
A proton moving at constant velocity passes through a region of space without any changes in its velocity. If E and B represent the electric and magnetic fields respectively identify which of the following options can be true for the space.
A. \[E=0,B=0\]
B. \[E=0,B\ne 0\]
C. \[E\ne 0,B=0\]
D. \[E\ne 0,B\ne 0\]
Answer
557.7k+ views
Hint: When a charged particle is moving in a magnetic field then a magnetic force acts on the moving charged particle. Furthermore, the direction of the magnetic force can be identified by using Fleming’s left hand rule. We also know that when a charged particle is placed in an electric field then it experiences an electric force in the direction of the field on positive charge.
Complete Step-By-Step answer:
Now, we will look into individual options and identify the correct answers.
We will start by looking into option A.
Suppose, when \[E=0,B=0\]
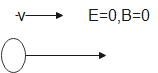
In this case, when the electric field E is zero then the electric force \[{{F}_{E}}\] acting on the proton will also be zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{E}}=0\]
Also, when the magnetic field B is zero then the magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\] acting on the charged particle is zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{M}}=0\]
This means that when both the forces are zero then the proton can pass space without any change in their velocities.
Now, we will look into option B,
Suppose, when \[E=0,B\ne 0\]
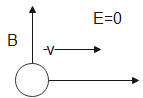
In this case, when the electric field E is zero then the electric force \[{{F}_{E}}\] acting on the proton will also be zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{E}}=0\]
However, \[B\ne 0\]so the magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\]is not zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{M}}\ne 0\]
In this case we can see that the magnetic force is acting on the charged particle, hence we can say that the velocity of the particle will change.
Now, we will look into option C,
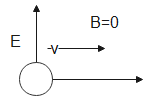
Suppose, \[E\ne 0,B=0\]
In this case, \[E\ne 0\] so the electric force acting on the charged particle will not be zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{E}}\ne 0\]
When the magnetic field B is zero then the magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\] acting on the charged particle is zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{M}}=0\]
In this case we can say that the electric force acting on the particle will change the velocity of the particle.
Now, we will look into option D,
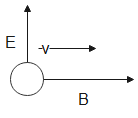
Suppose, \[E\ne 0,B\ne 0\]
In this case, \[E\ne 0\] so the electric force acting on the charged particle will not be zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{E}}\ne 0\] and \[{{F}_{E}}=qE\]
However, \[B\ne 0\]so the magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\]is not zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{M}}\ne 0\] and \[{{F}_{M}}=qvB\sin \theta \]
In this case we can say that it is possible that the forces are equal and opposite to each other in a particular instinct hence then the net force will be zero. When the force is zero then the velocity of the particle remains unchanged.
Hence, option A and D are the correct options.
Note:
When the proton is placed in magnetic field it experiences magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\],
\[{{F}_{M}}=qvB\sin \theta \]
Where, \[q\Rightarrow \]charge of the moving proton(+e)
\[v\Rightarrow \]velocity of the moving proton
\[B\Rightarrow \]magnetic field
\[\theta \Rightarrow \]angle formed between velocity and magnetic field
When the proton is placed in electric field it experiences electric force \[{{F}_{E}}\],
\[{{F}_{E}}=qE\]
Where, \[q\Rightarrow \]charge of the particle
\[E\Rightarrow \]electric field intensity
Complete Step-By-Step answer:
Now, we will look into individual options and identify the correct answers.
We will start by looking into option A.
Suppose, when \[E=0,B=0\]

In this case, when the electric field E is zero then the electric force \[{{F}_{E}}\] acting on the proton will also be zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{E}}=0\]
Also, when the magnetic field B is zero then the magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\] acting on the charged particle is zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{M}}=0\]
This means that when both the forces are zero then the proton can pass space without any change in their velocities.
Now, we will look into option B,
Suppose, when \[E=0,B\ne 0\]

In this case, when the electric field E is zero then the electric force \[{{F}_{E}}\] acting on the proton will also be zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{E}}=0\]
However, \[B\ne 0\]so the magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\]is not zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{M}}\ne 0\]
In this case we can see that the magnetic force is acting on the charged particle, hence we can say that the velocity of the particle will change.
Now, we will look into option C,

Suppose, \[E\ne 0,B=0\]
In this case, \[E\ne 0\] so the electric force acting on the charged particle will not be zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{E}}\ne 0\]
When the magnetic field B is zero then the magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\] acting on the charged particle is zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{M}}=0\]
In this case we can say that the electric force acting on the particle will change the velocity of the particle.
Now, we will look into option D,

Suppose, \[E\ne 0,B\ne 0\]
In this case, \[E\ne 0\] so the electric force acting on the charged particle will not be zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{E}}\ne 0\] and \[{{F}_{E}}=qE\]
However, \[B\ne 0\]so the magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\]is not zero.
i.e., \[{{F}_{M}}\ne 0\] and \[{{F}_{M}}=qvB\sin \theta \]
In this case we can say that it is possible that the forces are equal and opposite to each other in a particular instinct hence then the net force will be zero. When the force is zero then the velocity of the particle remains unchanged.
Hence, option A and D are the correct options.
Note:
When the proton is placed in magnetic field it experiences magnetic force \[{{F}_{M}}\],
\[{{F}_{M}}=qvB\sin \theta \]
Where, \[q\Rightarrow \]charge of the moving proton(+e)
\[v\Rightarrow \]velocity of the moving proton
\[B\Rightarrow \]magnetic field
\[\theta \Rightarrow \]angle formed between velocity and magnetic field
When the proton is placed in electric field it experiences electric force \[{{F}_{E}}\],
\[{{F}_{E}}=qE\]
Where, \[q\Rightarrow \]charge of the particle
\[E\Rightarrow \]electric field intensity
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




