
When a plane mirror is rotated through an angle $\theta$, the reflected ray turns through the angle $2\theta$, then size of the image:
a) is doubled
b) is halved
c) Remains the same
d) becomes infinite
Answer
532.5k+ views
Hint: When a plane mirror is rotated through an angle $\theta$, then the normal of the plane mirror also gets shifted by the same angle $\theta$. When a beam gets passed by the plane mirror turned at $\theta$ angle, then the image position is shifted by $2\theta$ but the size of image is the same. Only the position of the image changes, and size remains unchanged. Size of image is independent of the incidence angle.
Complete answer:
Consider a plane mirror and a fixed incident beam of light. Before the mirror has turned, the angle of incidence is $\theta$, as is the reflection angle. If the mirror turns through angle $\theta$, the normal is rotated by an angle $\theta$, the angle of incidence increases to $2\theta$. Therefore, the reflection angle must also rise by $\theta$ to $2\theta$. The difference between the final reflection angle and the initial angle of reflection is $2\theta$. It is shown in the figure given below
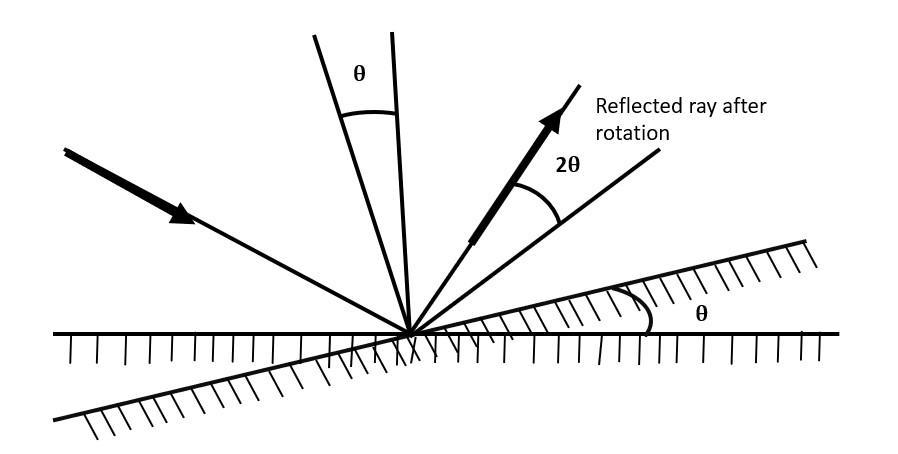
Thus, for a fixed incident ray, the reflection angle is twice the angle through which the mirror has rotated. When a plane mirror is rotated at an angle $\theta$, the reflected ray rotates through the angle $2\theta$. However, the size of the image remains unchanged only position shifts.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: For a fixed incident beam, the reflection angle is double the angle through which the reflector has rotated. The straight-line angle and the reflected radiation are double the angle of incidence called deviation of light and calculate the angle through which the light deviates from its initial straight path line. The angle difference of a mirror is equal to twice the angle of incidence.
Complete answer:
Consider a plane mirror and a fixed incident beam of light. Before the mirror has turned, the angle of incidence is $\theta$, as is the reflection angle. If the mirror turns through angle $\theta$, the normal is rotated by an angle $\theta$, the angle of incidence increases to $2\theta$. Therefore, the reflection angle must also rise by $\theta$ to $2\theta$. The difference between the final reflection angle and the initial angle of reflection is $2\theta$. It is shown in the figure given below

Thus, for a fixed incident ray, the reflection angle is twice the angle through which the mirror has rotated. When a plane mirror is rotated at an angle $\theta$, the reflected ray rotates through the angle $2\theta$. However, the size of the image remains unchanged only position shifts.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: For a fixed incident beam, the reflection angle is double the angle through which the reflector has rotated. The straight-line angle and the reflected radiation are double the angle of incidence called deviation of light and calculate the angle through which the light deviates from its initial straight path line. The angle difference of a mirror is equal to twice the angle of incidence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




