
A piston of cross-sectional area $100 cm^2$ is used in a hydraulic press to exert a force of 107 dynes on the water. The cross sectional area of the other piston which supports an object having a mass of 2000 kg is
(A) \[100cm^2\]
(B) \[ {10}^9cm^2\]
(C) \[2 \times {10}^4cm^2 \]
(D) \[2 \times {10}^{10}cm^2\]
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint:-The given problem can be solved by taking the consideration of hydraulic lift that is being used to lift the heavy loads. The working of hydraulic lift is based on Pascal’s law. Pascal’s law states that if gravity effect is neglected, the pressure at every point of liquid in equilibrium of rest is the same.
Complete step-by-step solution:
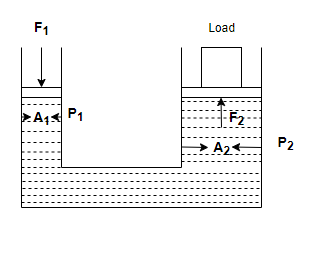
As given by the Pascal’s law pressure felt at every point of liquid that is being used in a hydraulic press will be same in equilibrium of rest i.e.,
\[ P_1 = P_2 \] -----(1)
Where \[ P_1 = \] pressure at one point and \[ P_2 = \] pressure at another point
We also know from Pascal’s law that the pressure increased using one piston will be communicated at each and every point in the liquid. Thus, the same pressure will act on the other piston.
Now given conditions are as below –
Cross-sectional area of piston 1 is \[ A_1 = 100cm^2\] or \[ A_1 = 0.01m^2\]
Force on piston 1 is \[ F_1 = {10}^7 \]dynes or \[ F_1 = 100N\]
And force on piston 2 is equal to weight of the mass that is kept on the piston i.e., \[ F_2 = M \times g\]
\[ F_2 = 2000 \times 10 = 2 \times {10}^4 \]N.
Now, let us consider the cross-sectional area of piston 2 is \[ A_2 = A\]
Step 2: Now we know from equation (1), that \[ P_1 = P_2 \]
And pressure can be defined by force per unit area i.e., \[P = \dfrac{F}{A}\]
So, \[\dfrac{{ F_1 }}{{ A_1 }} = \dfrac{{ F_2 }}{{ A_2 }}\] keeping the values from above
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{100}}{{0.01}} = \dfrac{{2 \times {10}^4 }}{A}\]on solving this equation further
\[\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{2 \times {10}^4 }}{{100}} \times 0.01\]
\[\Rightarrow A = 2m^2\] or \[A = 2 \times {10}^4 cm^2\]
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:-
Pascal’s law also holds for the principle of transmission of pressure in liquids or gases. In this form, Pascal’s law states that the increase in pressure at one point of the enclosed liquid equilibrium of rest is transmitted equally to all other points of the liquid and also to the walls of the container, provided that the effect of gravity is neglected.
Complete step-by-step solution:

As given by the Pascal’s law pressure felt at every point of liquid that is being used in a hydraulic press will be same in equilibrium of rest i.e.,
\[ P_1 = P_2 \] -----(1)
Where \[ P_1 = \] pressure at one point and \[ P_2 = \] pressure at another point
We also know from Pascal’s law that the pressure increased using one piston will be communicated at each and every point in the liquid. Thus, the same pressure will act on the other piston.
Now given conditions are as below –
Cross-sectional area of piston 1 is \[ A_1 = 100cm^2\] or \[ A_1 = 0.01m^2\]
Force on piston 1 is \[ F_1 = {10}^7 \]dynes or \[ F_1 = 100N\]
And force on piston 2 is equal to weight of the mass that is kept on the piston i.e., \[ F_2 = M \times g\]
\[ F_2 = 2000 \times 10 = 2 \times {10}^4 \]N.
Now, let us consider the cross-sectional area of piston 2 is \[ A_2 = A\]
Step 2: Now we know from equation (1), that \[ P_1 = P_2 \]
And pressure can be defined by force per unit area i.e., \[P = \dfrac{F}{A}\]
So, \[\dfrac{{ F_1 }}{{ A_1 }} = \dfrac{{ F_2 }}{{ A_2 }}\] keeping the values from above
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{100}}{{0.01}} = \dfrac{{2 \times {10}^4 }}{A}\]on solving this equation further
\[\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{2 \times {10}^4 }}{{100}} \times 0.01\]
\[\Rightarrow A = 2m^2\] or \[A = 2 \times {10}^4 cm^2\]
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:-
Pascal’s law also holds for the principle of transmission of pressure in liquids or gases. In this form, Pascal’s law states that the increase in pressure at one point of the enclosed liquid equilibrium of rest is transmitted equally to all other points of the liquid and also to the walls of the container, provided that the effect of gravity is neglected.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




