
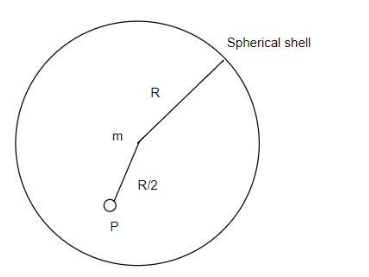
A particle of mass $m$ is placed at the center of a uniform spherical shell of same mass and radius $R$. Find the gravitational potential at a distance $\dfrac{R}{2}$ from the center.
Answer
579k+ views
Hint:Use the given parameters in the formula to know the gravitation potential of the particle and the sphere separately. The gravitational potential can be calculated by the sum of the gravitational potential of the particle and the shell.
Useful formula:
(1) The formula for the gravitational potential is given by
${V_P} = {V_s} + {V_p}$.
Where ${V_p}$ is the gravitational potential, ${V_s}$ is the gravitational potential of the spherical shell and the ${V_p}$ is the gravitational potential of the particle.
(2) Newton’s law of gravitation is given by
${V_P} \propto \dfrac{m}{d}$
Where $m$ is the mass of the particle and $d$ is the distance of the particle from the center.
Complete step by step solution:
Newton's law of gravitation states that the gravitational potential is directly proportional to the mass and it inversely proportional to the distance of the object from the center of the gravitation.
${V_P} \propto \dfrac{m}{d}$
In order to avoid the proportionality sign, the gravitational constant $G$ is included.
${V_P} = \dfrac{{Gm}}{d}$
Hence the total gravitational potential is the sum of the gravitational potential of the shell and the gravitational potential of the particle located in the center of the shell.
${V_P} = {V_s} + {V_p}$
By using the formula (2),
${V_p} = \dfrac{{Gm}}{R} + \dfrac{{Gm}}{{\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)}}$
The potential of gravity is always negative. So,
${V_p} = - \dfrac{{Gm}}{R} - \dfrac{{2Gm}}{R}$
By further simplification of the above equation,
${V_p} = - \dfrac{{3Gm}}{R}$
Hence the gravitational potential of the object at a distance of $\dfrac{R}{2}$ from the center is $ - \dfrac{{3Gm}}{R}$.
Note:The gravitational potential on the surface of the earth is always taken as the negative. This is because the work is done by the gravity on the surface of the earth to bring the object close to it which is away from the surface. The work is always done away from the surface.
Useful formula:
(1) The formula for the gravitational potential is given by
${V_P} = {V_s} + {V_p}$.
Where ${V_p}$ is the gravitational potential, ${V_s}$ is the gravitational potential of the spherical shell and the ${V_p}$ is the gravitational potential of the particle.
(2) Newton’s law of gravitation is given by
${V_P} \propto \dfrac{m}{d}$
Where $m$ is the mass of the particle and $d$ is the distance of the particle from the center.
Complete step by step solution:
Newton's law of gravitation states that the gravitational potential is directly proportional to the mass and it inversely proportional to the distance of the object from the center of the gravitation.

${V_P} \propto \dfrac{m}{d}$
In order to avoid the proportionality sign, the gravitational constant $G$ is included.
${V_P} = \dfrac{{Gm}}{d}$
Hence the total gravitational potential is the sum of the gravitational potential of the shell and the gravitational potential of the particle located in the center of the shell.
${V_P} = {V_s} + {V_p}$
By using the formula (2),
${V_p} = \dfrac{{Gm}}{R} + \dfrac{{Gm}}{{\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)}}$
The potential of gravity is always negative. So,
${V_p} = - \dfrac{{Gm}}{R} - \dfrac{{2Gm}}{R}$
By further simplification of the above equation,
${V_p} = - \dfrac{{3Gm}}{R}$
Hence the gravitational potential of the object at a distance of $\dfrac{R}{2}$ from the center is $ - \dfrac{{3Gm}}{R}$.
Note:The gravitational potential on the surface of the earth is always taken as the negative. This is because the work is done by the gravity on the surface of the earth to bring the object close to it which is away from the surface. The work is always done away from the surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




