
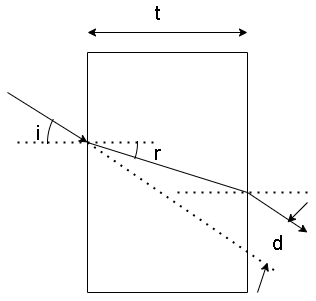
A ray of light is incident on a thick slab of a glass of thickness t as shown in the figure. The emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray but displaced sideways by a distance d. If the angles are small then $d$ is
A) $T(1 - \dfrac{i}{r})$
B) $Rt(1 - \dfrac{i}{r})$
C) $it(1 - \dfrac{r}{i})$
D) $T(\dfrac{{ - r}}{i})$

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: When the emergent ray is displaced then the phenomenon of lateral shift is observed. Lateral shift is the perpendicular distance between the incident ray and the emergent ray when the light ray undergoes refraction from a glass slab. The lateral displacement depends upon the thickness and the refractive index of the glass slab and the angle at which the incident ray enters the glass slab.
Formula used:
The formula of lateral displacement can be written as
$D = \dfrac{{t\sin (i - r)}}{{\cos r}}$
Where $D$ is the lateral displacement
$t$ is the thickness of the slab
$i$ is the angle of incidence
$r$ is the angle of refraction
Complete step by step answer:
The ray of light incident on the glass slab undergoes refraction twice and comes out from the other side of the slab as an emergent ray.
The formula of lateral displacement $D = \dfrac{{t\sin (i - r)}}{{\cos r}}$
Since the angle made by the incident and emergent ray, the angle is very small and when the angle is small then it can be written that
$\sin (i - r) \cong i - r$
And $\cos r \cong 1$
Substituting the values in the formula, and solving for the value of lateral displacement
$D = \dfrac{{t(i - r)}}{1}$
Taking ‘$i$’ common from the bracket, the equation reduces to the form
$D = it(1 - \dfrac{r}{i})$
Therefore, Option C is the right answer.
Note:
It is to be noted that the emergent ray shows a lateral shift of the ray from the original path. When the Light is passing through the glass its velocity decreases but when it comes out of the glass slab, its velocity increases. The light ray then follows the same direction in the air.
Formula used:
The formula of lateral displacement can be written as
$D = \dfrac{{t\sin (i - r)}}{{\cos r}}$
Where $D$ is the lateral displacement
$t$ is the thickness of the slab
$i$ is the angle of incidence
$r$ is the angle of refraction
Complete step by step answer:
The ray of light incident on the glass slab undergoes refraction twice and comes out from the other side of the slab as an emergent ray.
The formula of lateral displacement $D = \dfrac{{t\sin (i - r)}}{{\cos r}}$
Since the angle made by the incident and emergent ray, the angle is very small and when the angle is small then it can be written that
$\sin (i - r) \cong i - r$
And $\cos r \cong 1$
Substituting the values in the formula, and solving for the value of lateral displacement
$D = \dfrac{{t(i - r)}}{1}$
Taking ‘$i$’ common from the bracket, the equation reduces to the form
$D = it(1 - \dfrac{r}{i})$
Therefore, Option C is the right answer.
Note:
It is to be noted that the emergent ray shows a lateral shift of the ray from the original path. When the Light is passing through the glass its velocity decreases but when it comes out of the glass slab, its velocity increases. The light ray then follows the same direction in the air.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




