
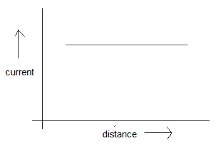
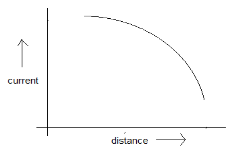
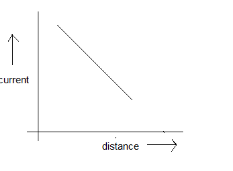
A point source causes photoelectric effect from a small metal plate. Which of the curves in figure may represent the saturation photo-current as a function of the distance between the source and the metal?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
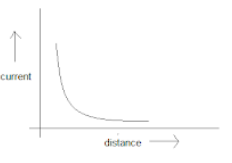




Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to see what the photoelectric effect is and what impact the distance has on the current, then, according to the relation between current and the distance, we can directly predict the nature of the curve between current and the distance.
As intensity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, so,
$ I \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r^2}}} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The saturation current is that maximum value of the current after which no more current flows no matter what intensity of light we strike on the surface. The saturation current is directly proportional to the number of electrons that are falling on the collector plate per second while it is directly proportional to the number of electrons falling on a cathode per second.
Here the number of photons striking directly impacts the number of electrons being ejected, which further depends on the intensity of the incident light. As intensity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, so,
$ I \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r^2}}} $
So, the correct graph is the one depicting the current decreasing with the power two of distance and it will be rapidly decreasing with higher power of $ r $ .
So, option D is the correct answer.
Note :
In the photoelectric effect experiment, we have a light ray striking on a metal surface that causes the electrons from the surface to be ejected and cause a flow of current. The number of the ejected electrons and so the current produced directly depends upon the intensity of the incident light.
As intensity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, so,
$ I \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r^2}}} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The saturation current is that maximum value of the current after which no more current flows no matter what intensity of light we strike on the surface. The saturation current is directly proportional to the number of electrons that are falling on the collector plate per second while it is directly proportional to the number of electrons falling on a cathode per second.
Here the number of photons striking directly impacts the number of electrons being ejected, which further depends on the intensity of the incident light. As intensity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, so,
$ I \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r^2}}} $
So, the correct graph is the one depicting the current decreasing with the power two of distance and it will be rapidly decreasing with higher power of $ r $ .
So, option D is the correct answer.
Note :
In the photoelectric effect experiment, we have a light ray striking on a metal surface that causes the electrons from the surface to be ejected and cause a flow of current. The number of the ejected electrons and so the current produced directly depends upon the intensity of the incident light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




