
A particle of charge q and mass m starts from the origin under the action of an electric field $\overrightarrow{E}={{E}_{0}}\widehat{i}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}={{B}_{0}}\widehat{i}$ with velocity $\overrightarrow{v}={{v}_{0}}\widehat{j}$. The speed of the particle will come $2{{v}_{0}}$ after a time.
A. $t=\dfrac{2m{{v}_{0}}}{qE}$
B. $t=\dfrac{2Bq}{m{{v}_{0}}}$
C. $t=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}Bq}{m{{v}_{0}}}$
D. $t=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}m{{v}_{0}}}{qE}$
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: The force acting on the particle is due to the electric field and magnetic field. Electric field provides the particle acceleration and magnetic field provides necessary centripetal force. Which in combination rotates the particle and forms helix motion. We will solve this question with the help of vector analysis.
Complete step by step answer:
Here electric field and magnetic field both are acting in x direction, therefore both electric field and magnetic field are parallel to each other.
$\overrightarrow{v}={{v}_{0}}\widehat{j}$ is the velocity of the particle in y direction.
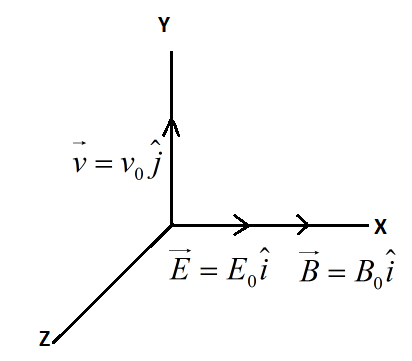
In Y-Z plane, magnitude of velocity ${{v}_{0}}$ is given by
$\begin{align}
& {{v}_{0}}=\sqrt{{{v}_{y}}^{2}+{{v}_{z}}^{2}} \\
& {{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{y}}^{2}+{{v}_{z}}^{2} \\
\end{align}$
And it is given that at time t velocity of particle is $2{{v}_{0}}$
${{\left( 2{{v}_{0}} \right)}^{2}}={{v}_{x}}^{2}+{{v}_{y}}^{2}+{{v}_{z}}^{2}$
$\begin{align}
& 4{{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{x}}^{2}+{{v}_{y}}^{2}+{{v}_{z}}^{2} \\
& 4{{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{x}}^{2}+{{v}_{0}}^{2} \\
& 3{{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{x}}^{2} \\
\end{align}$
Using equation of motion $v=u+at$ velocity of particle in x direction is given by
${{v}_{x}}={{u}_{x}}+{{a}_{x}}t$
Here initial velocity of the particle in x direction is zero
Therefore,
${{v}_{x}}={{a}_{x}}t$
Putting this in the above equation we get,
$3{{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{x}}^{2}$
Taking square root on both side
$\sqrt{3}{{v}_{0}}={{a}_{x}}t$
Acceleration acting on the particle of charge q and mass m in x direction is due to given electric field and we know that:
$\begin{align}
& F=qE \\
& ma=qE \\
& a=\dfrac{qE}{m} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the relation of velocity and time t is
$\sqrt{3}{{v}_{0}}=\left( \dfrac{qE}{m} \right)t$
$t=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}m{{v}_{0}}}{qE}$
Hence option D is the correct answer.
Note: Force acting on charged particle due to magnetic field is known as Lorentz force which acts normal to the velocity of the particle and magnetic field, because Lorentz force is given by $\overrightarrow{F}=q\left( \overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$.
If the question has vector notation carefully look in which direction the given quantity is acting and then execute the solution.
Complete step by step answer:
Here electric field and magnetic field both are acting in x direction, therefore both electric field and magnetic field are parallel to each other.
$\overrightarrow{v}={{v}_{0}}\widehat{j}$ is the velocity of the particle in y direction.

In Y-Z plane, magnitude of velocity ${{v}_{0}}$ is given by
$\begin{align}
& {{v}_{0}}=\sqrt{{{v}_{y}}^{2}+{{v}_{z}}^{2}} \\
& {{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{y}}^{2}+{{v}_{z}}^{2} \\
\end{align}$
And it is given that at time t velocity of particle is $2{{v}_{0}}$
${{\left( 2{{v}_{0}} \right)}^{2}}={{v}_{x}}^{2}+{{v}_{y}}^{2}+{{v}_{z}}^{2}$
$\begin{align}
& 4{{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{x}}^{2}+{{v}_{y}}^{2}+{{v}_{z}}^{2} \\
& 4{{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{x}}^{2}+{{v}_{0}}^{2} \\
& 3{{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{x}}^{2} \\
\end{align}$
Using equation of motion $v=u+at$ velocity of particle in x direction is given by
${{v}_{x}}={{u}_{x}}+{{a}_{x}}t$
Here initial velocity of the particle in x direction is zero
Therefore,
${{v}_{x}}={{a}_{x}}t$
Putting this in the above equation we get,
$3{{v}_{0}}^{2}={{v}_{x}}^{2}$
Taking square root on both side
$\sqrt{3}{{v}_{0}}={{a}_{x}}t$
Acceleration acting on the particle of charge q and mass m in x direction is due to given electric field and we know that:
$\begin{align}
& F=qE \\
& ma=qE \\
& a=\dfrac{qE}{m} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the relation of velocity and time t is
$\sqrt{3}{{v}_{0}}=\left( \dfrac{qE}{m} \right)t$
$t=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}m{{v}_{0}}}{qE}$
Hence option D is the correct answer.
Note: Force acting on charged particle due to magnetic field is known as Lorentz force which acts normal to the velocity of the particle and magnetic field, because Lorentz force is given by $\overrightarrow{F}=q\left( \overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$.
If the question has vector notation carefully look in which direction the given quantity is acting and then execute the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




