
A Plano convex lens has a thickness of $4cm$ when placed on the horizontal table with a curved surface in contact with it, the apparent depth of the bottommost part of the lens is found to be $3cm$. If the lens is inverted so that the plane face is in contact with the table the apparent depth is found to be $\dfrac{{25}}{8}cm$. The focal length of the lens is
a. $75cm$
b. $60cm$
c. $50cm$
d. $45cm$
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: Use the formula that relates the focal length, refractive index and the radius of the curvature. Finding the value of the radius of the curvature can be found with help of the refractive index formula.
Formula used:
To find the apparent depth:
$d' = \dfrac{d}{\mu }$
Where,
$d'$ and $d$ are apparent depth and distance respectively
$\mu $ is the refractive index.
To find the value of $R$:
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where,
${\mu _2}$ and ${\mu _1}$ are refractive index
Lens maker formula to find the focal length:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right]$
Where,
$f$ is the focal length,
${R_1}{R_2}$ radius of the curvature.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question they have given that a Plano convex lens has a thickness of $4cm$. The curved surface of the lens the refractive index is in contact with the table, the image of the bottom most part of the lens is formed due to the refractive index at the plane surface.
We can consider the given image.
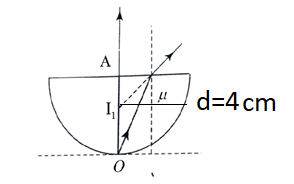
In the given image the image is formed at ${I_1}$. And the image distance is $4cm$. The apparent depth is 3.
We can find the refractive index value by using the apparent depth formula.
$d' = \dfrac{d}{\mu }$
Substitute the values in the equation. We get,
$ \Rightarrow d' = \dfrac{4}{\mu }$
This value is equal to 3. That is,
$ \Rightarrow d' = \dfrac{4}{\mu } = 3$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{4}{3}$
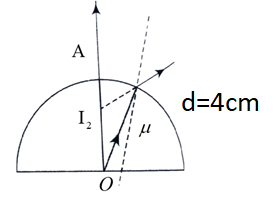
Consider the second image, here the image is formed at ${I_2}$ and the apparent depth is $\dfrac{{25}}{8}cm$.
Now we can find the value of $R$.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Substitute the values in the given equation. We have $v = \dfrac{{25}}{8}cm$ and $u = 4cm$. We can use the ${\mu _2}$ value the value of air that is 1.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{25}}{8}}} - \dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3}}}{4} = \dfrac{{1 - 4}}{{3R}}$
We can simplify the given equation. We get,
$ \Rightarrow - \dfrac{8}{{25}} - \dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3}}}{4} = \dfrac{{1 - \dfrac{4}{3}}}{{3R}}$
On further simplifications we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{75}} = \dfrac{1}{{3R}}$
$ \Rightarrow R = 25$
We have calculated necessary values. Now we can substitute all the values in the given formula to find the focal length. We have the formula for focal length:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{\infty }} \right]$
Here ${R_1} \to R$ and ${R_2} \to \infty $
Here we have to substitute the finding values in the formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3} - 1}}{{25}}$
We can use division to simplify the equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = 75cm$
$\therefore f = 75cm$
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: We have used the lens maker formula that is used to construct the lens with a specific focal length. Don’t forget to change the values of the radius of the curvature in the formula used. That is ${R_1} \to R$ and ${R_2} \to \infty $.
A plano-convex lens is a lens in which one surface of the lens is fat and another surface of the lens is a convex lens. This lens is considered as a best choice for focusing the rays that are parallel.
Formula used:
To find the apparent depth:
$d' = \dfrac{d}{\mu }$
Where,
$d'$ and $d$ are apparent depth and distance respectively
$\mu $ is the refractive index.
To find the value of $R$:
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where,
${\mu _2}$ and ${\mu _1}$ are refractive index
Lens maker formula to find the focal length:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right]$
Where,
$f$ is the focal length,
${R_1}{R_2}$ radius of the curvature.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question they have given that a Plano convex lens has a thickness of $4cm$. The curved surface of the lens the refractive index is in contact with the table, the image of the bottom most part of the lens is formed due to the refractive index at the plane surface.
We can consider the given image.

In the given image the image is formed at ${I_1}$. And the image distance is $4cm$. The apparent depth is 3.
We can find the refractive index value by using the apparent depth formula.
$d' = \dfrac{d}{\mu }$
Substitute the values in the equation. We get,
$ \Rightarrow d' = \dfrac{4}{\mu }$
This value is equal to 3. That is,
$ \Rightarrow d' = \dfrac{4}{\mu } = 3$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{4}{3}$

Consider the second image, here the image is formed at ${I_2}$ and the apparent depth is $\dfrac{{25}}{8}cm$.
Now we can find the value of $R$.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Substitute the values in the given equation. We have $v = \dfrac{{25}}{8}cm$ and $u = 4cm$. We can use the ${\mu _2}$ value the value of air that is 1.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{25}}{8}}} - \dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3}}}{4} = \dfrac{{1 - 4}}{{3R}}$
We can simplify the given equation. We get,
$ \Rightarrow - \dfrac{8}{{25}} - \dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3}}}{4} = \dfrac{{1 - \dfrac{4}{3}}}{{3R}}$
On further simplifications we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{75}} = \dfrac{1}{{3R}}$
$ \Rightarrow R = 25$
We have calculated necessary values. Now we can substitute all the values in the given formula to find the focal length. We have the formula for focal length:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{\infty }} \right]$
Here ${R_1} \to R$ and ${R_2} \to \infty $
Here we have to substitute the finding values in the formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3} - 1}}{{25}}$
We can use division to simplify the equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = 75cm$
$\therefore f = 75cm$
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: We have used the lens maker formula that is used to construct the lens with a specific focal length. Don’t forget to change the values of the radius of the curvature in the formula used. That is ${R_1} \to R$ and ${R_2} \to \infty $.
A plano-convex lens is a lens in which one surface of the lens is fat and another surface of the lens is a convex lens. This lens is considered as a best choice for focusing the rays that are parallel.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




