
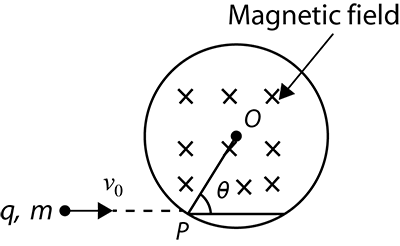
A particle of charge $q$and mass $m$is projected with a velocity ${{v}_{0}}$ towards a circular region having a uniform magnetic field $B$perpendicular and into the plane of paper from point P as shown in the figure. $R$Is the radius and O is the centre of that circular region. If the line OP makes an angle $\theta $ with the direction of ${{v}_{0}}$ then the value of ${{v}_{0}}$so that particle passes through O is
$\begin{align}
& A.\dfrac{qBR}{m\sin \theta } \\
& B.\dfrac{qBR}{2m\sin \theta } \\
& C.\dfrac{2qBR}{m\sin \theta } \\
& D.\dfrac{3qBR}{2m\sin \theta } \\
\end{align}$

Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: trigonometry is used in order to solve this question. Basic trigonometry functions like sine, cosine are used up here. Radius of the circular path can be found by using sine function and rearranging it.
Complete step by step answer:
The sine function is a trigonometric function based on angle. This function of sine of an acute angle is explained on the basis of a right triangle. For a particular angle, it is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite to that angle which may be altitude or base and to the length of the longest side of the triangle which is called a hypotenuse.
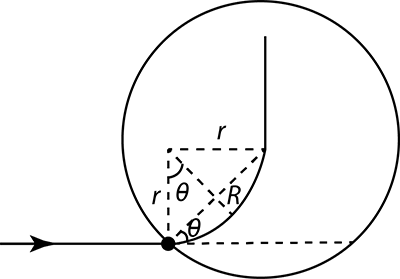
For this question, let $r$be the radius of the circular path and \[{{v}_{0}}=\dfrac{qBR}{2m\sin \theta }\]
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{R}{2} \right)}{r}$
Rearranging will give,
$=\dfrac{R}{2r}$
As we all know the radius of curvature is given by
$r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}$
Where $m$the mass of the object is, \[v\]is the velocity, \[q\] is the charge and \[B\] is the magnetic field.
Substituting $r$will give,
\[\dfrac{R}{2\sin \theta }=\dfrac{mv}{qB}\]
Now rearranging the terms can make the equation,
\[{{v}_{0}}=\dfrac{qBR}{2m\sin \theta }\]
Therefore the correct answer is option B.
Note: one period of the sine wave is the length of one cycle of the wave. The period of the sine wave is 2π. Magnetic field is the region in space where we can experience magnetic properties. It will be probably around any charge or around any current carrying conductor.
Complete step by step answer:
The sine function is a trigonometric function based on angle. This function of sine of an acute angle is explained on the basis of a right triangle. For a particular angle, it is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite to that angle which may be altitude or base and to the length of the longest side of the triangle which is called a hypotenuse.
For this question, let $r$be the radius of the circular path and \[{{v}_{0}}=\dfrac{qBR}{2m\sin \theta }\]
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{R}{2} \right)}{r}$
Rearranging will give,
$=\dfrac{R}{2r}$
As we all know the radius of curvature is given by
$r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}$
Where $m$the mass of the object is, \[v\]is the velocity, \[q\] is the charge and \[B\] is the magnetic field.
Substituting $r$will give,
\[\dfrac{R}{2\sin \theta }=\dfrac{mv}{qB}\]
Now rearranging the terms can make the equation,
\[{{v}_{0}}=\dfrac{qBR}{2m\sin \theta }\]

Therefore the correct answer is option B.
Note: one period of the sine wave is the length of one cycle of the wave. The period of the sine wave is 2π. Magnetic field is the region in space where we can experience magnetic properties. It will be probably around any charge or around any current carrying conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




