
A regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle of radius 6 cm. Find its area(in sq cm).
a. \[48\sqrt 3 \]
b. \[54\sqrt 3 \]
c. \[48\sqrt 2 \]
d. \[54\sqrt 2 \]
Answer
604.2k+ views
Hint:
Here we will be using the given information for forming the figure based on that. Then we will be finding the sides of the regular hexagon.
Complete step by step solution:
There is a regular hexagon. This regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle of radius 6 cm.
As per the given information, we know that a regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle of radius 6 cm, so we proceed by drawing the figure first
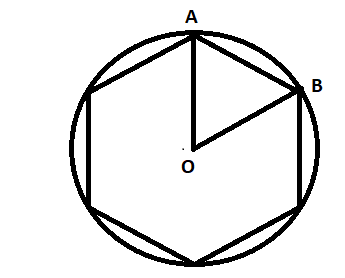
Here, we know that the angle subtended by the sides of a regular polygon (in this case hexagon) is equal to \[\dfrac{{2\pi }}{n}\] where n is the number of sides of the regular polygon.
In this case, \[n = 6\]. Thus, the angle \[\angle AOB = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{6} = {60^ \circ }\].
Now, we know that in triangle AOB, OA=OB, since both are radii of the same circle. So, we can say that triangle OAB is an equilateral triangle.
Thus, the side AB is of length 6 units.
The formula for area of an equilateral triangle is \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\left( {side} \right)^2}\]
Since the length of the side of regular hexagon is 6 cm, so the area of the equilateral triangle AOB is
\[\begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\left( {side} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\left( 6 \right)^2}\\
= \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}\left( {36} \right)\\
= 9\sqrt 3
\end{array}\]
Since there are six such equilateral triangles, the area of the regular hexagon is \[6 \times 9\sqrt 3 = 54\sqrt 3 \]sq cm.
Hence, the correct option is b.
Note:
We can directly use the formula for the area of a hexagon. There are six equilateral triangles in a hexagon
Here we will be using the given information for forming the figure based on that. Then we will be finding the sides of the regular hexagon.
Complete step by step solution:
There is a regular hexagon. This regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle of radius 6 cm.
As per the given information, we know that a regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle of radius 6 cm, so we proceed by drawing the figure first

Here, we know that the angle subtended by the sides of a regular polygon (in this case hexagon) is equal to \[\dfrac{{2\pi }}{n}\] where n is the number of sides of the regular polygon.
In this case, \[n = 6\]. Thus, the angle \[\angle AOB = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{6} = {60^ \circ }\].
Now, we know that in triangle AOB, OA=OB, since both are radii of the same circle. So, we can say that triangle OAB is an equilateral triangle.
Thus, the side AB is of length 6 units.
The formula for area of an equilateral triangle is \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\left( {side} \right)^2}\]
Since the length of the side of regular hexagon is 6 cm, so the area of the equilateral triangle AOB is
\[\begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\left( {side} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\left( 6 \right)^2}\\
= \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}\left( {36} \right)\\
= 9\sqrt 3
\end{array}\]
Since there are six such equilateral triangles, the area of the regular hexagon is \[6 \times 9\sqrt 3 = 54\sqrt 3 \]sq cm.
Hence, the correct option is b.
Note:
We can directly use the formula for the area of a hexagon. There are six equilateral triangles in a hexagon
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Find the greatest fivedigit number which is a perfect class 9 maths CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE




