
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
(A) Infinity
(B) Pole
(C) Focus
(D) 15 cm behind the mirror
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: To solve this question you should know what a convex mirror is and what a mirror is. With the general equation of the mirror equation, we can find where the image is formed with the given details in the question. Convex Mirror: A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outwards is called a convex mirror. Mirrors are good reflectors. A mirror can be made by silvering a metal surface with glass in front and paint at its back.
Complete step by step solution:
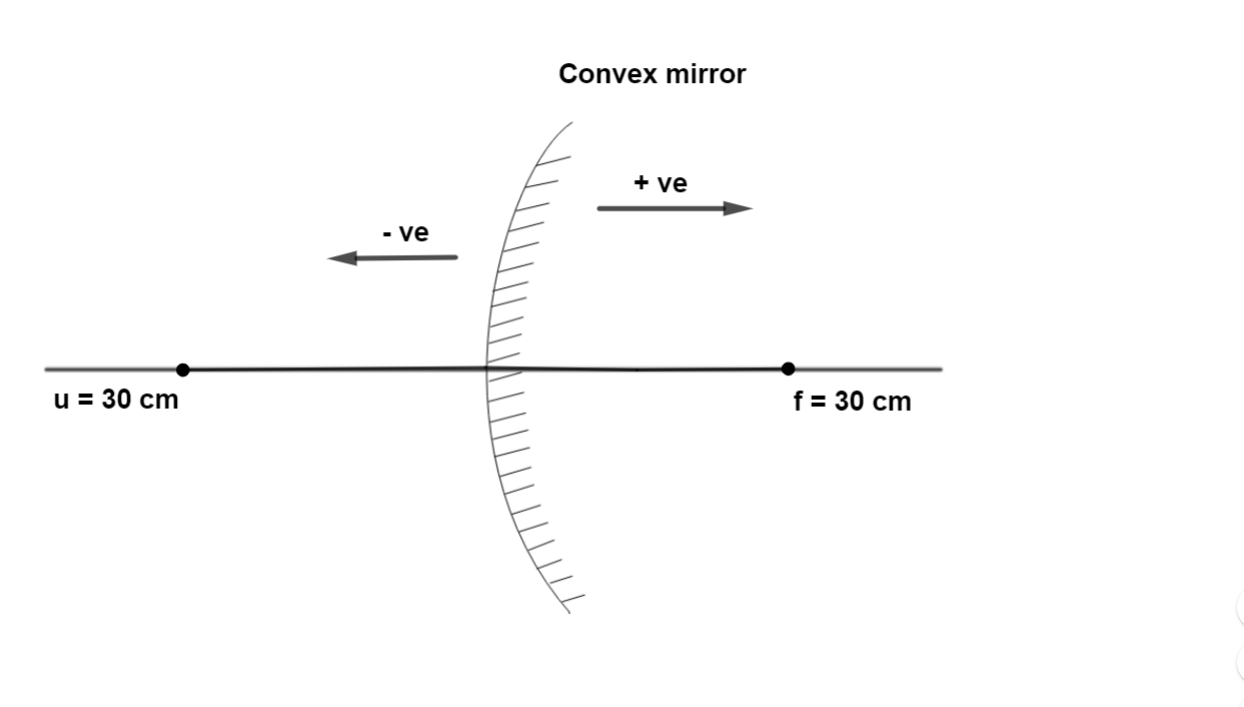
A point object is placed 30 cm from the convex mirror of focal length 30 cm.
Mirror formula: In a spherical mirror, there is a relation between object's distance u, image distance v and principal focus of the mirror f.
