
A rectangular current carrying loop $EFGH$ is kept in a uniform magnetic field as shown in the figure.
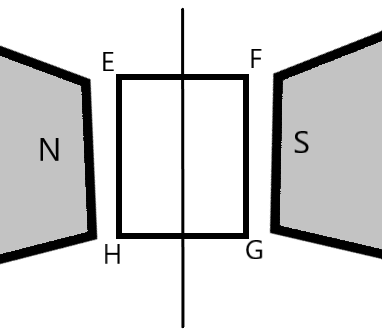
1) What is the direction of the magnetic moment of the current loop?
2) When is the torque acting on the loop a) maximum b) zero?

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: 1) As clear from the figure, direction of magnetic field is from north(N) to south(S). This magnetic field will direct the current in a rectangular loop in a direction given by $HEFG$. Magnetic moment of a current carrying loop kept in a uniform magnetic field refers to the measure of torque exerted on the loop due to the magnetic field. Direction of the magnetic moment is determined using right hand rule.
2) Torque acting on the current loop is nothing but a measure of the magnetic moment generated due to the magnetic field from north(N) to south(S). It is a vector quantity, which is equal to the cross product of magnetic field vector and the magnetic moment vector.
Formula used:
$\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{M}\times \overrightarrow{B}=MB\sin \theta $
Complete answer:
1) We are given with a rectangular current carrying loop $EFGH$, kept in a uniform magnetic field, as shown in the following figure. We are required to determine the direction of magnetic moment of the current loop.
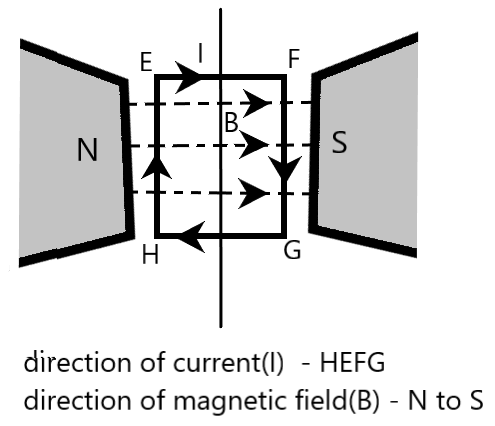
As clear from the figure, a magnet is used to generate a uniform magnetic field. Magnetic moment of the current loop is nothing but a measure of the torque exerted on the loop due to the magnetic field. Direction of the magnetic moment is determined using right hand rule.
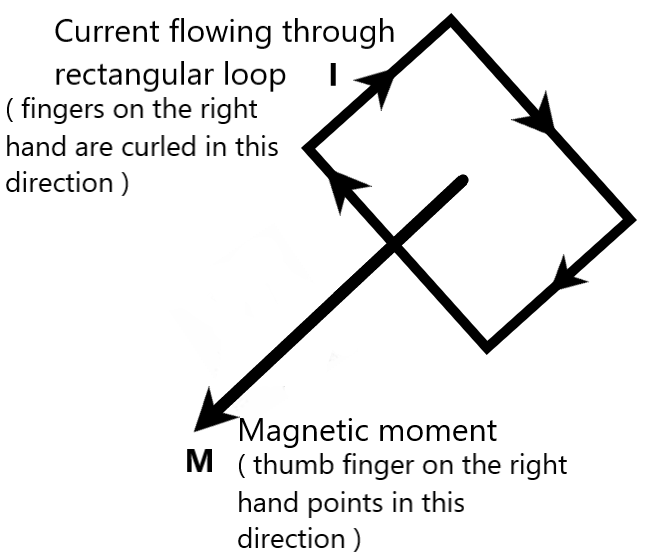
Right hand rule suggests that:
When we curl our fingers on the right hand in the direction of the axis of current flow in a current carrying loop kept in a uniform magnetic field, then, the pointing of the right thumb gives the direction of magnetic moment of the current loop.
