
How can a Peptide Bond be identified?
Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint: We need to know that the peptide bond is a bond that links two alpha-amino acids. The linkage occurs between $C1$ of one alpha- amino acid to ${N_2}$ of the adjacent amino acid through a protein or peptide chain. It is also called a peptide bond so as to differentiate it from the isopeptide bonds, which is another type of bond between amino acids.
Complete answer:
We need to know that the peptide bond is a bond formed between two amino acids when the carbonyl group of one amino acid interacts with another molecule’s amino group. Water molecules are eliminated resulting in a $CO - NH$ bond which is the peptide bond. The resulting molecule formed is an amide. Peptide bond is a variant of amide bond that connects peptide or protein chain via $C1$ of one alpha amino acid to the ${N_2}$ of another alpha amino acid.
The process of formation of peptide bonds is a condensation reaction resulting in removal of water (dehydration). The reaction of shown below:
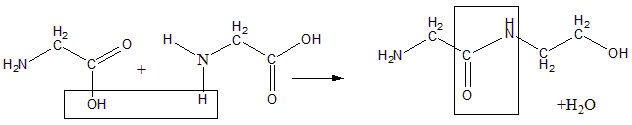
The peptide bond formation consists of three steps:
Two amino groups are brought together such that the acid group of one is close to the amine group of the other.
Water molecule is eliminated leaving a bond between acid carbon and amine nitrogen of second.
The [peptide bond is left between the two amino acids.
The ribosomes are macroscopic and complex cell structures which consist of proteins, RNA and Numerous other components. Peptide bond is one of the strongest and stable bonds that connects amino acids. The formation of peptide bonds requires energy which is given by ATP. Organisms use enzymes to produce nonribosomal peptides, and ribosomes to produce proteins.
Note:
We need to remember that a peptide bond can be broken by hydrolysis. The process is very slow with half life of $350 - 600$ years per bond. In living organisms’ enzymes like Peptidases or proteases catalyze this process.
Complete answer:
We need to know that the peptide bond is a bond formed between two amino acids when the carbonyl group of one amino acid interacts with another molecule’s amino group. Water molecules are eliminated resulting in a $CO - NH$ bond which is the peptide bond. The resulting molecule formed is an amide. Peptide bond is a variant of amide bond that connects peptide or protein chain via $C1$ of one alpha amino acid to the ${N_2}$ of another alpha amino acid.
The process of formation of peptide bonds is a condensation reaction resulting in removal of water (dehydration). The reaction of shown below:

The peptide bond formation consists of three steps:
Two amino groups are brought together such that the acid group of one is close to the amine group of the other.
Water molecule is eliminated leaving a bond between acid carbon and amine nitrogen of second.
The [peptide bond is left between the two amino acids.
The ribosomes are macroscopic and complex cell structures which consist of proteins, RNA and Numerous other components. Peptide bond is one of the strongest and stable bonds that connects amino acids. The formation of peptide bonds requires energy which is given by ATP. Organisms use enzymes to produce nonribosomal peptides, and ribosomes to produce proteins.
Note:
We need to remember that a peptide bond can be broken by hydrolysis. The process is very slow with half life of $350 - 600$ years per bond. In living organisms’ enzymes like Peptidases or proteases catalyze this process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




