
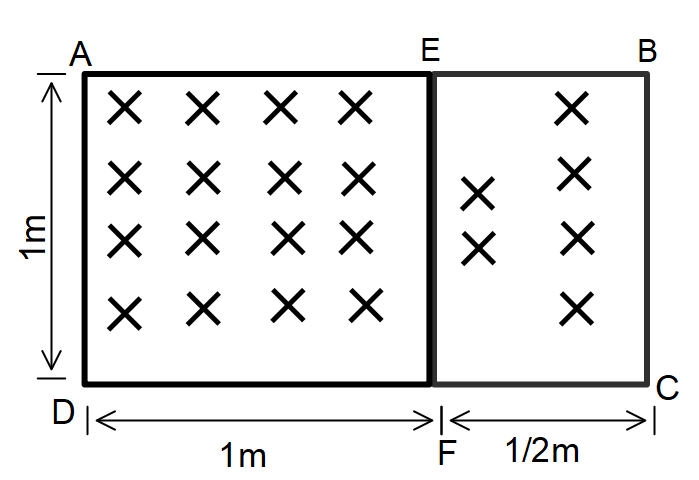
A rectangular frame ABCD made of a uniform metal wire has a straight connection between E and F made of the same wire as shown in the figure. AEFD is a square of side $1m$ and $EB = FC = 0.5m$. The entire circuit is placed in a steadily increasing, uniform magnetic field directed into the plane of paper and normal to it. The rate of change of the magnetic field is $1T{s^{ - 1}}$. The resistance per unit length of the wire is $1\Omega {m^{ - 1}}$. Find the magnitude and direction of the current in the segment AE, BE and EF.

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Initially we have to find the induced emf due to change in the magnetic field, from Faraday’s law. Then draw an analogous circuit from the induced emf and the given resistance per unit length. Apply Kirchhoff's Voltage law to each of the loops ADFEA and FCBEF. Solve the obtained equations.
Formula used:
$\varepsilon = A\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}$, KVL
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, they have given a metal wire ABCD, with a straight wire EF of the same kind. And this system is subjected to a magnetic field $1T{s^{ - 1}}$.
From Faraday's law of induction, when a closed circuit or a loop is subjected to change in flux, emf is induced. The emf induced is given by
$\eqalign{
& \varepsilon = \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{d\left( {BA} \right)}}{{dt}} = A\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\varepsilon _{AEFD}} = 1{m^2} \times 1\Omega {m^{ - 1}} = 1V \cr
& \Rightarrow {\varepsilon _{EBCF}} = 0.5{m^2} \times 1\Omega {m^{ - 1}} = 0.5V \cr
& \cr} $
From this formula, we can find the emf induced in each loop. Flemming’s left-hand rule gives the direction of the current to be in the clockwise direction.
In the question, it is mentioned that the wire has the resistance per unit length as $1\Omega {m^{ - 1}}$. From the given data and the emf obtained above, we can resolve the given rectangular frame into an equivalent electric circuit that is as follows.
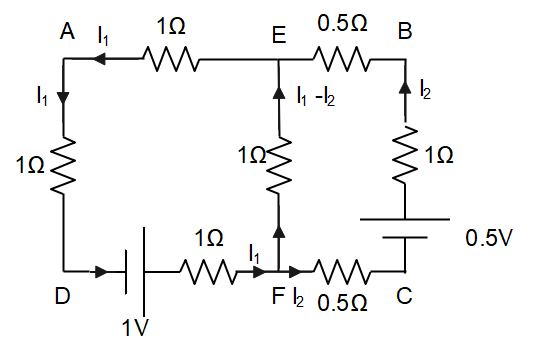
Applying KVL to the loop ADFEA, we have
$\eqalign{
& - {I_1}\left( {1\Omega } \right) + 1V - {I_1}\left( {1\Omega } \right) - \left( {{I_1} - {I_2}} \right)\left( {1\Omega } \right) - {I_1}\left( {1\Omega } \right) = 0 \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_1}\left( {4\Omega } \right) - {I_2}\left( {1\Omega } \right) = 1V - - > eq.1 \cr
& \cr} $
Applying KVL to the loop FCBEF, we have
$\eqalign{
& - {I_2}\left( {0.5\Omega } \right) + 0.5V - {I_2}\left( {1\Omega } \right) - {I_2}\left( {0.5\Omega } \right) + \left( {{I_1} - {I_2}} \right)\left( {1\Omega } \right) = 0 \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_2}\left( {3\Omega } \right) - {I_1}\left( {1\Omega } \right) = - 0.5V - - > eq.2 \cr
& \cr} $
Solving eq.1 and eq.2, we get
$\eqalign{
& {I_1} = \dfrac{{3.5}}{{11}}A = 0.32A \cr
& {I_2} = 0.28A \cr} $
Therefore, the current through the wires AE, BE, EF along with the direction are as follows
$\Rightarrow {I_{AE}} = {I_1} = 0.32A$, along A 🡪 E
$\Rightarrow {I_{BE}} = {I_2} = 0.28A$, along B 🡪 E
$\Rightarrow {I_{EF}} = {I_1} - {1_2} = 0.04A$, along E 🡪 F.