From the figure, it is clear that the direction of the magnetic field is from the north end of the magnet to the south end of the magnet. This magnetic field will direct the current in a rectangular loop in a direction given by $HEFG$, as shown. Applying right hand rule, direction of magnetic moment of the rectangular current carrying loop is into the plane of paper, acting downwards, as shown in the following figure.
Hence, the direction of magnetic moment is into the paper, acting downwards.
2) Torque acting on a current carrying loop kept in a magnetic field is nothing but a measure of the magnetic moment generated in the loop due to the magnetic field. It is a vector quantity and is equal to the cross product of magnetic field vector and the magnetic moment vector. Mathematically, torque acting on a current carrying loop kept in a uniform magnetic field is given by
$\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{M}\times \overrightarrow{B}$
where
$\overrightarrow{\tau }$ is the torque acting on a current carrying loop kept in a magnetic field
$\overrightarrow{M}$ is the magnetic moment of current loop
$\overrightarrow{B}$ is the uniform magnetic field in which the current carrying loop is kept
Let this be equation 1.
Coming to our question, we are given with a rectangular current carrying loop $EFGH$, kept in a uniform magnetic field, as shown in the following figure. We are required to determine the maximum torque acting on the loop as well as the minimum torque acting on the loop.
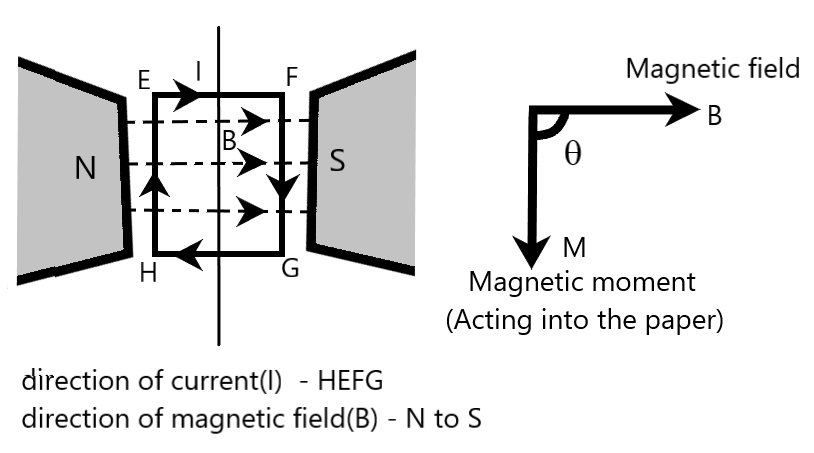
Using equation 1, we have
$\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{M}\times \overrightarrow{B}=MB\sin \theta $
where
$\overrightarrow{\tau }$ is the torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop $EFGH$
$\overrightarrow{M}$ is the magnetic moment of the rectangular current carrying loop
$\overrightarrow{B}$ is the uniform magnetic field acting from the north end to the south end of the magnet
$\theta $ is the angle between uniform magnetic field and the magnetic moment of current carrying loop, as shown in the figure
Let this be equation 2.
Here, we know that $\theta =90{}^\circ $ is the maximum value of $\theta $ whereas $\theta =0{}^\circ $ is the minimum value of $\theta $.
Substituting these values in equation 2, we have,
$\overrightarrow{{{\tau }_{\max }}}=MB\sin \theta =MB\sin 90{}^\circ =MB$
and
$\overrightarrow{{{\tau }_{\min }}}=MB\sin \theta =MB\sin 0{}^\circ =0$
where
$\overrightarrow{{{\tau }_{max}}}$ and $\overrightarrow{{{\tau }_{\min }}}$ are the maximum torque and the minimum torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop $EFGH$, respectively.
Therefore, torque acting on the loop is maximum when the angle between uniform magnetic field and magnetic moment of the loop is $90{}^\circ $ whereas torque acting on the loop is minimum when the angle between uniform magnetic field and magnetic moment of the loop is $0{}^\circ $.
Note:
From both these explanations, it is clear that torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop is a measure of the magnetic moment of the current loop and vice versa. Therefore, it is obvious that the direction of torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop is the same as that of the magnetic moment of the current loop, determined using right hand rule. And this is true for both maximum torque as well as minimum torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop.
