
What is a p-type semiconductor? What are the majority and minority charge carriers in it?
Answer
605.7k+ views
Hint: The p-type semiconductors are formed when the pure semiconductor combines with the impurities. It generates a hole in the combination. This is due to the three electrons of the impurity bonded with four electrons of the valence shell leaves the fourth one as hole.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) Semiconductors:
The semiconductors are the materials which have the properties of conductivity are same as both the conductors and insulators.
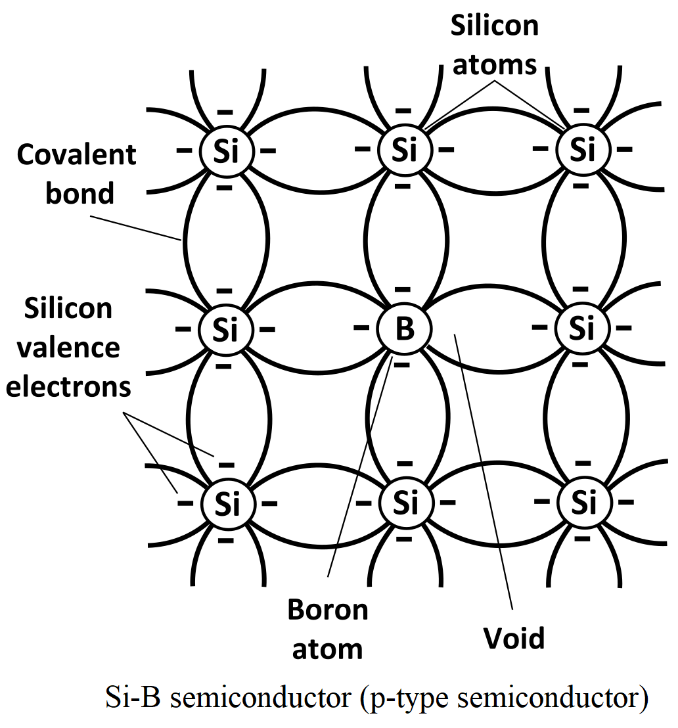
(ii) p-type semiconductors:
When a pure semiconductor is doped with a trivalent impurity (B, Al, In, Ga ) then, the three valence electrons of the impurity bond with three of the four valence electrons of the semiconductor.
This makes a vacant electron (hole) in the impurity atom. Those impurity atoms having holes are acceptors, because they can easily accept the bonding electron from the other atom.
Since, there is an increase in the holes of the semiconductor due to the increase in the number of impurities. Thus, these semiconductors are called p-type semiconductors.
Semiconductors are most often made from silicon. Silicon is an element with four valence electrons in its outermost valence shell. To make a p-type semiconductor additional materials like boron or aluminium are prepend to the silicon. These materials have three valence electrons in their outermost valence shell. When some extra new material replaces some of the silicon it leaves a 'hole' and the fourth electron would have been if the semiconductor was pure silicon.
Crystal as a whole is neutral, but the acceptors become an immobile negative ion. As conduction is due to a large number of holes, the holes in the p-type semiconductor are majority carriers and electrons are minority carriers.
Note: The p-type semiconductors are made by doping the pure semiconductor material. The amount of impurity added is extremely small compared to the quantity of semiconductor. The character of the semiconductors can be easily varied by changing the amount of impurities added to the semiconductor. In p type semiconductor the holes are numerous when compared to the thermal electrons.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) Semiconductors:
The semiconductors are the materials which have the properties of conductivity are same as both the conductors and insulators.

(ii) p-type semiconductors:
When a pure semiconductor is doped with a trivalent impurity (B, Al, In, Ga ) then, the three valence electrons of the impurity bond with three of the four valence electrons of the semiconductor.
This makes a vacant electron (hole) in the impurity atom. Those impurity atoms having holes are acceptors, because they can easily accept the bonding electron from the other atom.
Since, there is an increase in the holes of the semiconductor due to the increase in the number of impurities. Thus, these semiconductors are called p-type semiconductors.
Semiconductors are most often made from silicon. Silicon is an element with four valence electrons in its outermost valence shell. To make a p-type semiconductor additional materials like boron or aluminium are prepend to the silicon. These materials have three valence electrons in their outermost valence shell. When some extra new material replaces some of the silicon it leaves a 'hole' and the fourth electron would have been if the semiconductor was pure silicon.
Crystal as a whole is neutral, but the acceptors become an immobile negative ion. As conduction is due to a large number of holes, the holes in the p-type semiconductor are majority carriers and electrons are minority carriers.
Note: The p-type semiconductors are made by doping the pure semiconductor material. The amount of impurity added is extremely small compared to the quantity of semiconductor. The character of the semiconductors can be easily varied by changing the amount of impurities added to the semiconductor. In p type semiconductor the holes are numerous when compared to the thermal electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




