
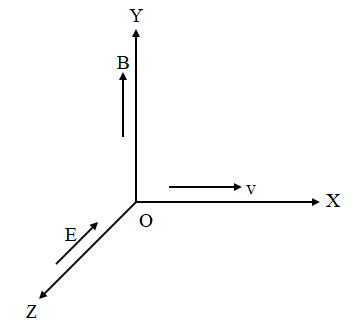
A particle of charge \[ - 16 \times {10^{ - 18}}\,C\] moving with velocity 10 m/s along the X-axis enters region where a magnetic field of induction B is along Y-axis and field of magnitude \[{10^4}\,V/m\] is along negative Z-axis. If the charged particle continuous moving along the X-axis, the magnitude of B is:
A. \[{10^6}\,Wb/{m^2}\]
B. \[{10^5}\,Wb/{m^2}\]
C. \[{10^3}\,Wb/{m^2}\]
D. \[{10^7}\,Wb/{m^2}\]

Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: The particle continues to move along the X-axis implies that there is no net force along Z-axis and Y-axis. In that case, the electric force equals the magnetic force on the particle.
Formula used:
\[{F_e} = qE\]
Here, q is the charge of the particle.
\[{F_B} = qvB\]
Here, v is the velocity of the particle.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the electric force acting on the charged particle placed in the uniform electric field \[E\] is,
\[{F_e} = qE\]
Here, q is the charge of the particle.
Also, the magnetic force on the particle placed in the magnetic field \[B\] is,
\[{F_B} = qvB\]
Here, v is the velocity of the particle.
Since the particle continues to move along the X-axis, the electric force along the negative Z-axis is equal to the magnetic force on the particle along the Y-axis. The net force on the particle is zero except along the X-axis.
Therefore, we can write,
\[qE = qvB\]
\[ \Rightarrow B = \dfrac{E}{v}\]
Substitute \[{10^4}\,V/m\] for E and 10 m/s for v in the above equation.
\[B = \dfrac{{{{10}^4}}}{{10}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow B = {10^3}\,Wb/{m^2}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
If the electric force along the negative Z-axis does not equal the magnetic force along the Y-axis, the particle could have moved along the direction whichever the force has maximum value. The unit of magnetic field is Tesla or \[Wb/{m^2}\], therefore, if the magnetic field is given in Tesla, we don’t need to convert it into S.I. unit.
Formula used:
\[{F_e} = qE\]
Here, q is the charge of the particle.
\[{F_B} = qvB\]
Here, v is the velocity of the particle.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the electric force acting on the charged particle placed in the uniform electric field \[E\] is,
\[{F_e} = qE\]
Here, q is the charge of the particle.
Also, the magnetic force on the particle placed in the magnetic field \[B\] is,
\[{F_B} = qvB\]
Here, v is the velocity of the particle.
Since the particle continues to move along the X-axis, the electric force along the negative Z-axis is equal to the magnetic force on the particle along the Y-axis. The net force on the particle is zero except along the X-axis.
Therefore, we can write,
\[qE = qvB\]
\[ \Rightarrow B = \dfrac{E}{v}\]
Substitute \[{10^4}\,V/m\] for E and 10 m/s for v in the above equation.
\[B = \dfrac{{{{10}^4}}}{{10}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow B = {10^3}\,Wb/{m^2}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
If the electric force along the negative Z-axis does not equal the magnetic force along the Y-axis, the particle could have moved along the direction whichever the force has maximum value. The unit of magnetic field is Tesla or \[Wb/{m^2}\], therefore, if the magnetic field is given in Tesla, we don’t need to convert it into S.I. unit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




