
A particle of mass $2\times {{10}^{-5}}Kg$ moves horizontally between two horizontal plates of a charged parallel plate capacitor between which there is an electric field of 200 N/C acting upward. A magnetic induction of 2.0 T is applied at right angles to the electric field in a direction normal to both B and v. If g is $9.8m/{{s}^{2}}$ and the charge on the particle is ${{10}^{-6}}C$, then find the velocity of charge particle so that it continues to move horizontally.
A: 2m/s
B: 20m/s
C: 0.2 m/s
D:100m/s
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: This comes under the application of Lorentz force that is the force which is generated on a charged particle due to the presence of an electric field and a magnetic field. We are given a similar condition here. We can approach this question by keeping the principle of Lorentz force in our minds.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that
Mass of the particle is $2\times {{10}^{-5}}Kg$
Upward electric field acting on the particle is 200N/C
Magnetic induction is 2.0 T
Charge on the particle is ${{10}^{-6}}C$
Acceleration due gravity is $9.8m/{{s}^{2}}$
We have to find the velocity of the charged particle to maintain the horizontal motion.
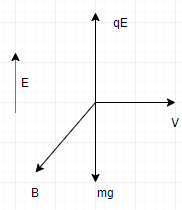
The electric force acting on the particle is \[F=qE={{10}^{-6}}\times 200=2\times {{10}^{-4}}N\]
The weight that acts downwards is $W=mg=2\times {{10}^{-5}}\times 9.8=1.96\times {{10}^{-4}}$
This implies that $F>W$. Hence to make the net force zero, F has to act downwards.
$
F=(2-1.96)\times {{10}^{-4}}=4\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
\implies {{10}^{-6}}\times 2\times v=4\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
\therefore v=2m/s \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The Lorenz force is best explained using the right hand rule, where the middle finger represents the force, index finger represents the magnetic field and as a result the thumb represents the direction of the current. This method helps the students to find the directions in a simpler way.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that
Mass of the particle is $2\times {{10}^{-5}}Kg$
Upward electric field acting on the particle is 200N/C
Magnetic induction is 2.0 T
Charge on the particle is ${{10}^{-6}}C$
Acceleration due gravity is $9.8m/{{s}^{2}}$
We have to find the velocity of the charged particle to maintain the horizontal motion.

The electric force acting on the particle is \[F=qE={{10}^{-6}}\times 200=2\times {{10}^{-4}}N\]
The weight that acts downwards is $W=mg=2\times {{10}^{-5}}\times 9.8=1.96\times {{10}^{-4}}$
This implies that $F>W$. Hence to make the net force zero, F has to act downwards.
$
F=(2-1.96)\times {{10}^{-4}}=4\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
\implies {{10}^{-6}}\times 2\times v=4\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
\therefore v=2m/s \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The Lorenz force is best explained using the right hand rule, where the middle finger represents the force, index finger represents the magnetic field and as a result the thumb represents the direction of the current. This method helps the students to find the directions in a simpler way.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




