
A polaroid is placed at 45° to an incoming light of intensity ${{I}_{0}}$ now the intensity of light passing through the polaroid after polarization would be:
A. ${{I}_{0}}$
B. $\dfrac{{{I}_{0}}}{2}$
C. $\dfrac{{{I}_{0}}}{4}$
D. Zero
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Polaroids are the materials which restrict the vibrations of waves from many planes into a single plane. The light passing through a polaroid is governed by a simple formula. We are going to use this formula to solve the problem.
Formula used:
$I={{I}_{0}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $
Complete answer:
We know that the intensity of light passing through a polaroid after polarization is given by:
$I={{I}_{0}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $ ----(i)
Where, $I$ is the intensity of the light incident on the polaroid before polarization.
${{I}_{0}}$ is the intensity of light coming out of the polaroid after polarization.
And, $\theta $ is the angle of incidence of the light on the polaroid.
Here, according to question, $\theta =45{}^\circ $
Hence, $I={{I}_{0}}{{\cos }^{2}}45$
$\Rightarrow I={{I}_{0}}{{\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{{{I}_{0}}}{2}$ ---(ii)
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
In unpolarized light the vibrations are not confined to any particular plane. These vibrations are unwanted in certain scenarios. So we need to restrict these vibrations to a particular desired plane as per our need. This restriction of the vibrations of the light wave from many planes into a single desired plane is done with the help of polaroid. Polaroid only allows those waves to pass through it which vibrate in a particular plane while restricting others from passing through it.
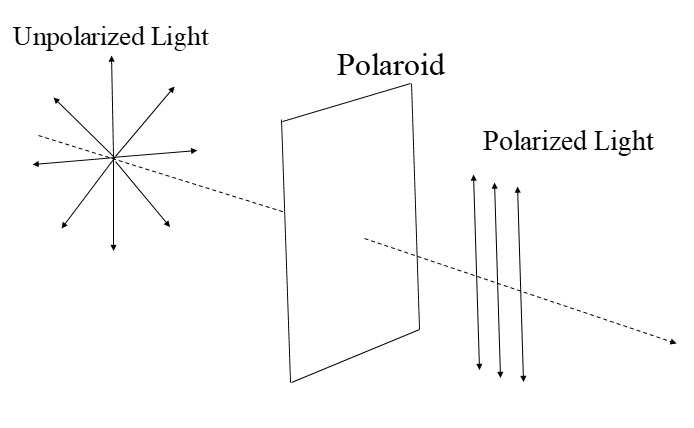
There are many applications of these polaroids. For example, these polaroids are used in certain eye wears so that the glare of the sun could be reduced. Hardness of a molecule could also be determined with the help of polaroids.
Note:
The angle of incidence on a polaroid is measured from the normal to the polaroid to the incident wave. Do not take the angle of incidence as the angle from the plane of polaroid to the incident wave. Also, note that the formula of output intensity has ${{\cos }^{2}}$ and not $\cos $.
Formula used:
$I={{I}_{0}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $
Complete answer:
We know that the intensity of light passing through a polaroid after polarization is given by:
$I={{I}_{0}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $ ----(i)
Where, $I$ is the intensity of the light incident on the polaroid before polarization.
${{I}_{0}}$ is the intensity of light coming out of the polaroid after polarization.
And, $\theta $ is the angle of incidence of the light on the polaroid.
Here, according to question, $\theta =45{}^\circ $
Hence, $I={{I}_{0}}{{\cos }^{2}}45$
$\Rightarrow I={{I}_{0}}{{\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{{{I}_{0}}}{2}$ ---(ii)
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
In unpolarized light the vibrations are not confined to any particular plane. These vibrations are unwanted in certain scenarios. So we need to restrict these vibrations to a particular desired plane as per our need. This restriction of the vibrations of the light wave from many planes into a single desired plane is done with the help of polaroid. Polaroid only allows those waves to pass through it which vibrate in a particular plane while restricting others from passing through it.

There are many applications of these polaroids. For example, these polaroids are used in certain eye wears so that the glare of the sun could be reduced. Hardness of a molecule could also be determined with the help of polaroids.
Note:
The angle of incidence on a polaroid is measured from the normal to the polaroid to the incident wave. Do not take the angle of incidence as the angle from the plane of polaroid to the incident wave. Also, note that the formula of output intensity has ${{\cos }^{2}}$ and not $\cos $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




