
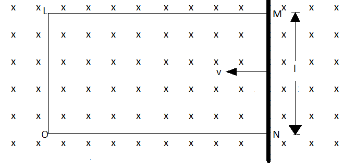
A rectangular conductor LMNO placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.5T. The field is directed perpendicular to the plane the conductor. When the arm MN of length of 20 cm is moved towards the left with a velocity of 10 ms\[^{ - 1}\], calculate the emf induced in the arm. Given the resistance of the arm to be $5\Omega $(assuming that other arms and of negligible resistance) find the value of the current in the arm.

Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint:To find out the induced emf on a conductor, the component of magnetic field(B) which is perpendicular to length (l) and velocity (v) is taken into account. Induced emf is given as $e = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$. Where, $\phi = B.A$. Then applying ohm's law we find the current in this arm $I = \dfrac{e}{R}$, where R is the resistance of the arm.
Complete step by step answer:
Given the magnetic field B$ = 0.5T$. The length of the rod, l$ = 20cm = 0.2m$ and its velocity, v$ = 10m/s$. We know that according to Faraday's law the induced EMF is negative of the rate of change of flux. $e = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$.Where, $\phi $ is the flux $ = B.A$
The negative sign is neglected as it shows the direction which is opposite to the direction of change of flux.
$e = \dfrac{{d\left( {BA} \right)}}{{dx}}$
As the magnetic field B is constant and area ( A) is equal to the product of length (l) and breadth(b) of the rod, we get the induced EMF as
$e = B\dfrac{{d\left( {lb} \right)}}{{dt}}$
$\Rightarrow e = Bl\dfrac{{db}}{{dt}}$
We know that it is the velocity of the rod v$ = \dfrac{{db}}{{dt}}$.
Substituting the value, we get $e = Blv$.
So,$e = 0.5 \times 0.2 \times 10 = 1V$
To find the current in this arm we use ohm's law, $I = \dfrac{e}{R}$
Substituting the value of potential difference $e$ and resistance $R$ we get,
$I = \dfrac{1}{5} \\
\therefore I= 0.2A$
Hence, the value of current is 0.2 A.
Note:We should know that the electromotive force induced in a current carrying wire of length ‘l’, moving with a velocity of ‘v’ in a magnetic field of intensity ‘B’ is given as $e = Blv$. Also, emf is induced only when one of the three conditions are fulfilled: The magnetic field changes, or the area of the conductor changes or the angle between the external field and the area vector changes continuously. If emf is induced then there will always be flow of electric current and the same can be found easily using Ohm's law if the resistance of the conductor is known.
Complete step by step answer:
Given the magnetic field B$ = 0.5T$. The length of the rod, l$ = 20cm = 0.2m$ and its velocity, v$ = 10m/s$. We know that according to Faraday's law the induced EMF is negative of the rate of change of flux. $e = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$.Where, $\phi $ is the flux $ = B.A$
The negative sign is neglected as it shows the direction which is opposite to the direction of change of flux.
$e = \dfrac{{d\left( {BA} \right)}}{{dx}}$
As the magnetic field B is constant and area ( A) is equal to the product of length (l) and breadth(b) of the rod, we get the induced EMF as
$e = B\dfrac{{d\left( {lb} \right)}}{{dt}}$
$\Rightarrow e = Bl\dfrac{{db}}{{dt}}$
We know that it is the velocity of the rod v$ = \dfrac{{db}}{{dt}}$.
Substituting the value, we get $e = Blv$.
So,$e = 0.5 \times 0.2 \times 10 = 1V$
To find the current in this arm we use ohm's law, $I = \dfrac{e}{R}$
Substituting the value of potential difference $e$ and resistance $R$ we get,
$I = \dfrac{1}{5} \\
\therefore I= 0.2A$
Hence, the value of current is 0.2 A.
Note:We should know that the electromotive force induced in a current carrying wire of length ‘l’, moving with a velocity of ‘v’ in a magnetic field of intensity ‘B’ is given as $e = Blv$. Also, emf is induced only when one of the three conditions are fulfilled: The magnetic field changes, or the area of the conductor changes or the angle between the external field and the area vector changes continuously. If emf is induced then there will always be flow of electric current and the same can be found easily using Ohm's law if the resistance of the conductor is known.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




