
A rectangular coil 20cm x 20cm has 100 turns and carries a current of 1 A. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field B=0.5 T with the direction of magnetic field parallel to the plane of the coil. The magnitude of the torque required to hold this coil in this position is
A. Zero
B. 200N-m
C. 2N-m
D. 10N-m
Answer
507.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we are going to use the mentioned concept and then substitute values accordingly. The magnetic moment in a loop is defined as the product of the current flowing in the loop and the area of the rectangular loop. Mathematically,
\[\mu = IA\]
Here, A is equal to the area of the rectangular loop and I is the current flowing in the loop. So the torque exerted on a current-carrying coil placed in a magnetic field is given by the cross product of the magnetic moment and the magnetic field.
\[\tau = \mu \times B\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
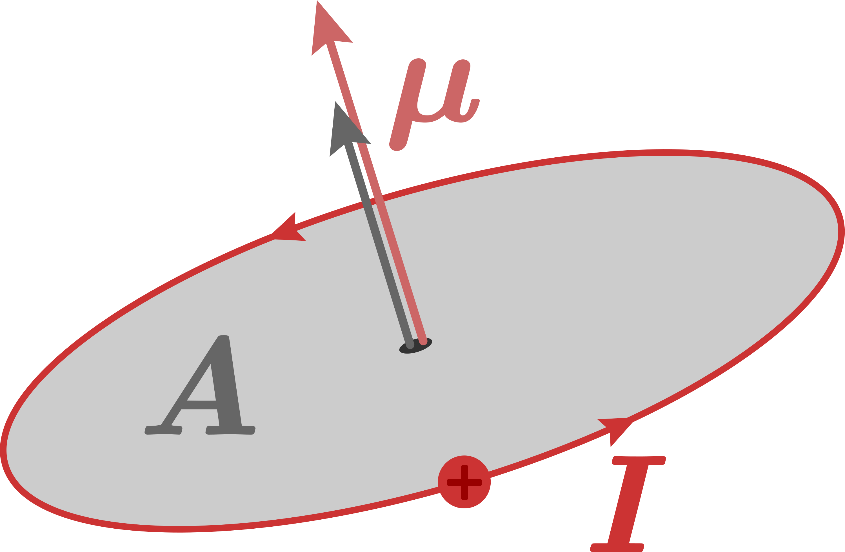
Magnitude of the torque \[\tau \] is given by
\[\tau = NIAB\]
Where N is the number of turns
I is the current flowing
A is the area of the loop
B is the uniform magnetic field.
Therefore, substituting the values we get
\[
\tau = 100 \times 1 \times 400 \times {10^{ - 4}} \times 0.5 \\
\tau = 2N - m \\
\]
Hence Option(C) is correct.
Note:Torque is a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis. Just as force causes an object to accelerate in linear kinematics, torque causes an object to acquire angular acceleration. Torque is a vector quantity which can be either static or dynamic. A static torque does not produce an angular acceleration whereas dynamic torque does.
\[\mu = IA\]
Here, A is equal to the area of the rectangular loop and I is the current flowing in the loop. So the torque exerted on a current-carrying coil placed in a magnetic field is given by the cross product of the magnetic moment and the magnetic field.
\[\tau = \mu \times B\]
Complete step-by-step solution:

Magnitude of the torque \[\tau \] is given by
\[\tau = NIAB\]
Where N is the number of turns
I is the current flowing
A is the area of the loop
B is the uniform magnetic field.
Therefore, substituting the values we get
\[
\tau = 100 \times 1 \times 400 \times {10^{ - 4}} \times 0.5 \\
\tau = 2N - m \\
\]
Hence Option(C) is correct.
Note:Torque is a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis. Just as force causes an object to accelerate in linear kinematics, torque causes an object to acquire angular acceleration. Torque is a vector quantity which can be either static or dynamic. A static torque does not produce an angular acceleration whereas dynamic torque does.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




