
A potentiometer wire of length 10 m and resistance \[30\text{ }\Omega\] is connected in series with a battery of emf 2.5 V, internal resistance 5 Ω, and an external resistance R. If the fall of potential along the potentiometer wire is \[50\mu Vm{{m}^{-1}}\], then the value of R is found to be 23n Ω. What is n?
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: At first, we have to understand which system is given. Accordingly, write all given information and using standard formulas, calculate the required answer. Potential gradient is the ratio of potential difference and the length of potentiometer wire.
Complete answer:
Let I be the current in the circuit. E be emf, r is internal resistance and ${{R}_{s}}$ is the resistance of wire connected in series with battery.
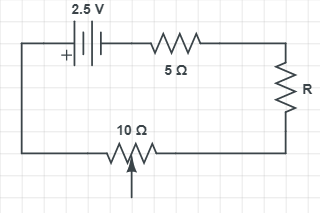
We know that the equation of emf,
\[E=I(R+{{R}_{s}}+r)\]
So, we can rearrange it to determine current I as
\[I=\dfrac{E}{(R+{{R}_{s}}+r)}..........(1)\]
The potential gradient k of the wire is
\[k=\dfrac{I{{R}_{s}}}{L}......(2)\]
where L is the length of the potentiometer wire.
Substituting value of I from equation (1) in equation (2) we get,
\[k=\dfrac{E{{R}_{s}}}{(R+{{R}_{s}}+r)L}..........(3)\]
Here it is given that, \[L=10m,\text{ }E=2.5V,\text{ }r=5\Omega ,\text{ }{{R}_{s}}=30\Omega ,\text{ }k=50\mu Vm{{m}^{-1}}\text{, }R=23n\Omega \]
Putting all these values in equation (3) we get,
\[\dfrac{50\times {{10}^{-6}}}{{{10}^{-3}}}=\dfrac{2.5\times 30}{(R+30+5)10}\]
Solving above equation and doing correct calculations we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 50\times {{10}^{-6+3}}=\dfrac{2.5\times 3}{(R+35)} \\
& \Rightarrow (R+35)=\dfrac{7.5}{50\times {{10}^{-3}}} \\
& \Rightarrow (R+35)=0.15\times {{10}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow R=150-35=115 \\
\end{align}\]
But given R = 23n, so above equation can be written as,
\[23n=115\]
Dividing throughout by 23, we get
\[n=5\]
Note:
Students must remember to convert the unit of potential gradient into SI unit because all the remaining values are in SI unit. Don’t forget to add internal resistance with the resistance R because they are in series with battery. Do calculations accurately otherwise it leads to wrong answers.
Students sometimes just take E = IR and ignore internal resistance, this will lead to wrong answers.
Complete answer:
Let I be the current in the circuit. E be emf, r is internal resistance and ${{R}_{s}}$ is the resistance of wire connected in series with battery.

We know that the equation of emf,
\[E=I(R+{{R}_{s}}+r)\]
So, we can rearrange it to determine current I as
\[I=\dfrac{E}{(R+{{R}_{s}}+r)}..........(1)\]
The potential gradient k of the wire is
\[k=\dfrac{I{{R}_{s}}}{L}......(2)\]
where L is the length of the potentiometer wire.
Substituting value of I from equation (1) in equation (2) we get,
\[k=\dfrac{E{{R}_{s}}}{(R+{{R}_{s}}+r)L}..........(3)\]
Here it is given that, \[L=10m,\text{ }E=2.5V,\text{ }r=5\Omega ,\text{ }{{R}_{s}}=30\Omega ,\text{ }k=50\mu Vm{{m}^{-1}}\text{, }R=23n\Omega \]
Putting all these values in equation (3) we get,
\[\dfrac{50\times {{10}^{-6}}}{{{10}^{-3}}}=\dfrac{2.5\times 30}{(R+30+5)10}\]
Solving above equation and doing correct calculations we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 50\times {{10}^{-6+3}}=\dfrac{2.5\times 3}{(R+35)} \\
& \Rightarrow (R+35)=\dfrac{7.5}{50\times {{10}^{-3}}} \\
& \Rightarrow (R+35)=0.15\times {{10}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow R=150-35=115 \\
\end{align}\]
But given R = 23n, so above equation can be written as,
\[23n=115\]
Dividing throughout by 23, we get
\[n=5\]
Note:
Students must remember to convert the unit of potential gradient into SI unit because all the remaining values are in SI unit. Don’t forget to add internal resistance with the resistance R because they are in series with battery. Do calculations accurately otherwise it leads to wrong answers.
Students sometimes just take E = IR and ignore internal resistance, this will lead to wrong answers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