Note:
The sign convention for Kirchhoff's Voltage law; while traversing a loop, there’s a rise in the potential while - moving from negative to the positive terminal of a battery and while moving opposite to the direction of current in a resistor.
Formula used:
$\varepsilon = A\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}$, KVL
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, they have given a metal wire ABCD, with a straight wire EF of the same kind. And this system is subjected to a magnetic field $1T{s^{ - 1}}$.
From Faraday's law of induction, when a closed circuit or a loop is subjected to change in flux, emf is induced. The emf induced is given by
$\eqalign{
& \varepsilon = \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{d\left( {BA} \right)}}{{dt}} = A\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\varepsilon _{AEFD}} = 1{m^2} \times 1\Omega {m^{ - 1}} = 1V \cr
& \Rightarrow {\varepsilon _{EBCF}} = 0.5{m^2} \times 1\Omega {m^{ - 1}} = 0.5V \cr
& \cr} $
From this formula, we can find the emf induced in each loop. Flemming’s left-hand rule gives the direction of the current to be in the clockwise direction.
In the question, it is mentioned that the wire has the resistance per unit length as $1\Omega {m^{ - 1}}$. From the given data and the emf obtained above, we can resolve the given rectangular frame into an equivalent electric circuit that is as follows.

Applying KVL to the loop ADFEA, we have
$\eqalign{
& - {I_1}\left( {1\Omega } \right) + 1V - {I_1}\left( {1\Omega } \right) - \left( {{I_1} - {I_2}} \right)\left( {1\Omega } \right) - {I_1}\left( {1\Omega } \right) = 0 \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_1}\left( {4\Omega } \right) - {I_2}\left( {1\Omega } \right) = 1V - - > eq.1 \cr
& \cr} $
Applying KVL to the loop FCBEF, we have
$\eqalign{
& - {I_2}\left( {0.5\Omega } \right) + 0.5V - {I_2}\left( {1\Omega } \right) - {I_2}\left( {0.5\Omega } \right) + \left( {{I_1} - {I_2}} \right)\left( {1\Omega } \right) = 0 \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_2}\left( {3\Omega } \right) - {I_1}\left( {1\Omega } \right) = - 0.5V - - > eq.2 \cr
& \cr} $
Solving eq.1 and eq.2, we get
$\eqalign{
& {I_1} = \dfrac{{3.5}}{{11}}A = 0.32A \cr
& {I_2} = 0.28A \cr} $
Therefore, the current through the wires AE, BE, EF along with the direction are as follows
$\Rightarrow {I_{AE}} = {I_1} = 0.32A$, along A 🡪 E
$\Rightarrow {I_{BE}} = {I_2} = 0.28A$, along B 🡪 E
$\Rightarrow {I_{EF}} = {I_1} - {1_2} = 0.04A$, along E 🡪 F.
Note:
The sign convention for Kirchhoff's Voltage law; while traversing a loop, there’s a rise in the potential while - moving from negative to the positive terminal of a battery and while moving opposite to the direction of current in a resistor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




