
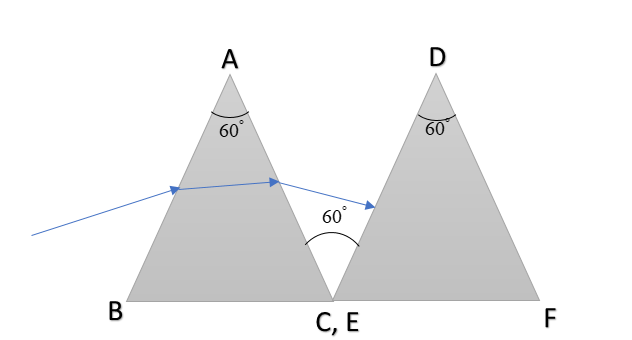
A ray of light is incident on a prism ABC of refractive index $\sqrt3$ as shown in figure.
(a)Find the angle of incidence for which the deviation of light ray by the prism ABC is minimum.
(b) By what angle the second prism must be rotated, so that the final ray suffers net minimum deviation.
$\text{A.}\quad 30^{\circ},\ 60^{\circ}.$
$\text{B.}\quad 60^{\circ},\ 30^{\circ}.$
$\text{C.}\quad 60^{\circ},\ 60^{\circ}.$
$\text{D.}\quad None.$

Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: A prism is not just an instrument. It’s basically a concept that could be applied when a light ray passes through a denser medium and gets out after suffering some deviation. Deviation of light ray is defined as the angle turned by the light ray after suffering refraction, measured with respect to the initial direction of light ray.
Formula used:
$\mu = \dfrac{sin(\dfrac{A+\delta}{2})}{sin(\dfrac A2)}$
Complete answer:
We have a well-known formula relating the angle of prism, minimum deviation and refractive index of the material of prism:
$\mu = \dfrac{sin(\dfrac{A+\delta}{2})}{sin(\dfrac A2)}$
Given; $A = 60^{\circ}\ and \ \mu = \sqrt3$
Hence we can use the relation. Putting all the known values in the relation, we get;
$\mu = \dfrac{sin(\dfrac{A+\delta}{2})}{sin(\dfrac A2)}$
$\implies\sqrt3 = \dfrac{sin(\dfrac{60^{\circ}+\delta_{min}}{2})}{sin(\dfrac {60^\circ}{2})}$
$\implies sin(\dfrac{60^\circ+\delta_{min}}{2}) = \sqrt3 \times sin30^\circ = \sqrt3/2$
Hence, $\dfrac{60^\circ+\delta_{min}}{2} = 60^\circ$ [as $sin\ 60^\circ = \dfrac{\sqrt3}{2}$]
$\implies \delta_{min} = 120^\circ -60^{\circ} = 60^{\circ}$
Now, for part (b) of the question, as the two prisms are symmetric, hence the deviation of the second prism will also be the same. Hence to minimize the net deviation from the combination of prisms, we need to place the prism such that the deviation produced from the first prism gets neutralized and hence becomes zero. Hence we have to turn the prism by $60^\circ$, anticlockwise, as shown in the figure.
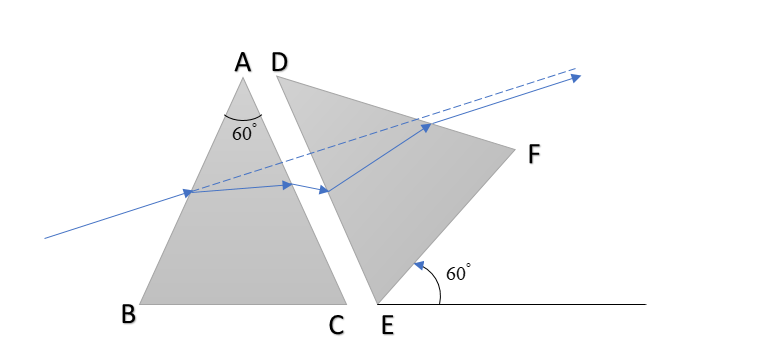
Hence, we can see that incident rays and the final transmitted rays are parallel and hence by definition, net deviation becomes zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The angle of the prism is not always the angle of the top of the prism. This is a misconception, which needs to be removed. The angle of the prism is the angle which is opposite to the side, which is along the direction of incident ray. The relations used in prism analysis are derived by applying basic geometry and most importantly, Snell’s laws.
Formula used:
$\mu = \dfrac{sin(\dfrac{A+\delta}{2})}{sin(\dfrac A2)}$
Complete answer:
We have a well-known formula relating the angle of prism, minimum deviation and refractive index of the material of prism:
$\mu = \dfrac{sin(\dfrac{A+\delta}{2})}{sin(\dfrac A2)}$
Given; $A = 60^{\circ}\ and \ \mu = \sqrt3$
Hence we can use the relation. Putting all the known values in the relation, we get;
$\mu = \dfrac{sin(\dfrac{A+\delta}{2})}{sin(\dfrac A2)}$
$\implies\sqrt3 = \dfrac{sin(\dfrac{60^{\circ}+\delta_{min}}{2})}{sin(\dfrac {60^\circ}{2})}$
$\implies sin(\dfrac{60^\circ+\delta_{min}}{2}) = \sqrt3 \times sin30^\circ = \sqrt3/2$
Hence, $\dfrac{60^\circ+\delta_{min}}{2} = 60^\circ$ [as $sin\ 60^\circ = \dfrac{\sqrt3}{2}$]
$\implies \delta_{min} = 120^\circ -60^{\circ} = 60^{\circ}$
Now, for part (b) of the question, as the two prisms are symmetric, hence the deviation of the second prism will also be the same. Hence to minimize the net deviation from the combination of prisms, we need to place the prism such that the deviation produced from the first prism gets neutralized and hence becomes zero. Hence we have to turn the prism by $60^\circ$, anticlockwise, as shown in the figure.

Hence, we can see that incident rays and the final transmitted rays are parallel and hence by definition, net deviation becomes zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The angle of the prism is not always the angle of the top of the prism. This is a misconception, which needs to be removed. The angle of the prism is the angle which is opposite to the side, which is along the direction of incident ray. The relations used in prism analysis are derived by applying basic geometry and most importantly, Snell’s laws.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




