
A ray of light incident normally on a refracted surface does not suffer any refraction.
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: The question stated the incident ray incidence normally on refracted surface, it means angle must be zero between normal and incident angle. Relation between incident ray and refracted ray is given by Snell’s law. So use Snell’s law to put the value of the incident angle equal to zero and find the angle of refraction and draw the conclusion.
Complete step by step answer:
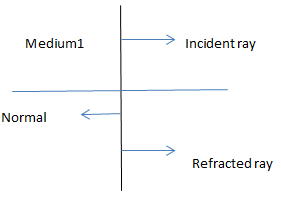
In this question, the ray of light incident normally on a surface i.e. angle between normal and incident ray must be zero. Now we need to find the nature of refracted ray, if incident ray incidence normally. The relation between the angle of incidence and angle of refraction is given by law named as Snell’s law.
The relation between the angle of incidence and angle of refraction was discovered by Dutch physicist Snell in 1621. This law gives important conclusion about refracted ray which states that:
1) At the point of incidence, the incident ray and refracted ray are on opposite sides of the normal. These trees lie in the same phase.
2) For a given pair of medium that is medium 1 and medium 2, the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant.
Mathematically, Snell’s is given as,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{{{\mu }_{1}}} \\
& \therefore {{\mu }_{1}}\sin i={{\mu }_{2}}\sin r......(1) \\
\end{align}$
When incident ray is normal i.e. perpendicular to the surface then i = 0.
Put in equation (1) we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\mu }_{1}}\sin 0={{\mu }_{2}}\sin r \\
& \Rightarrow \sin r=0 \\
& \Rightarrow r={{0}^{o}} \\
\end{align}$
It means that, when ray incident normally on a refracting surface, refracted ray does not suffer any refraction.
Note: When a light ray passes from a denser medium to a rarer medium, in this case also bending takes place and it bends away from the normal. Students misjudge this and commit a mistake.
Complete step by step answer:

In this question, the ray of light incident normally on a surface i.e. angle between normal and incident ray must be zero. Now we need to find the nature of refracted ray, if incident ray incidence normally. The relation between the angle of incidence and angle of refraction is given by law named as Snell’s law.
The relation between the angle of incidence and angle of refraction was discovered by Dutch physicist Snell in 1621. This law gives important conclusion about refracted ray which states that:
1) At the point of incidence, the incident ray and refracted ray are on opposite sides of the normal. These trees lie in the same phase.
2) For a given pair of medium that is medium 1 and medium 2, the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant.
Mathematically, Snell’s is given as,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{{{\mu }_{1}}} \\
& \therefore {{\mu }_{1}}\sin i={{\mu }_{2}}\sin r......(1) \\
\end{align}$
When incident ray is normal i.e. perpendicular to the surface then i = 0.
Put in equation (1) we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\mu }_{1}}\sin 0={{\mu }_{2}}\sin r \\
& \Rightarrow \sin r=0 \\
& \Rightarrow r={{0}^{o}} \\
\end{align}$
It means that, when ray incident normally on a refracting surface, refracted ray does not suffer any refraction.
Note: When a light ray passes from a denser medium to a rarer medium, in this case also bending takes place and it bends away from the normal. Students misjudge this and commit a mistake.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