2) Torque acting on the current loop is nothing but a measure of the magnetic moment generated due to the magnetic field from north(N) to south(S). It is a vector quantity, which is equal to the cross product of magnetic field vector and the magnetic moment vector.
Formula used:
$\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{M}\times \overrightarrow{B}=MB\sin \theta $
Complete answer:
1) We are given with a rectangular current carrying loop $EFGH$, kept in a uniform magnetic field, as shown in the following figure. We are required to determine the direction of magnetic moment of the current loop.

As clear from the figure, a magnet is used to generate a uniform magnetic field. Magnetic moment of the current loop is nothing but a measure of the torque exerted on the loop due to the magnetic field. Direction of the magnetic moment is determined using right hand rule.
Right hand rule suggests that:
When we curl our fingers on the right hand in the direction of the axis of current flow in a current carrying loop kept in a uniform magnetic field, then, the pointing of the right thumb gives the direction of magnetic moment of the current loop.
From the figure, it is clear that the direction of the magnetic field is from the north end of the magnet to the south end of the magnet. This magnetic field will direct the current in a rectangular loop in a direction given by $HEFG$, as shown. Applying right hand rule, direction of magnetic moment of the rectangular current carrying loop is into the plane of paper, acting downwards, as shown in the following figure.

Hence, the direction of magnetic moment is into the paper, acting downwards.
2) Torque acting on a current carrying loop kept in a magnetic field is nothing but a measure of the magnetic moment generated in the loop due to the magnetic field. It is a vector quantity and is equal to the cross product of magnetic field vector and the magnetic moment vector. Mathematically, torque acting on a current carrying loop kept in a uniform magnetic field is given by
$\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{M}\times \overrightarrow{B}$
where
$\overrightarrow{\tau }$ is the torque acting on a current carrying loop kept in a magnetic field
$\overrightarrow{M}$ is the magnetic moment of current loop
$\overrightarrow{B}$ is the uniform magnetic field in which the current carrying loop is kept
Let this be equation 1.
Coming to our question, we are given with a rectangular current carrying loop $EFGH$, kept in a uniform magnetic field, as shown in the following figure. We are required to determine the maximum torque acting on the loop as well as the minimum torque acting on the loop.

Using equation 1, we have
$\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{M}\times \overrightarrow{B}=MB\sin \theta $
where
$\overrightarrow{\tau }$ is the torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop $EFGH$
$\overrightarrow{M}$ is the magnetic moment of the rectangular current carrying loop
$\overrightarrow{B}$ is the uniform magnetic field acting from the north end to the south end of the magnet
$\theta $ is the angle between uniform magnetic field and the magnetic moment of current carrying loop, as shown in the figure
Let this be equation 2.
Here, we know that $\theta =90{}^\circ $ is the maximum value of $\theta $ whereas $\theta =0{}^\circ $ is the minimum value of $\theta $.
Substituting these values in equation 2, we have,
$\overrightarrow{{{\tau }_{\max }}}=MB\sin \theta =MB\sin 90{}^\circ =MB$
and
$\overrightarrow{{{\tau }_{\min }}}=MB\sin \theta =MB\sin 0{}^\circ =0$
where
$\overrightarrow{{{\tau }_{max}}}$ and $\overrightarrow{{{\tau }_{\min }}}$ are the maximum torque and the minimum torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop $EFGH$, respectively.
Therefore, torque acting on the loop is maximum when the angle between uniform magnetic field and magnetic moment of the loop is $90{}^\circ $ whereas torque acting on the loop is minimum when the angle between uniform magnetic field and magnetic moment of the loop is $0{}^\circ $.
Note:
From both these explanations, it is clear that torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop is a measure of the magnetic moment of the current loop and vice versa. Therefore, it is obvious that the direction of torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop is the same as that of the magnetic moment of the current loop, determined using right hand rule. And this is true for both maximum torque as well as minimum torque acting on the rectangular current carrying loop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




