
A ray of light from denser medium strikes a rarer medium at an angle of incidence$i$. The reflected and refracted rays make an angle of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$with each other. If the angles of reflection and refraction are r and r’, then the critical angle will be:
A. ${\tan ^{ - 1}}(\sin i)$
B. ${\sin ^{ - 1}}(\sin r)$
C. ${\sin ^{ - 1}}(\tan i)$
D. ${\sin ^{ - 1}}(\tan r)$
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint:Snell’s law is a law which states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction of a wave is constant when it passes between two given media. Or in other words, we can say Snell's law is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. The relationship is something like this: \[n1\sin \theta 1 = n2\sin \theta 2\]
The critical angle is the angle of incidence where the angle of refraction is${90^ \circ }$. For this, the light must travel from optically denser to a rarer medium.
Complete step by step solution:
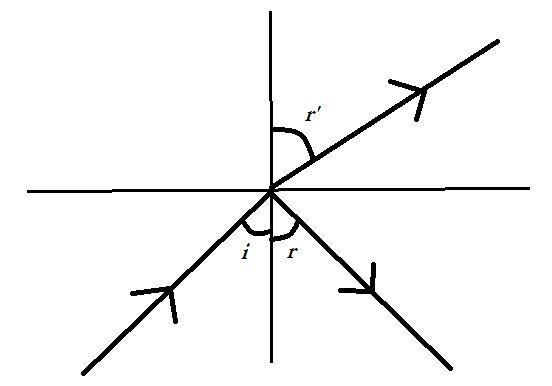
Let $\mu 1$ be the refractive index of a rarer medium and $\mu 2$be the refractive index of the denser medium.
According to the question:
$i$is the angle of incidence; $r$is the angle of reflection and $r'$is the angle of refraction.
And angle between angle of reflection and angle of refraction is $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
$\begin{gathered}
r + r' = \dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\Rightarrow r' = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - r \\
\end{gathered} $
Let the required critical angle be C. then,
$\begin{gathered}
This \Rightarrow \mu 1\sin C = \mu 2 \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\mu 2}}{{\mu 1}} \\
\end{gathered} $
Now applying snell’s law,
\[\begin{gathered}
\mu 1\sin i = \mu 2\sin r' \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu 2}}{{\mu 1}} = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r'}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r'}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - r)}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\cos r}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\cos i}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \tan i \\
\Rightarrow C = {\sin ^{ - 1}}(\tan i) \\
\end{gathered} \]
Hence the required critical angle is \[C = {\sin ^{ - 1}}(\tan i)\]
Note:Always note that to find the critical angle the light must be travelling from optically denser to a rarer medium. Be careful while applying snell’s law.
The critical angle is the angle of incidence where the angle of refraction is${90^ \circ }$. For this, the light must travel from optically denser to a rarer medium.
Complete step by step solution:

Let $\mu 1$ be the refractive index of a rarer medium and $\mu 2$be the refractive index of the denser medium.
According to the question:
$i$is the angle of incidence; $r$is the angle of reflection and $r'$is the angle of refraction.
And angle between angle of reflection and angle of refraction is $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
$\begin{gathered}
r + r' = \dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\Rightarrow r' = \dfrac{\pi }{2} - r \\
\end{gathered} $
Let the required critical angle be C. then,
$\begin{gathered}
This \Rightarrow \mu 1\sin C = \mu 2 \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\mu 2}}{{\mu 1}} \\
\end{gathered} $
Now applying snell’s law,
\[\begin{gathered}
\mu 1\sin i = \mu 2\sin r' \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu 2}}{{\mu 1}} = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r'}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r'}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin (\dfrac{\pi }{2} - r)}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\cos r}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\cos i}} \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \tan i \\
\Rightarrow C = {\sin ^{ - 1}}(\tan i) \\
\end{gathered} \]
Hence the required critical angle is \[C = {\sin ^{ - 1}}(\tan i)\]
Note:Always note that to find the critical angle the light must be travelling from optically denser to a rarer medium. Be careful while applying snell’s law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




