consists of inductor L, capacitor C and resistor R as shown is in the diagram.
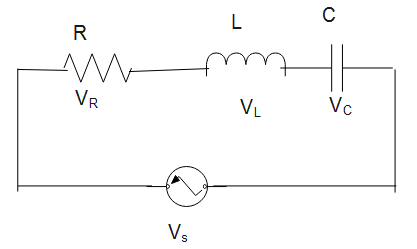
As we know that the quality factor or Q factor is defined as a dimensionless parameter that tells us how under damped an oscillator or resonator is. It can also be defined as the ratio of the peak energy stored in the resonator in a cycle of oscillation to the energy lost per radian of the cycle.
Now, mathematically Q-factor is given as:
$Q - factor = \dfrac{1}{R}\sqrt {\dfrac{L}{C}} $
Now, substituting the given values in the above equation, we get:
$Q - factor = \dfrac{1}{6}\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{{17.36 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}} $
$\therefore Q - factor = 40$
Therefore, we get the required answer, which tells us the quality factor.
Additional information:
An LCR circuit also known as resonant circuit, tuned circuit or RLC circuit is an electrical circuit.
The LCR circuit analysis is understood in terms of phasors.
Resistance, Inductance, and Capacitance have very different phase relationships to each other when connected to a sinusoidal alternating supply.
A capacitor consists of two or more parallel conductive or metal plates. These plates are not connected or touching each other, but rather they are electrically separated either by air or by some form of a good insulating material like waxed paper, mica, ceramic, plastic or some form of a liquid gel as used in electrolytic capacitors. This insulating layer between capacitor’s plates is commonly called the Dielectric.
Note:
Here, we should note that capacitance is measured in Farad, or can be said as one coulomb per volt. Capacitance is dependent on the dielectric constant as well as on the distance between the two plates. The parallel plate capacitor is the simplest form of capacitor.
Formula used:
$Q - factor = \dfrac{1}{R}\sqrt {\dfrac{L}{C}} $
Complete step by step solution:
It consists of inductor L, capacitor C and resistor R as shown is in the diagram.

As we know that the quality factor or Q factor is defined as a dimensionless parameter that tells us how under damped an oscillator or resonator is. It can also be defined as the ratio of the peak energy stored in the resonator in a cycle of oscillation to the energy lost per radian of the cycle.
Now, mathematically Q-factor is given as:
$Q - factor = \dfrac{1}{R}\sqrt {\dfrac{L}{C}} $
Now, substituting the given values in the above equation, we get:
$Q - factor = \dfrac{1}{6}\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{{17.36 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}} $
$\therefore Q - factor = 40$
Therefore, we get the required answer, which tells us the quality factor.
Additional information:
An LCR circuit also known as resonant circuit, tuned circuit or RLC circuit is an electrical circuit.
The LCR circuit analysis is understood in terms of phasors.
Resistance, Inductance, and Capacitance have very different phase relationships to each other when connected to a sinusoidal alternating supply.
A capacitor consists of two or more parallel conductive or metal plates. These plates are not connected or touching each other, but rather they are electrically separated either by air or by some form of a good insulating material like waxed paper, mica, ceramic, plastic or some form of a liquid gel as used in electrolytic capacitors. This insulating layer between capacitor’s plates is commonly called the Dielectric.
Note:
Here, we should note that capacitance is measured in Farad, or can be said as one coulomb per volt. Capacitance is dependent on the dielectric constant as well as on the distance between the two plates. The parallel plate capacitor is the simplest form of capacitor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