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Therefore, from the figure and given data
$u{\text{ = - 30 cm}}$
$f{\text{ = 30 cm}}$
Using the mirror formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Substituting the values,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{{ - 30}} = \dfrac{1}{{30}}$
Upon simplifying, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{2}{{30}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{15}}$
$\therefore v{\text{ = 15 cm}}$
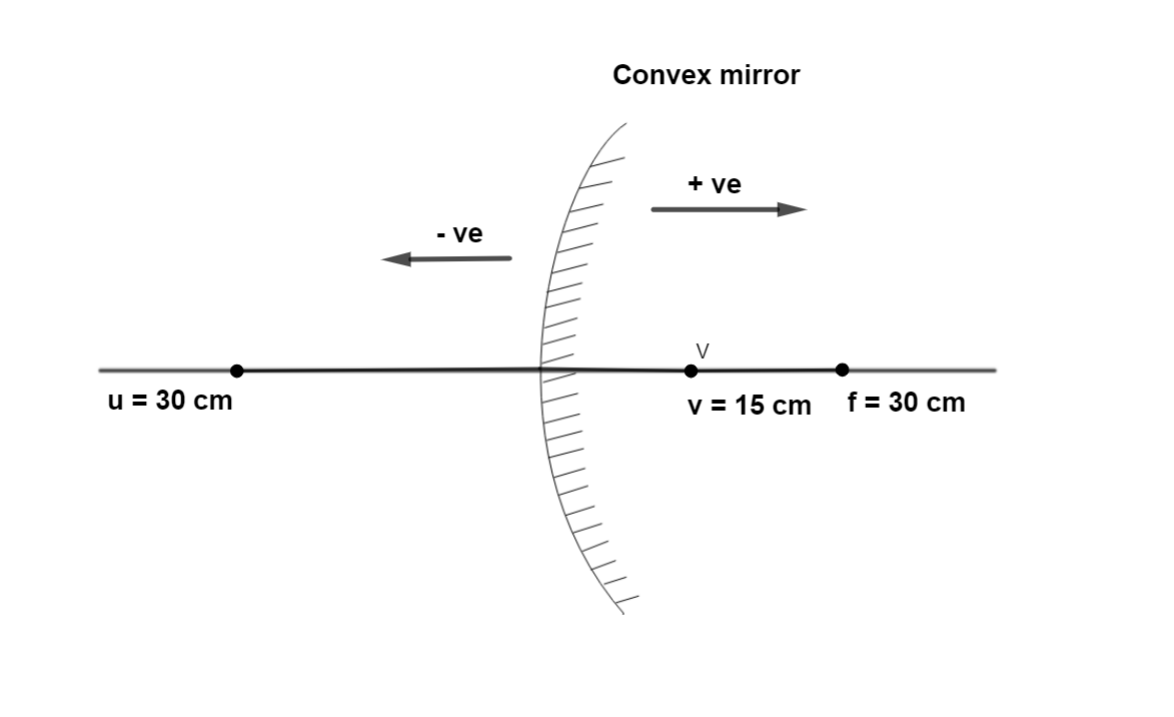
Therefore, the image is formed 15 cm behind the convex mirror.
So, the correct answer is option (D)
Additional information:
Concave Mirror: A spherical mirror, whose reflecting surface is curved inwards is called a concave mirror It means reflecting (polished) surface faces the center of the sphere from which it is made.
Magnification by Mirror: The extent by which a mirror extends or reduces the size of an image with respect to an object is called the magnification factor of a mirror. It is represented by m. If the size of an object is h and its image by a spherical mirror is h’. Then magnification factor of mirror is
$m{\text{ = - }}\dfrac{v}{u} = \dfrac{{h'}}{h}$
Note:
Convex mirrors are preferred over plane mirrors as rear-view mirrors because they give diminished images of objects and hence can cover a larger field of view. A convex mirror always produces a virtual image, because f is always greater than zero and u is less than zero so from the mirror formula the v will be always positive. Hence the image is always virtual.
Complete step by step solution:

A point object is placed 30 cm from the convex mirror of focal length 30 cm.
Mirror formula: In a spherical mirror, there is a relation between object's distance u, image distance v and principal focus of the mirror f.
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Therefore, from the figure and given data
$u{\text{ = - 30 cm}}$
$f{\text{ = 30 cm}}$
Using the mirror formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Substituting the values,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{{ - 30}} = \dfrac{1}{{30}}$
Upon simplifying, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{2}{{30}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{15}}$
$\therefore v{\text{ = 15 cm}}$

Therefore, the image is formed 15 cm behind the convex mirror.
So, the correct answer is option (D)
Additional information:
Concave Mirror: A spherical mirror, whose reflecting surface is curved inwards is called a concave mirror It means reflecting (polished) surface faces the center of the sphere from which it is made.
Magnification by Mirror: The extent by which a mirror extends or reduces the size of an image with respect to an object is called the magnification factor of a mirror. It is represented by m. If the size of an object is h and its image by a spherical mirror is h’. Then magnification factor of mirror is
$m{\text{ = - }}\dfrac{v}{u} = \dfrac{{h'}}{h}$
Note:
Convex mirrors are preferred over plane mirrors as rear-view mirrors because they give diminished images of objects and hence can cover a larger field of view. A convex mirror always produces a virtual image, because f is always greater than zero and u is less than zero so from the mirror formula the v will be always positive. Hence the image is always virtual.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




