
A regular hexagon of side $10 cm$ has a charge $5μC$ at each of its vertices. Calculate the potential at the centre of the hexagon.
Answer
561k+ views
Hint:A hexagon is a regular figure having six sides. At each corner 6 charges are placed and we need to find the potential at the centre of the regular hexagon. We know electric potential is a scalar quantity, so we do not have concern about the direction. Since, the distance of all the charges is the same so we just find out potential due to a single charge and then multiply it by 6.
Complete step by step answer:
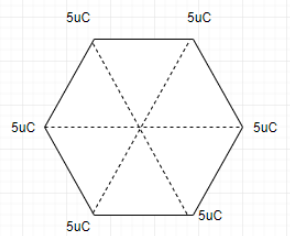
when all the corners are joined to the centre of the hexagon, it forms an equilateral triangle. So, the distance between the centre to any of the corner is 10 cm = 0.1 m.We know electric potential is given by the formula:
\[V=k\dfrac{Q}{r}\],
where Q is the charge and r is the distance between the charge and the point where the potential is to be determined and k is a constant whose value is \[k=9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}/{{C}^{2}}\].
Given, \[Q=5\mu C=5\times {{10}^{-6}}C\]
$V=k\dfrac{Q}{r} \\
\Rightarrow V=\dfrac{9\times {{10}^{9}}\times 5\times {{10}^{-6}}}{0.1} \\
\Rightarrow V=450000V \\$
For total 6 charges, \[6\times 450000=2.7\times {{10}^{6}}V\]
Hence, the potential at the centre of the hexagon is $2.7\times {{10}^{6}}V$.
Note:Electric potential is a scalar quantity and it is assumed to be zero at the infinity. If we want to move a charge from one point to another and if the electric potential is same at both the points work done will be zero because no work is required to be done to move a charge on an equipotential surface.The electric potential is related to electric field and electric field is defined as the negative gradient of electric potential.
Complete step by step answer:

when all the corners are joined to the centre of the hexagon, it forms an equilateral triangle. So, the distance between the centre to any of the corner is 10 cm = 0.1 m.We know electric potential is given by the formula:
\[V=k\dfrac{Q}{r}\],
where Q is the charge and r is the distance between the charge and the point where the potential is to be determined and k is a constant whose value is \[k=9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}/{{C}^{2}}\].
Given, \[Q=5\mu C=5\times {{10}^{-6}}C\]
$V=k\dfrac{Q}{r} \\
\Rightarrow V=\dfrac{9\times {{10}^{9}}\times 5\times {{10}^{-6}}}{0.1} \\
\Rightarrow V=450000V \\$
For total 6 charges, \[6\times 450000=2.7\times {{10}^{6}}V\]
Hence, the potential at the centre of the hexagon is $2.7\times {{10}^{6}}V$.
Note:Electric potential is a scalar quantity and it is assumed to be zero at the infinity. If we want to move a charge from one point to another and if the electric potential is same at both the points work done will be zero because no work is required to be done to move a charge on an equipotential surface.The electric potential is related to electric field and electric field is defined as the negative gradient of electric potential.
Watch videos on
A regular hexagon of side $10 cm$ has a charge $5μC$ at each of its vertices. Calculate the potential at the centre of the hexagon.

Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Class 12 Physics - NCERT EXERCISE 2.2 | Vishal Kumar Sir
Subscribe
 Share
Share likes
263 Views
2 years ago
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE



 Watch Video
Watch Video
