
A rectangular coil of 500 turns ${10^{ - 2}}{m^2}$ area carrying 1A is in a magnetic field of 1T at ${60^0}$ to its plane. The net rotating effect it could experience in (Nm) is
A. 250
B. 25
C. 2.5
D. 0.25
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: When the charge is at rest it produces only electric fields but when the charge is under motion it produces both electric and magnetic fields. So a current-carrying produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field magnetic moment is also produced and it will result in torque when placed in an external magnetic field.
Formula used:
$ \mathop {\rm T}\limits^ \to = \mathop M\limits^ \to \times \mathop B\limits^ \to $
$ \mathop M\limits^ \to = NI\mathop A\limits^ \to $
Complete step-by-step solution:
Due to the magnetic effect produced because of current flowing in the wire loop, a magnetic field is produced which in turn creates the magnetic moment.
When this current-carrying wire is placed in some external magnetic field then it will be acted upon by the torque.
That torque will depend on various factors like current flowing(I) and the number of turns of coil(N) and area of the loop(A) and magnetic flux density(B). This is shown diagrammatically below.
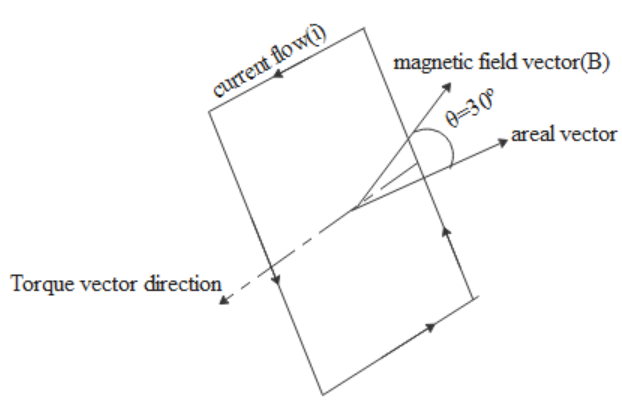
First, we have the formula for the magnetic moment produced due to the current-carrying loop which will be $\mathop M\limits^ \to = NI\mathop A\limits^ \to $
From the formula itself, it is clearly evident that the direction of the magnetic moment is the same as the area directly.
Now when loop is placed in external magnetic field, torque acting on it will be $\mathop {\rm T}\limits^ \to = \mathop M\limits^ \to \times \mathop B\limits^ \to $
Whose magnitude will be ${\rm T} = MB\sin \theta $ where $\theta $ is the angle between the areal vector and magnetic field vector.
From the question angle between plane and magnetic field is given as ${60^0}$. Which means the angle between areal vector and magnetic field vector will be ${90^0} - {60^0} = {30^0}$
Hence magnitude of torque or turning effect would be
${\rm T} = MB\sin \theta $
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {\rm T} = NIAB\sin \theta \cr
& \Rightarrow {\rm T} = (500)(1)({10^{ - 2}})(1)\sin {30^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow \sin {30^0} = 0.5 \cr
& \Rightarrow {\rm T} = 2.5Nm \cr} $
Hence torque will be 2.5Nm. Hence the answer would be option C.
Note: Many people get confused in considering the angle. Since the current is not a vector the direction of the area is considered as the direction of the magnetic moment. Now the angle between the magnetic moment vector and external magnetic field vector should be considered, not the angle between the plane of loop and external magnetic field.
Formula used:
$ \mathop {\rm T}\limits^ \to = \mathop M\limits^ \to \times \mathop B\limits^ \to $
$ \mathop M\limits^ \to = NI\mathop A\limits^ \to $
Complete step-by-step solution:
Due to the magnetic effect produced because of current flowing in the wire loop, a magnetic field is produced which in turn creates the magnetic moment.
When this current-carrying wire is placed in some external magnetic field then it will be acted upon by the torque.
That torque will depend on various factors like current flowing(I) and the number of turns of coil(N) and area of the loop(A) and magnetic flux density(B). This is shown diagrammatically below.

First, we have the formula for the magnetic moment produced due to the current-carrying loop which will be $\mathop M\limits^ \to = NI\mathop A\limits^ \to $
From the formula itself, it is clearly evident that the direction of the magnetic moment is the same as the area directly.
Now when loop is placed in external magnetic field, torque acting on it will be $\mathop {\rm T}\limits^ \to = \mathop M\limits^ \to \times \mathop B\limits^ \to $
Whose magnitude will be ${\rm T} = MB\sin \theta $ where $\theta $ is the angle between the areal vector and magnetic field vector.
From the question angle between plane and magnetic field is given as ${60^0}$. Which means the angle between areal vector and magnetic field vector will be ${90^0} - {60^0} = {30^0}$
Hence magnitude of torque or turning effect would be
${\rm T} = MB\sin \theta $
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {\rm T} = NIAB\sin \theta \cr
& \Rightarrow {\rm T} = (500)(1)({10^{ - 2}})(1)\sin {30^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow \sin {30^0} = 0.5 \cr
& \Rightarrow {\rm T} = 2.5Nm \cr} $
Hence torque will be 2.5Nm. Hence the answer would be option C.
Note: Many people get confused in considering the angle. Since the current is not a vector the direction of the area is considered as the direction of the magnetic moment. Now the angle between the magnetic moment vector and external magnetic field vector should be considered, not the angle between the plane of loop and external magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




